J Korean Med Sci.
2023 Jan;38(4):e23. 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e23.
Proper Depth of Percutaneous Central Venous Catheter via the Great Saphenous Vein for Very Low Birth Weight Infants: A Single-Center, Prospective Cohort Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Jeonbuk National University School of Medicine, Jeonju, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Inha University Hospital, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea
- 3Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Jeonbuk National University-Biomedical Research Institute of Jeonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea
- KMID: 2539189
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e23
Abstract
- Background
A proper depth of percutaneous central venous catheter (PCVC) is very important to reduce procedural time and prevent various complications in very low birth weight (VLBW) infants who require minimal handling or have a sensitive skin. The objective of this study was to suggest a formula for faster and proper insertion of PCVC in VLBWIs to prevent unintended consequences of patients’ conditions.
Methods
Prospective data of VLBW infants admitted from June 2015 to January 2018 who had PCVC inserted via the great saphenous vein within seven days after birth were analyzed. Correlations of length of inserted PCVC with body weight, body length, and postmenstrual age at the date of PCVC insertion were determined with a linear regression analysis. Using results of this analysis, a formula to determine the optimal insertion length of PCVC was derived. Coefficient of determination was used to assess how well outcomes were replicated by the formula.
Results
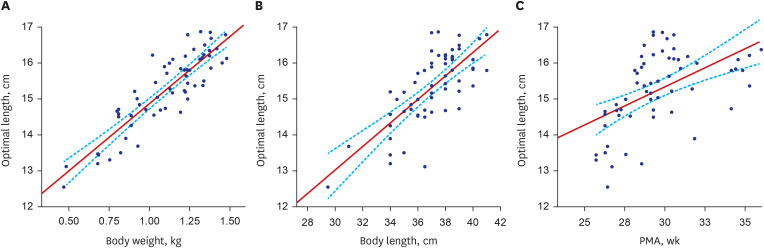
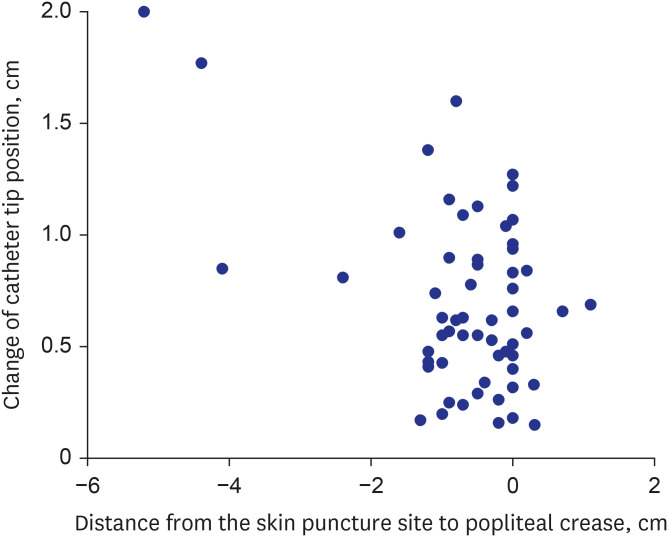
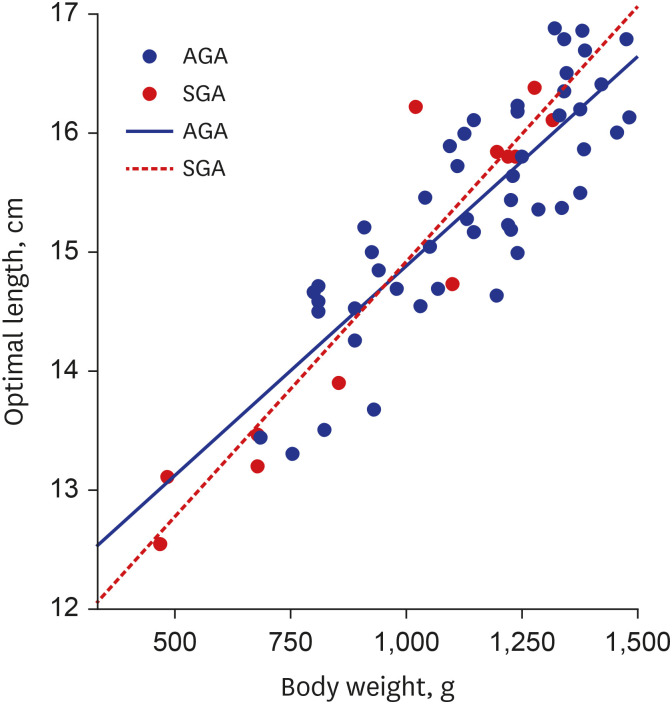
The formula to predict the proper insertion length of PCVC via the great saphenous vein at popliteal crease level was obtained as follows: Optimal Length (cm) = 3.8 × Body Weight (kg) + 11.1. With everyday movements such as flexion and extension of the lower extremities, the mean difference in catheter tip position was 7.0 ± 3.9 mm, which was not significant enough to escalate the risk of catheter tip displacement. The rate of catheterrelated complications was as low as 4.9% in this study.
Conclusions
The formula derived from this study to predict the optimal PCVC insertion length could benefit VLBW infants by reducing procedural time and lowering the risk of complications.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gavelli V, Wackernagel D. Peripherally inserted central catheters in extremely preterm infants: Placement success rates and complications. Acta Paediatr. 2022; 111(3):554–556. PMID: 34757656.2. Kim H, Kim SH, Byun HS, Choi YY. Clinical use and complications of percutaneous central venous catheterization in very low birth weight infants. Korean J Pediatr. 2005; 48(9):953–959.3. Huang HC, Su LT, Liu YC, Chang HY, Ou-Yang MC, Chung MY, et al. The role of ultrasonography for detecting tip location of percutaneous central venous catheters in neonates-a single-center, prospective cohort study. Pediatr Neonatol. 2021; 62(3):265–270. PMID: 33637475.4. Lee ES, Lee YH, Shin SM. Clinical experiences on PCVC (pereutaneous central venous cathetization) in newborn infants. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 1995; 2(1):34–41.5. Lee J, Kim M, Cho CY, Choi YY. Effects of percutaneous central venous catheterization in very low birth weight infants. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2000; 7(2):81–88.6. Soong WJ, Hwang B. Percutaneous central venous catheterization: five year experiment in a neonatal intensive care unit. Zhonghua Min Guo Xiao Er Ke Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1993; 34(5):356–366. PMID: 8237354.7. Thiagarajan RR, Ramamoorthy C, Gettmann T, Bratton SL. Survey of the use of peripherally inserted central venous catheters in children. Pediatrics. 1997; 99(2):E4.8. Sung SI, Ahn SY, Seo HJ, Yoo HS, Han YM, Lee MS, et al. Insensible water loss during the first week of life of extremely low birth weight infants less than 25 gestational weeks under high humidification. Neonatal Med. 2013; 20(1):51–57.9. Kristoff K, Wang R, Munson D, Dysart K, Stracuzzi L, Wade K, Birnbaum S. A quality improvement initiative to provide timely central vascular access in a neonatal intensive care unit. Adv Neonatal Care. 2022; 22(3):203–209. PMID: 34407057.10. Alhatem A, Estrella Y, Jones A, Algarrahi K, Fofah O, Heller DS. Percutaneous route of life: chylothorax or total parenteral nutrition-related bilateral pleural effusion in a neonate? Fetal Pediatr Pathol. 2021; 40(5):505–510. PMID: 32000556.11. Colacchio K, Deng Y, Northrup V, Bizzarro MJ. Complications associated with central and non-central venous catheters in a neonatal intensive care unit. J Perinatol. 2012; 32(12):941–946. PMID: 22343397.12. Nadroo AM, Glass RB, Lin J, Green RS, Holzman IR. Changes in upper extremity position cause migration of peripherally inserted central catheters in neonates. Pediatrics. 2002; 110(1 Pt 1):131–136. PMID: 12093958.13. Chen H, Zhang X, Wang H, Hu X. Complications of upper extremity versus lower extremity placed peripherally inserted central catheters in neonatal intensive care units: A meta-analysis. Intensive Crit Care Nurs. 2020; 56:102753. PMID: 31445794.14. Dhillon SS, Connolly B, Shearkhani O, Brown M, Hamilton R. Arrhythmias in children with peripherally inserted central catheters (PICCs). Pediatr Cardiol. 2020; 41(2):407–413. PMID: 31853581.15. Perin G. PICC placement in the neonate. N Engl J Med. 2014; 370(22):2153–2154.16. Finn D, Kinoshita H, Livingstone V, Dempsey EM. Optimal line and tube placement in very preterm neonates: an audit of practice. Children (Basel). 2017; 4(11):99. PMID: 29149032.17. Chen IL, Ou-Yang MC, Chen FS, Chung MY, Chen CC, Liu YC, et al. The equations of the inserted length of percutaneous central venous catheters on neonates in NICU. Pediatr Neonatol. 2019; 60(3):305–310. PMID: 30217481.18. Kim JH, Kim CS, Bahk JH, Cha KJ, Park YS, Jeon YT, et al. The optimal depth of central venous catheter for infants less than 5 kg. Anesth Analg. 2005; 101(5):1301–1303. PMID: 16243984.19. Mussa B. Advantages, disadvantages, and indications of PICCs in inpatients and outpatients. Sandrucci S, Mussa B, editors. Peripherally Inserted Central Venous Catheters. Milano, Italia: Springer;2014. p. 43–51.20. Ohki Y, Nako Y, Morikawa A, Maruyama K, Koizumi T. Percutaneous central venous catheterization via the great saphenous vein in neonates. Acta Paediatr Jpn. 1997; 39(3):312–316. PMID: 9241891.21. O’Grady NP, Alexander M, Burns LA, Dellinger EP, Garland J, Heard SO, et al. Summary of recommendations: guidelines for the prevention of intravascular catheter-related infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2011; 52(9):1087–1099. PMID: 21467014.22. Wrightson DD. Peripherally inserted central catheter complications in neonates with upper versus lower extremity insertion sites. Adv Neonatal Care. 2013; 13(3):198–204. PMID: 23722492.23. Elmekkawi A, Maulidi H, Mak W, Aziz A, Lee KS. Outcomes of upper extremity versus lower extremity placed peripherally inserted central catheters in a medical-surgical neonatal intensive care unit1. J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2019; 12(1):57–63. PMID: 30149479.24. Kwak KJ, Park JH, Choi HJ, Kim CS, Lee SL. Early-onset pericardial effusion after peripherally inserted central venous catheterization in a preterm infant. Korean J Perinatol. 2015; 26(4):355.25. Ateş Y, Yücesoy CA, Unlü MA, Saygin B, Akkaş N. The mechanical properties of intact and traumatized epidural catheters. Anesth Analg. 2000; 90(2):393–399. PMID: 10648328.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clincal Trial of Percutaneous Central Vein Catherization Via Great Saphenous Vein
- A Safe Method of Central Venous Catheterization by Peripheral Venous Cutdown in Infants
- Prevalence and Clinical Implication of Nonsaphenous Vein Reflux with or without Pelvic Venous Disease
- Perforation of azygos vein and right-sided hydrothorax caused by peripherally inserted central catheter in extremely low birth weight infant
- Effects of Percutaneous Central Venous Catheterization in very Low Birth Weight Infants