J Dent Rehabil Appl Sci.
2022 Dec;38(4):196-203. 10.14368/jdras.2022.38.4.196.
Deep learning algorithms for identifying 79 dental implant types
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, College of Dentistry, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Republic of Korea
- 2HERIBio Co. Ltd., Seoul, Republic of Korea
- 3Korea Platform Service Technology Co. Ltd., Daejeon, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2538517
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14368/jdras.2022.38.4.196
Abstract
- Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the accuracy and clinical usability of an identification model using deep learning for 79 dental implant types.
Materials and Methods
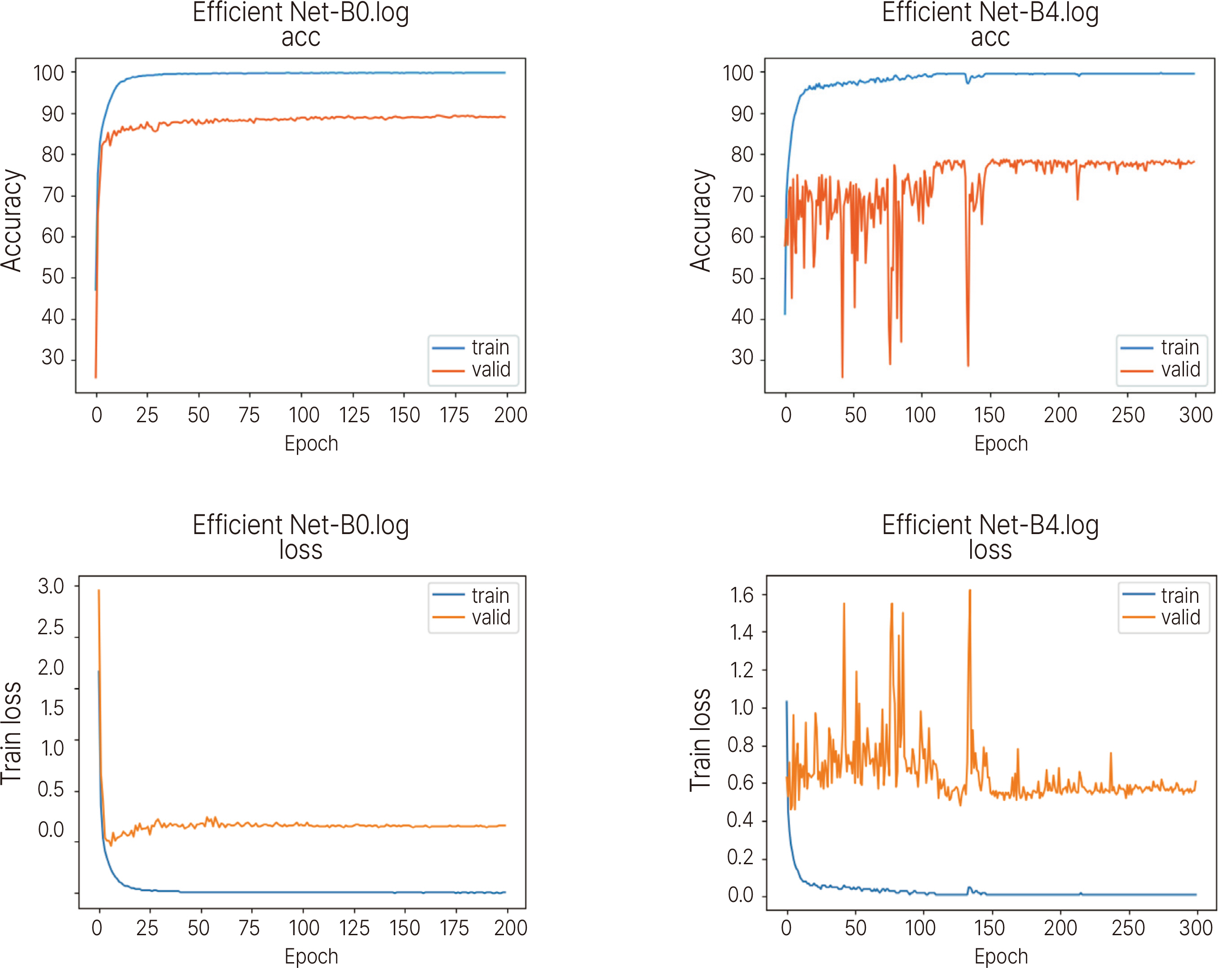
A total of 45396 implant fixture images were collected through panoramic radiographs of patients who received implant treatment from 2001 to 2020 at 30 dental clinics. The collected implant images were 79 types from 18 manufacturers. EfficientNet and Meta Pseudo Labels algorithms were used. For EfficientNet, EfficientNet-B0 and EfficientNet-B4 were used as submodels. For Meta Pseudo Labels, two models were applied according to the widen factor. Top 1 accuracy was measured for EfficientNet and top 1 and top 5 accuracy for Meta Pseudo Labels were measured.
