J Korean Med Sci.
2023 Jan;38(4):e29. 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e29.
Status of the Newborn Hearing Screening in the 4-Months Age National Infant Health Checkup in Korea: A Nationwide PopulationBased Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Hallym University College of Medicine, Kangnam Sacred-Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Biostatistics, College of Medicine, Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 6Division of Speech Pathology and Audiology, Hallym University College of Natural Sciences, Chuncheon, Korea
- 7Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, School of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2539191
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e29
Abstract
- Background
The aims of this study are to review data on 4-months age National Health Screening Program for Infants and Children (NHSPIC) using a National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) database, and to analyze the newborn hearing screening (NHS) results and related characteristics of the 4-months NHSPIC for 7 years in South Korea.
Methods
We analyzed a NHIS database of infants who had participated in the 4-month age NHSPIC from 2010 to 2016. According to the results of hearing questionnaires and physical examination, we analyzed the outcomes of NHS and related infantile and socioeconomic factors.
Results
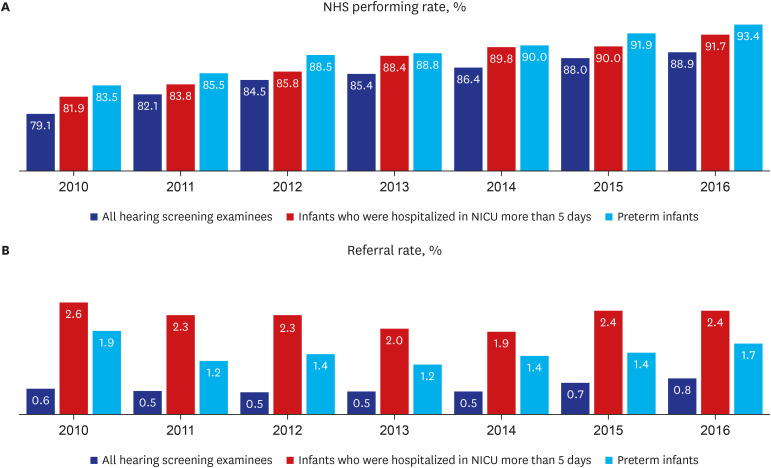
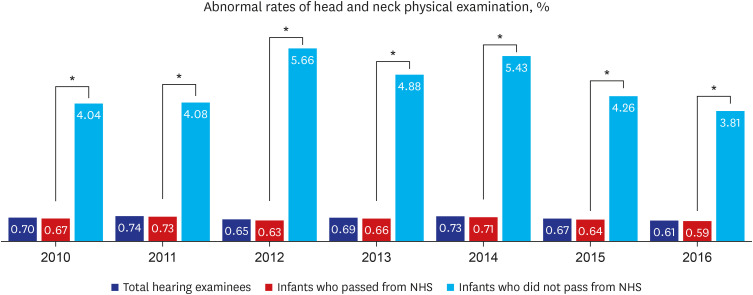
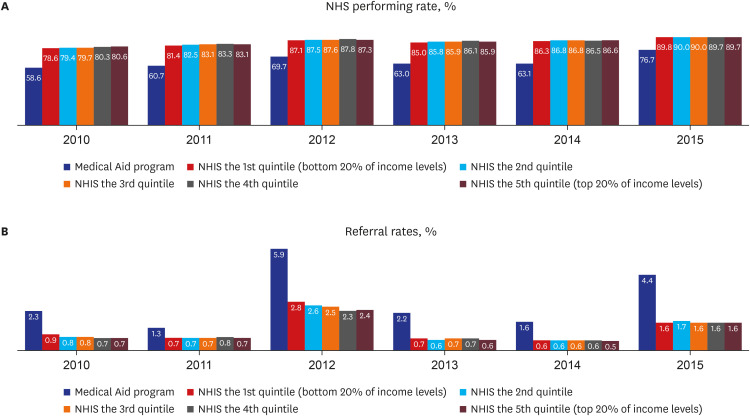
Among 3,128,924 of total eligible infants in Korea between the year 2010 and 2016, 69.2% (2,164,621 infants) conducted 4-months age NHSPIC, and 94.4% (2,042,577 infants) of which performed hearing questionnaires regarding NHS. Among the total hearing examinees, premature infants accounted for 3.6%, infants who were hospitalized in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) for more than 5 days accounted for 5.6%, and infants with head and neck abnormalities were 0.6%. The NHS performing rate was 79.1% for total hearing examinees in 2010, but gradually increased to 88.9% in 2016. The NHS performing rate in 2016 was 93.4% for premature infants, 91.7% for NICU hospitalized babies. The mean referral rate was 0.6% for total hearing examinees, 1.4% for premature infants, and 2.3% for NICU hospitalized babies. When we analyzed the NHS performing rate and the referral rate according to the household income level, the NHS performing rate of infants in Medical Aid programs was the lowest as 65.6%, and the NHS performing rates in other five levels of NHIS was higher ranging between 85.1% to 86.0%. The referral rate of infants in the Medical Aid program (3.8%) was significantly higher than those of infants in other classes (1.10–1.25%).
