J Surg Ultrasound.
2022 Nov;9(2):36-41. 10.46268/jsu.2022.9.2.36.
Ultrasonography-Guided Breast Tissue Marker Insertion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Breast Cancer Center, Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2538383
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.46268/jsu.2022.9.2.36
Abstract
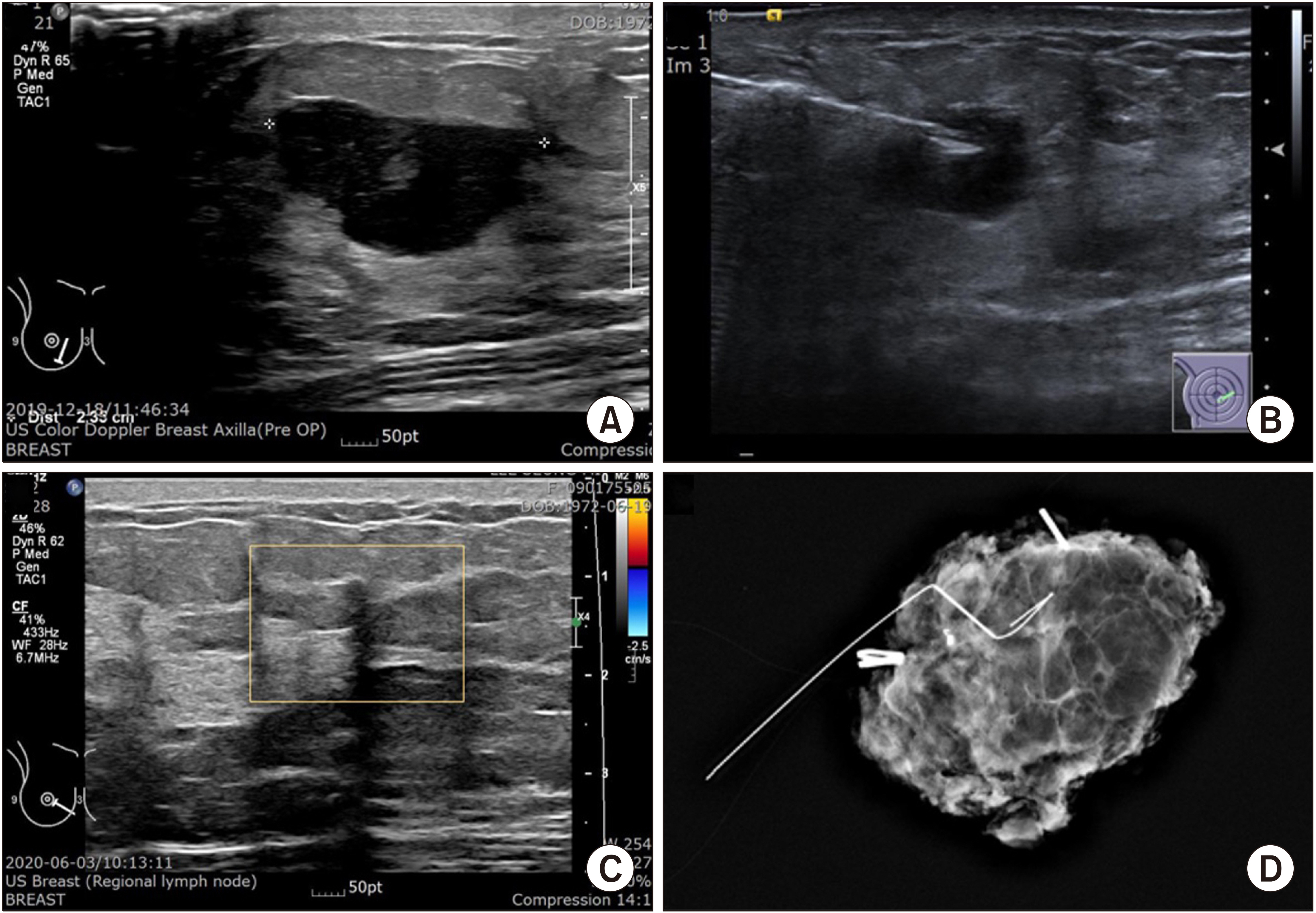
- Recently, Non-palpable lesion detection has been increasing in breast cancer management due to early detection and better response of neoadjuvant treatment. Therefore, localising the lesions more accurately in real-time with minimal tissue injury has assumed greater importance. Traditionally, mammography-guided wire localization has been the most commonly used technique. However, tissue injury might be inevitable when the distance between wire insertion and the lesion is far, as accurate 3-dimensional localization is not easy, and scheduling for the procedure delays the time of the surgery. Therefore, ultrasonographyguided wire localization is a useful method, as many surgeons routinely use ultrasonography in their clinics in Korea. However, it is not easy to find the marker as predicted when breast lesions disappear after neoadjuvant treatment, and this procedure needs to be scheduled just prior to surgery. This review article discusses practical aspects and multiple approaches using tissue markers to enhance the localization of non-palpable lesions.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Burbank F, Forcier N. 1997; Tissue marking clip for stereotactic breast biopsy: initial placement accuracy, long-term stability, and usefulness as a guide for wire localization. Radiology. 205:407–15. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.205.2.9356621. PMID: 9356621.
Article2. Liberman L, Dershaw DD, Morris EA, Abramson AF, Thornton CM, Rosen PP. 1997; Clip placement after stereotactic vacuum-assisted breast biopsy. Radiology. 205:417–22. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.205.2.9356622. PMID: 9356622.