Results
EfficientNet-B0 and EfficientNet-B4 showed top 1 accuracy of 89.4. Meta Pseudo Labels 1 showed top 1 accuracy of 87.96, and Meta pseudo labels 2 with increased widen factor showed 88.35. In Top5 Accuracy, the score of Meta Pseudo Labels 1 was 97.90, which was 0.11% higher than 97.79 of Meta Pseudo Labels 2.
Conclusion
All four deep learning algorithms used for implant identification in this study showed close to 90% accuracy. In order to increase the clinical applicability of deep learning for implant identification, it will be necessary to collect a wider amount of data and develop a fine-tuned algorithm for implant identification.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Hämmerle CH, Glauser R. 2004; Clinical evaluation of dental implant treatment. Periodontol 2000. 34:230–9. DOI: 10.1046/j.0906-6713.2003.003434.x. PMID: 14717865. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=1542402165&origin=inward.
Article2. Romeo E, Lops D, Margutti E, Ghisolfi M, Chiapasco M, Vogel G. 2004; Long-term survival and success of oral implants in the treatment of full and partial arches: a 7-year prospective study with the ITI dental implant system. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 19:247–59. PMID: 15101597. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=2342431804&origin=inward.3. Grossmann Y, Nissan J, Levin L. 2009; Clinical effectiveness of implant-supported removable partial dentures: a review of the literature and retrospective case evaluation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 67:1941–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.joms.2009.04.081. PMID: 19686933. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=68749102397&origin=inward.4. Simonis P, Dufour T, Tenenbaum H. 2010; Long-term implant survival and success: a 10-16-year follow-up of non-submerged dental implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 21:772–7. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2010.01912.x. PMID: 20636731. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=77954616080&origin=inward.
Article5. Hadj Saïd M, Le Roux MK, Catherine JH, Lan R. 2020; Development of an artificial intelligence model to identify a dental implant from a radiograph. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 36:1077–82. DOI: 10.11607/jomi.8060. PMID: 33270045. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85097120934&origin=inward.
Article6. Misch K, Wang HL. 2008; Implant surgery complications: etiology and treatment. Implant Dent. 17:159–68. DOI: 10.1097/ID.0b013e3181752f61. PMID: 18545047. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=50949086798&origin=inward.
Article7. Annibali S, Ripari M, LA Monaca G, Tonoli F, Cristalli MP. 2008; Local complications in dental implant surgery: prevention and treatment. Oral Implantol. 1:21–33. PMID: 23285333. PMCID: PMC3476500.8. Nedir R, Bischof M, Szmukler-Moncler S, Belser UC, Samson J. 2006; Prosthetic complications with dental implants: from an up-to-8-year experience in private practice. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 21:919–28. PMID: 17190302. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=33748363075&origin=inward.9. Sahiwal IG, Woody RD, Benson BW, Guillen GE. 2002; Radiographic identification of nonthreaded endosseous dental implants. J Prosthet Dent. 87:552–62. DOI: 10.1067/mpr.2002.124431. PMID: 12070519. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=0036561659&origin=inward.10. Sewerin I. 1992; Identification of dental implants on radiographs. Quintessence Int. 23:611–8. PMID: 1287712. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=0026920620&origin=inward.11. Chan HP, Samala RK, Hadjiiski LM, Zhou C. 2020; Deep learning in medical image analysis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1213:3–21. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-33128-3_1. PMID: 32030660. PMCID: PMC7442218. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85079081079&origin=inward.
