Clin Endosc.
2023 Jan;56(1):38-49. 10.5946/ce.2022.179.
Hybrid argon plasma coagulation in Barrett’s esophagus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Los Angeles Medical Center, University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA
- 2Division of Internal Medicine, MetroHealth Medical Center, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, USA
- 3H.H. Chao Comprehensive Digestive Disease Center and Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology, University of California, Irvine, CA, USA
- KMID: 2538749
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2022.179
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Patients with Barrett’s esophagus are at increased risk of developing esophageal adenocarcinoma. Endoscopic therapies aim to eradicate dysplastic and metaplastic tissues. Hybrid argon plasma coagulation (hybrid-APC) utilizes submucosal fluid injection to create a protective cushion prior to ablation that shields the submucosa from injury. We performed a pooled meta-analysis to evaluate the safety and efficacy of hybrid-APC.
Methods
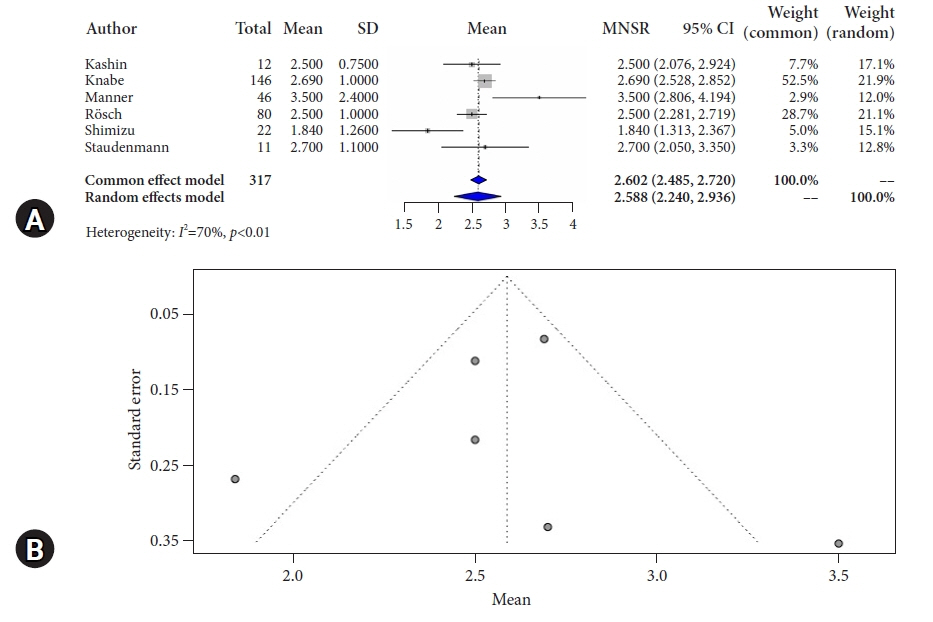
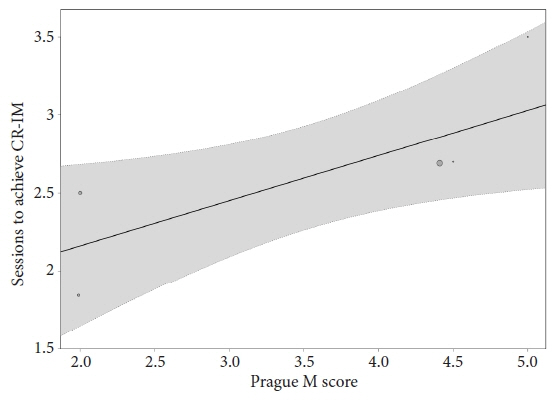
We conducted a systematic search of major electronic databases in April 2022. Studies that included patients with dysplastic and non-dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus undergoing treatment with hybrid-APC were eligible for inclusion. Outcome measures included complete remission of intestinal metaplasia (CR-IM), stricture formation, serious adverse events, and number of sessions necessary to achieve CR-IM.
