J Neurocrit Care.
2022 Dec;15(2):146-147. 10.18700/jnc.220080.
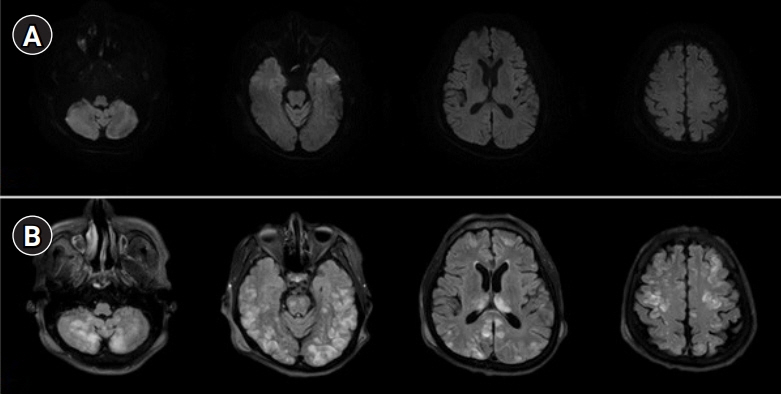
Axitinib-induced posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in a patient with renal cell carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2538774
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18700/jnc.220080
Figure
Reference
-
1. Moghaddam AS, Ramaiah G, Jumaa M, Zaidi S. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) secondary to use of axitinib in renal cell cancer (P4. 012). Neurology. 2018; 90(15 Suppl):P4.012.2. Levy A, Benmoussa L, Ammari S, Albiges L, Escudier B. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome induced by axitinib. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2014; 12:e33–4.
Article3. Tlemsani C, Mir O, Boudou-Rouquette P, Huillard O, Maley K, Ropert S, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome induced by anti-VEGF agents. Target Oncol. 2011; 6:253–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hypertension-induced Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy after Quetiapine Overdose
- A Case of Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient having Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient with Intoxication of Arisaema amurense
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome after Massive Blood Transfusion in a Normotensive Patient