Article12. Hwang JJ, Jung YH, Cho BH, Heo MS. 2019; An overview of deep learning in the field of dentistry. Imaging Sci Dent. 49:1–7. DOI: 10.5624/isd.2019.49.1.1. PMID: 30941282. PMCID: PMC6444007. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85065124911&origin=inward.
Article13. Lee JH, Kim YT, Lee JB, Jeong SN. 2020; A performance comparison between automated deep learning and dental professionals in classification of dental implant systems from dental imaging: a multi-center study. Diagnostics. 10:910. DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics10110910. PMID: 33171758. PMCID: PMC7694989. PMID: 6b6b369966a945058a6b2fd1b01278df. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85106410473&origin=inward.
Article14. Takahashi T, Nozaki K, Gonda T, Mameno T, Wada M, Ikebe K. 2020; Identification of dental implants using deep learning-pilot study. Int J Implant Dent. 6:53. DOI: 10.1186/s40729-020-00250-6. PMID: 32959154. PMCID: PMC7505912. PMID: 6f5754f801aa47dc83ad2947fbc03011.
Article15. Sukegawa S, Yoshii K, Hara T, Yamashita K, Nakano K, Yamamoto N, Nagatsuka H, Furuki Y. 2020; Deep neural networks for dental implant system classification. Biomolecules. 10:984. DOI: 10.3390/biom10070984. PMID: 32630195. PMCID: PMC7407934. PMID: c17a561a9e424951a6cd1b4254138aed. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85087385076&origin=inward.
Article16. Kim JE, Nam NE, Shim JS, Jung YH, Cho BH, Hwang JJ. 2020; Transfer learning via deep neural networks for implant fixture system classification using periapical radiographs. J Clin Med. 9:1117. DOI: 10.3390/jcm9041117. PMID: 32295304. PMCID: PMC7230319. PMID: 7310646b9c69425ea1064de40afe19c9. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85086727912&origin=inward.
Article17. Tan M, Le QV. 2019; Efficientnet: rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. Proc Mach Learn Res. 97:6105–14. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=0026920620&origin=inward.18. Michelinakis G, Sharrock A, Barclay CW. 2006; Identification of dental implants through the use of Implant Recognition Software (IRS). Int Dent J. 56:203–8. DOI: 10.1111/j.1875-595X.2006.tb00095.x. PMID: 16972394. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=33748373581&origin=inward.
Article19. Zheng Q, Yang M, Tian X, Jiang N, Wang D. 2020; A full stage data augmentation method in deep convolutional neural network for natural image classification. Discrete Dyn Nat Soc. 1:1–11. DOI: 10.1155/2020/4706576. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85078185391&origin=inward.
Article20. Truhlar RS, Morris HF, Ochi S. 1993; A review of panoramic radiography and its potential use in implant dentistry. Implant Dent. 2:122–30. DOI: 10.1097/00008505-199305000-00010. PMID: 8242015. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=0027621050&origin=inward.
Article21. Kayal RA. 2016; Distortion of digital panoramic radiographs used for implant site assessment. J Orthod Sci. 5:117–20. DOI: 10.4103/2278-0203.192113. PMID: 27843885. PMCID: PMC5084472. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85054704369&origin=inward.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Deep Learning in Dental Radiographic Imaging
- Development of an Optimized Deep Learning Model for Medical Imaging
- Application of Deep Learning in Dentistry and Implantology
- An Overview of Deep Learning Algorithms and Their Applications in Neuropsychiatry
- Deep learning convolutional neural network algorithms for the early detection and diagnosis of dental caries on periapical radiographs: A systematic review