Results
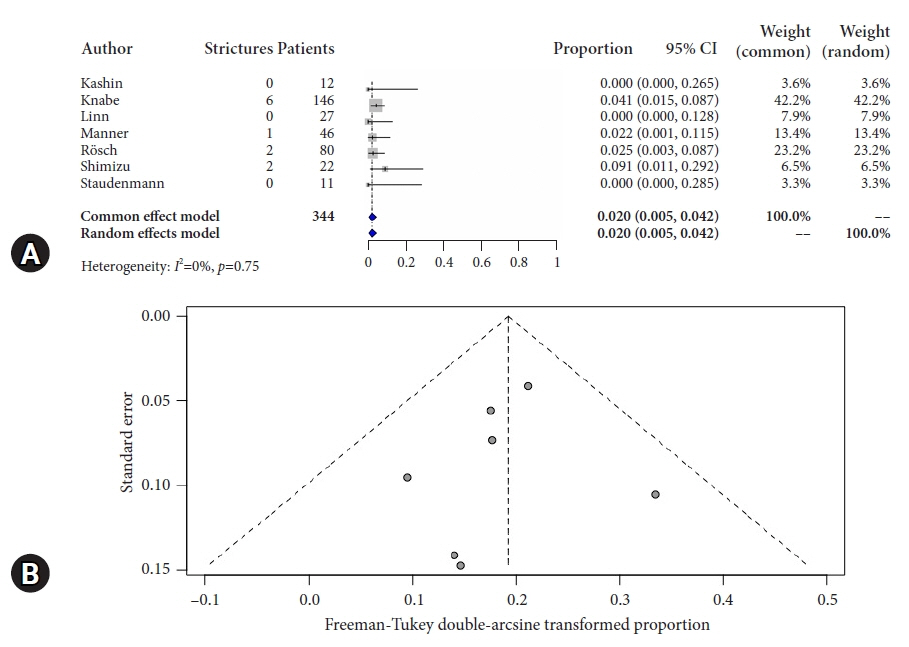
Overall pooled CR-IM rate for patients undergoing hybrid-APC was 90.8% (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.872–0.939; I2=0%). Pooled stricture rate was 2.0% (95% CI, 0.005–0.042; I2=0%). Overall serious adverse event rate was 2.7% (95% CI, 0.007–0.055; I2=0%).
Conclusions
Results of the current meta-analysis suggest that hybrid-APC is associated with high rates of CR-IM and a favorable safety profile. Interpretation of these results is limited by the inclusion of retrospective cohort and case series data. Randomized controlled trials that standardize treatment and outcome evaluation protocols are necessary to understand how this treatment option is comparable to the current standards of care.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Burke ZD, Tosh D. Barrett’s metaplasia as a paradigm for understanding the development of cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2012; 22:494–499.2. Wang DH, Clemons NJ, Miyashita T, et al. Aberrant epithelial-mesenchymal Hedgehog signaling characterizes Barrett’s metaplasia. Gastroenterology. 2010; 138:1810–1822.3. Lagergren J, Lagergren P. Recent developments in esophageal adenocarcinoma. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013; 63:232–248.4. Shaheen NJ, Falk GW, Iyer PG, et al. ACG clinical guideline: diagnosis and management of Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016; 111:30–50.5. Pech O, May A, Manner H, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of endoscopic resection for patients with mucosal adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2014; 146:652–660.6. Kolb JM, Wani S. Endoscopic eradication therapy for Barrett’s oesophagus: state of the art. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2020; 36:351–358.7. Garman KS, Shaheen NJ. Ablative therapies for Barrett’s esophagus. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2011; 13:226–239.8. Ganz RA, Utley DS, Stern RA, et al. Complete ablation of esophageal epithelium with a balloon-based bipolar electrode: a phased evaluation in the porcine and in the human esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 60:1002–1010.9. Dunkin BJ, Martinez J, Bejarano PA, et al. Thin-layer ablation of human esophageal epithelium using a bipolar radiofrequency balloon device. Surg Endosc. 2006; 20:125–130.10. van Vilsteren FG, Pouw RE, Seewald S, et al. Stepwise radical endoscopic resection versus radiofrequency ablation for Barrett’s oesophagus with high-grade dysplasia or early cancer: a multicentre randomised trial. Gut. 2011; 60:765–773.11. Kolb JM, Shah S, Chahine A, et al. Hybrid argon plasma coagulation for Barrett’s esophagus. VideoGIE. 2021; 6:339–341.12. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 151:264–269.13. Cotton PB, Eisen GM, Aabakken L, et al. A lexicon for endoscopic adverse events: report of an ASGE workshop. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:446–454.14. Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2005; 5:13.15. Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analysis. Ottawa: Ottawa Hospital Research Institute;2011. p. 1–12.16. Murad MH, Sultan S, Haffar S, et al. Methodological quality and synthesis of case series and case reports. BMJ Evid Based Med. 2018; 23:60–63.17. Bazerbachi F, Sawas T, Vargas EJ, et al. Metal stents versus plastic stents for the management of pancreatic walled-off necrosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018; 87:30–42.18. Lin L, Xu C. Arcsine-based transformations for meta-analysis of proportions: pros, cons, and alternatives. Health Sci Rep. 2020; 3:e178.19. Nyaga VN, Arbyn M, Aerts M. Metaprop: a Stata command to perform meta-analysis of binomial data. Arch Public Health. 2014; 72:39.20. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, et al. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315:629–634.21. Easterbrook PJ, Berlin JA, Gopalan R, et al. Publication bias in clinical research. Lancet. 1991; 337:867–872.22. Viechtbauer W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J Stat Softw. 2010; 36:1–48.23. Barker TH, Migliavaca CB, Stein C, et al. Conducting proportional meta-analysis in different types of systematic reviews: a guide for synthesisers of evidence. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2021; 21:189.24. Han J, Shimizu T, Yu A, et al. Efficacy, tolerance, and safety of hybrid argon plasma coagulation for the treatment of Barrett’s esophagus: a US pilot study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018; 113:S213–S214.25. Nieto J, Casas D. 935 Salvage hybrid APC after failed radiofrequency ablation and cryotherapy for Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019; 114:S544–S545.26. Kroupa R, Dastych M, Konečný Š, et al. Hybrid argon plasma coagulation in the ablation treatment of Barrett’s esophagus-long term results. United European Gastroenterol J. 2021; 9 (Supplement):297.27. Trindade AJ, Wee D, Wander P, et al. Successful treatment of refractory Barrett’s neoplasia with hybrid argon plasma coagulation: a case series. Endoscopy. 