Conclusion
The estimated overall NHS performing rate in Korea gradually increased and was 88.9% in 2016. The overall referral rate was low as 0.6%, and it was significantly different depending on the infant’s health condition and household income levels. We assume that our finding would help to establish policies managing hearing impaired children, and to develop the customized hearing care service programs considering the household economic levels.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yoshinaga-Itano C, Sedey AL, Coulter DK, Mehl AL. Language of early- and later-identified children with hearing loss. Pediatrics. 1998; 102(5):1161–1171. PMID: 9794949.2. Evelyn C. Joint Committee on Infant Hearing. Year 2000 position statement: principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. Am J Audiol. 2000; 9(1):9–29.3. Japan Healthcare info. Baby checkups. Accessed October 10, 2022. https://japanhealthinfo.com/child-health-and-childcare/baby-checkups .4. Pediatric Practice Berlin. Preventive check-ups. Accessed October 10, 2022. https://www.kinderarzt-berlin-zia.de/en/preventive-check-ups .5. Council on Children with Disabilities. Section on Developmental Behavioral Pediatrics. Bright Futures Steering Committee. Medical Home Initiatives for Children with Special Needs Project Advisory Committee. Identifying infants and young children with developmental disorders in the medical home: an algorithm for developmental surveillance and screening. Pediatrics. 2006; 118(1):405–420. PMID: 16818591.6. KOrean Statistical Information Service (KOSIS). Vital statistics. Projected population by age (Korea). Updated December 9, 2021. Accessed October 10, 2022. https://kosis.kr/statHtml/statHtml.do?orgId=101&tblId=DT_1B08024&vw_cd=MT_ETITLE&list_id=A1_13&scrId=&seqNo=&language=en&lang_mode=en&obj_var_id=&itm_id=&conn_path=MT_ETITLE&path=Population%2520%253E%2520Population%2520Census%2520%253E%2520Population%2520Density .7. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Introduction to manual revision of the National Health Screening Program for Infants and Children (NHSPIC). Accessed October 10, 2022. https://www.kdca.go.kr/filepath/boardDownload.es?bid=0034&list_no=62341&seq=1 .8. Lee J, Rhee J, Park SK, Chang J, Kim JS, Park KH, et al. Development of a more effective Hearing Screening Questionnaire for Infants and Children during medical check-ups. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2016; 59(4):273–280.9. American Academy of Pediatrics. Joint Committee on Infant Hearing. Year 2007 position statement: Principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. Pediatrics. 2007; 120(4):898–921. PMID: 17908777.10. Erenberg A, Lemons J, Sia C, Trunkel D, Ziring P. Newborn and infant hearing loss: detection and intervention. American Academy of Pediatrics. Task Force on Newborn and Infant Hearing, 1998-1999. Pediatrics. 1999; 103(2):527–530. PMID: 9925859.11. The Korean Audiological Society. Korean Newborn Hearing Screening Guideline Update. 2nd ed. Seoul, Korea: Korean Audiological Society;2018.12. Chung YS, Oh SH, Park SK. Referral rates for newborn hearing screening based on the test time. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019; 127:109664. PMID: 31521889.13. Chang J, Oh SH, Park SK. Comparison of newborn hearing screening results between well babies and neonates admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit for more than 5 days: Analysis based on the national database in Korea for 9 years. PLoS One. 2020; 15(6):e0235019. PMID: 32559227.14. Washington State Department of Health. Protocol for newborn hearing screening, 2022. Accessed October 10, 2022. https://www.doh.wa.gov/Portals/1/Documents/Pubs/344-023_E HDDINBScrnProto.pdf .15. Tennessee Department of Health. Newborn hearing screening guidelines for hospitals and birthing centers, 2009. Accessed October 10, 2022. https://www.infanthearing.org/stateguidelines/Tennessee/Screening%20Guidelines.pdf .16. Mason JA, Herrmann KR. Universal infant hearing screening by automated auditory brainstem response measurement. Pediatrics. 1998; 101(2):221–228. PMID: 9445495.17. van Dommelen P, van Straaten HL, Verkerk PH. Dutch NICU Neonatal Hearing Screening Working Group. Ten-year quality assurance of the nationwide hearing screening programme in Dutch neonatal intensive care units. Acta Paediatr. 2011; 100(8):1097–1103. PMID: 21342253.18. Colella-Santos MF, Hein TA, de Souza GL, do Amaral MI, Casali RL. Newborn hearing screening and early diagnostic in the NICU. BioMed Res Int. 2014; 2014:845308. PMID: 24999481.19. Li PC, Chen WI, Huang CM, Liu CJ, Chang HW, Lin HC. Comparison of newborn hearing screening in well-baby nursery and NICU: a study applied to reduce referral rate in NICU. PLoS One. 2016; 11(3):e0152028. PMID: 27023324.20. Martínez-Cruz CF, Poblano A, Fernández-Carrocera LA. Risk factors associated with sensorineural hearing loss in infants at the neonatal intensive care unit: 15-year experience at the National Institute of Perinatology (Mexico City). Arch Med Res. 2008; 39(7):686–694. PMID: 18760198.21. Vrabec JT, Lin JW. Inner ear anomalies in congenital aural atresia. Otol Neurotol. 2010; 31(9):1421–1426. PMID: 21113986.22. Park E, Lee G, Jung HH, Im GJ. Analysis of inner ear anomalies in unilateral congenital aural atresia combined with microtia. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2019; 12(2):176–180. PMID: 30403837.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Early Detection of Childhood Hearing Impairment
- Newborn Hearing Loss and Newborn Hearing Screening
- Newborn hearing screening
- Current status of newborn hearing screening in low-income families in the southeastern region of Korea
- Changes in the Hearing Thresholds of Infants Who Failed the Newborn Hearing Screening Test and in Infants Treated in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit