Child Kidney Dis.
2022 Dec;26(2):74-79. 10.3339/ckd.22.035.
Impact of COVID-19 on the clinical course of nephrotic syndrome in children: a single-center study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2538737
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3339/ckd.22.035
Abstract
- Purpose
Children with nephrotic syndrome may experience disease relapse or aggravation triggered by various viral infections. Limited studies on the clinical implications of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic in children with nephrotic syndrome have been published worldwide. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the effects of COVID-19 on the clinical course of nephrotic syndrome in children.
Methods
The medical records of 59 patients with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome who visited our hospital between February and June 2022 were retrospectively analyzed.
Results
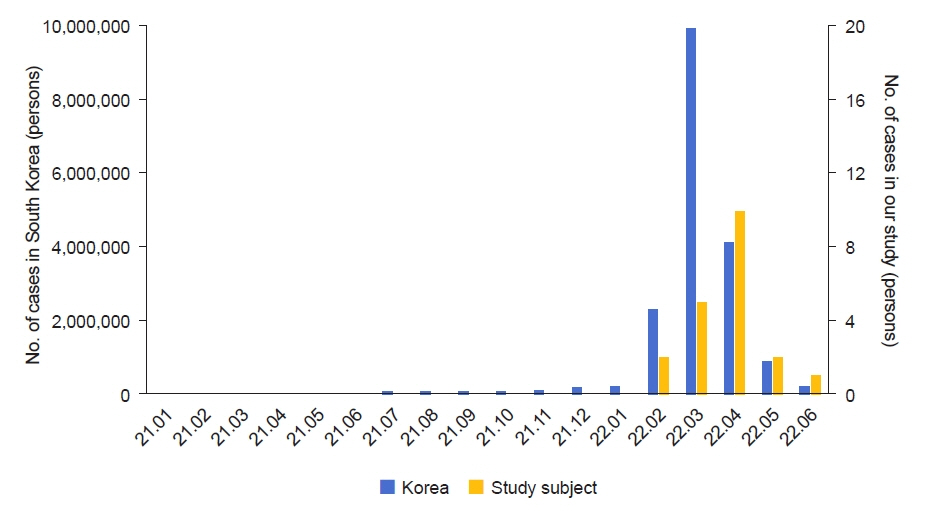
Twenty of the total 59 patients with nephrotic syndrome were diagnosed with COVID-19 during the study period. The mean age at the time of the diagnosis of nephrotic syndrome and COVID-19 in all 20 patients was 4.6±3.5 and 8.9±3.9 years, respectively. Three patients (15%) were diagnosed with nephrotic syndrome relapse during COVID-19 and the relapse rate was similar to them without COVID-19 (20.5%, 8/39 patients). At the time of the COVID-19 diagnosis, fever (85%) and cough (40%) were the most common symptoms. After the diagnosis of COVID-19, all patients showed improvement with symptomatic treatment, including antipyretic analgesics and cold medicine. None of the critical patients required hospitalization or oral antiviral medications.
Conclusions
Despite the use of immunosuppressants, the clinical manifestations of COVID-19 in children with nephrotic syndrome were not severe and are expected to be similar to that in the general population. The relapse rate of nephrotic syndrome in children with COVID-19 was also not different from them without COVID-19.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Coronavirus (COVID-19) [Internet]. Cheongju: Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency;c2022. [cited 2022 Sep 5]. Available from: http://ncov.mohw.go.kr/en/.2. Lebedev L, Sapojnikov M, Wechsler A, Varadi-Levi R, Zamir D, Tobar A, et al. Minimal change disease following the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021; 78:142–5.
Article3. Klomjit N, Alexander MP, Fervenza FC, Zoghby Z, Garg A, Hogan MC, et al. COVID-19 vaccination and glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int Rep. 2021; 6:2969–78.
Article4. Kudose S, Batal I, Santoriello D, Xu K, Barasch J, Peleg Y, et al. Kidney biopsy findings in patients with COVID-19. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020; 31:1959–68.
Article5. Batlle D, Soler MJ, Sparks MA, Hiremath S, South AM, Welling PA, et al. Acute kidney injury in COVID-19: emerging evidence of a distinct pathophysiology. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020; 31:1380–3.
Article6. Bomback AS, Kudose S, D’Agati VD. De novo and relapsing glomerular diseases after COVID-19 vaccination: what do we know so far? Am J Kidney Dis. 2021; 78:477–80.
Article7. Bjornstad EC, Krallman KA, Askenazi D, Zappitelli M, Goldstein SL, Basu RK, et al. Preliminary assessment of acute kidney injury in critically ill children associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multicenter cross-sectional analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021; 16:446–8.8. Serafinelli J, Mastrangelo A, Morello W, Cerioni VF, Salim A, Nebuloni M, et al. Kidney involvement and histological findings in two pediatric COVID-19 patients. Pediatr Nephrol. 2021; 36:3789–93.
Article9. Hanna C, Herrera Hernandez LP, Bu L, Kizilbash S, Najera L, Rheault MN, et al. IgA nephropathy presenting as macroscopic hematuria in 2 pediatric patients after receiving the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine. Kidney Int. 2021; 100:705–6.
Article10. Kim L, Whitaker M, O’Halloran A, Kambhampati A, Chai SJ, Reingold A, et al. Hospitalization rates and characteristics of children aged <18 years hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19: COVID-NET, 14 States, March 1-July 25, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020; 69:1081–8.11. de Souza TH, Nadal JA, Nogueira RJ, Pereira RM, Brandao MB. Clinical manifestations of children with COVID-19: a systematic review. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020; 55:1892–9.
Article12. Badal S, Thapa Bajgain K, Badal S, Thapa R, Bajgain BB, Santana MJ. Prevalence, clinical characteristics, and outcomes of pediatric COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Virol. 2021; 135:104715.
Article13. Parcha V, Booker KS, Kalra R, Kuranz S, Berra L, Arora G, et al. A retrospective cohort study of 12,306 pediatric COVID-19 patients in the United States. Sci Rep. 2021; 11:10231.
Article14. Valverde I, Singh Y, Sanchez-de-Toledo J, Theocharis P, Chikermane A, Di Filippo S, et al. Acute cardiovascular manifestations in 286 children with multisystem inflammatory syndrome associated with COVID-19 infection in Europe. Circulation. 2021; 143:21–32.
Article15. Gupta A, Madhavan MV, Sehgal K, Nair N, Mahajan S, Sehrawat TS, et al. Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19. Nat Med. 2020; 26:1017–32.
Article16. Basalely A, Gurusinghe S, Schneider J, Shah SS, Siegel LB, Pollack G, et al. Acute kidney injury in pediatric patients hospitalized with acute COVID-19 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children associated with COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2021; 100:138–45.
Article17. Shah SA, Carter HP. New-onset nephrotic syndrome in a child associated with COVID-19 infection. Front Pediatr. 2020; 8:471.
Article18. Alvarado A, Franceschi G, Resplandor E, Sumba J, Orta N. COVID-19 associated with onset nephrotic syndrome in a pediatric patient: coincidence or related conditions? Pediatr Nephrol. 2021; 36:205–7.
Article19. MacDonald NE, Wolfish N, McLaine P, Phipps P, Rossier E. Role of respiratory viruses in exacerbations of primary nephrotic syndrome. J Pediatr. 1986; 108:378–82.
Article20. Uwaezuoke SN. Steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome in children: triggers of relapse and evolving hypotheses on pathogenesis. Ital J Pediatr. 2015; 41:19.
Article21. Zhang H, Wang Z, Dong L, Guo Y, Wu J, Zhai S. New insight into the pathogenesis of minimal change nephrotic syndrome: role of the persistence of respiratory tract virus in immune disorders. Autoimmun Rev. 2016; 15:632–7.
Article22. Crane C, Bakhoum C, Ingulli E. Rates of idiopathic childhood nephrotic syndrome relapse are lower during the COVID-19 pandemic. Pediatr Nephrol. 2022; 37:2679–85.
Article23. Morello W, Vianello FA, Proverbio E, Peruzzi L, Pasini A, Montini G. COVID-19 and idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children: systematic review of the literature and recommendations from a highly affected area. Pediatr Nephrol. 2022; 37:757–64.
Article24. Angeletti A, Drovandi S, Sanguineri F, Santaniello M, Ferrando G, Forno R, et al. COVID-19 in children with nephrotic syndrome on anti-CD20 chronic immunosuppression. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020; 15:1494–5.
Article25. Marlais M, Wlodkowski T, Al-Akash S, Ananin P, Bandi VK, Baudouin V, et al. COVID-19 in children treated with immunosuppressive medication for kidney diseases. Arch Dis Child. 2020; 106:798–801.
Article26. Sinha R, Marlais M, Sarkar S, Obukhova V, Lucchetti L, Vasudevan A, et al. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on use of rituximab among children with difficult nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Res. 2022; 92:3–5.
Article27. Angeletti A, Bruschi M, Bigatti C, Palmeri S, Lugani F, Verrina E, et al. An update on COVID-19 in paediatric and young adults with nephrotic syndrome, receiving chronic immunosuppression during the Omicron pandemic. J Nephrol. 2022; 35:1775–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Kidney complications associated with COVID-19 infection and vaccination in children and adolescents: a brief review
- A Study of Serum Cytokines in Nephrotic Syndrome
- COVID-19 in immunocompromised children and adolescents
- The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on in-hospital mortality in patients admitted through the emergency department
- Therapeutics in the Treatment of COVID-19 for Children and Adolescents