2020; 52:812–813.28. Arshad HM, Ahsan N, Aldridge T, et al. Safety and efficacy of endoscopic hybridapc for management of Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85(5 Supplement):AB562–AB563.29. Staudenmann DA, Skacel EP, Tsoutsman T, et al. Safety and long-term efficacy of hybrid-argon plasma coagulation for the treatment of Barrett’s esophagus: an Australian pilot study (with video). Int J Gastrointest Interv. 2021; 10:128–132.30. Knabe M, Beyna T, Rösch T, et al. Hybrid APC in combination with resection for the endoscopic treatment of neoplastic Barrett’s esophagus: a prospective, multicenter study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022; 117:110–119.31. Manner H, May A, Kouti I, et al. Efficacy and safety of hybrid-APC for the ablation of Barrett’s esophagus. Surg Endosc. 2016; 30:1364–1370.32. Rösch T, Manner H, May A, et al. Multicenter feasibility study of combined injection and argon plasma coagulation (Hybrid-APC) in the ablation therapy of neoplastic Barrett esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85(5 Supplement):AB154.33. Linn B, Mangels-Dick T, Clemens MA, et al. Hybrid argon plasma coagulation and radiofrequency ablation in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020; 91(6 Supplement):AB413.34. Kashin SV, Kuvaev R, Nadezhin AS, et al. The new hybrid argon plasma coagulation (hybrid APC) for endoscopic ablation of Barrett’s esophagus (BE): the results of the pilot trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83(5 Supplement):AB495.35. Shimizu T, Samarasena JB, Fortinsky KJ, et al. Benefit, tolerance, and safety of hybrid argon plasma coagulation for treatment of Barrett’s esophagus: US pilot study. Endosc Int Open. 2021; 9:E1870–E1876.36. Manner H, Neugebauer A, Scharpf M, et al. The tissue effect of argon-plasma coagulation with prior submucosal injection (Hybrid-APC) versus standard APC: a randomized ex-vivo study. United European Gastroenterol J. 2014; 2:383–390.37. Norton ID, Wang L, Levine SA, et al. Efficacy of colonic submucosal saline solution injection for the reduction of iatrogenic thermal injury. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 56:95–99.38. Qumseya BJ, Wani S, Desai M, et al. Adverse events after radiofrequency ablation in patients with Barrett’s esophagus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016; 14:1086–1095.39. Pandey G, Mulla M, Lewis WG, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation in low grade dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus. Endoscopy. 2018; 50:953–960.40. Orman ES, Li N, Shaheen NJ. Efficacy and durability of radiofrequency ablation for Barrett’s esophagus: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 11:1245–1255.41. Desai M, Rösch T, Sundaram S, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the long-term efficacy of Barrett’s endoscopic therapy-stringent selection criteria and a proposal for definitions. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2021; 54:222–233.42. Shaheen NJ, Sharma P, Overholt BF, et al. Radiofrequency ablation in Barrett’s esophagus with dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:2277–2288.43. Phoa KN, van Vilsteren FG, Weusten BL, et al. Radiofrequency ablation vs endoscopic surveillance for patients with Barrett esophagus and low-grade dysplasia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2014; 311:1209–1217.44. Spechler SJ. Buried (but not dead) Barrett’s metaplasia: tales from the crypts. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:41–43.45. Gray NA, Odze RD, Spechler SJ. Buried metaplasia after endoscopic ablation of Barrett’s esophagus: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011; 106:1899–1908.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy and Safety of Argon Plasma Coagulation for the Ablation of Barrett’s Esophagus: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Two Cases of Asymptomatic Pneumoperitoneum after Argon Plasma Coagulation Treatment
- Safety and long-term efficacy of hybrid-argon plasma coagulation for the treatment of Barrett’s esophagus: An Australian pilot study (with video)
- Barrett's Esophagus-With Emphasis on Endoscopic Disgnosis
- Trial of Argon Plasma Coagulation in Patients with Heterotopic Gastric Mucosa Presenting with Laryngopharyngeal Symptoms