Article3. Kaufman CS, Delbecq R, Jacobson L. 1998; Excising the reexcision: stereotactic core-needle biopsy decreases need for reexcision of breast cancer. World J Surg. 22:1023–7. discussion 1028DOI: 10.1007/s002689900510. PMID: 9747160.
Article4. Rahusen FD, van Diest PJ, Borgstein PJ, Bleichrodt RP, Meijer S. Taets van Amerongen AH. 1999; Ultrasound-guided lumpectomy of nonpalpable breast cancers: a feasibility study looking at the accuracy of obtained margins. J Surg Oncol. 72:72–6. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9098(199910)72:2<72::AID-JSO6>3.0.CO;2-M. PMID: 10518102.
Article5. Cangiarella J, Gross J, Symmans WF, Waisman J, Petersen B, D'Angelo D, et al. 2000; The incidence of positive margins with breast conserving therapy following mammotome biopsy for microcalcification. J Surg Oncol. 74:263–6. DOI: 10.1002/1096-9098(200008)74:4<263::AID-JSO4>3.0.CO;2-1. PMID: 10962457.
Article6. Nurko J, Mancino AT, Whitacre E, Edwards MJ. 2005; Surgical benefits conveyed by biopsy site marking system using ultrasound localization. Am J Surg. 618–22. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2005.06.027. PMID: 16164935.
Article7. Thomassin-Naggara I, Lalonde L, David J, Darai E, Uzan S, Trop I. 2012; A plea for the biopsy marker: how, why and why not clipping after breast biopsy? Breast Cancer Res Treat. 132:881–93. DOI: 10.1007/s10549-011-1847-x. PMID: 22042370.
Article8. Rosen EL, Baker JA, Soo MS. 2003; Accuracy of a collagen-plug biopsy site marking device deployed after stereotactic core needle breast biopsy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 181:1295–9. DOI: 10.2214/ajr.181.5.1811295. PMID: 14573422.
Article9. Phillips SW, Gabriel H, Comstock CE, Venta LA. 2000; Sonographically guided metallic clip placement after core needle biopsy of the breast. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 175:1353–5. DOI: 10.2214/ajr.175.5.1751353. PMID: 11044040.
Article10. McMahon MA, James JJ, Cornford EJ, Hamilton LJ, Burrell HC. 2011; Does the insertion of a gel-based marker at stereotactic breast biopsy allow subsequent wire localizations to be carried out under ultrasound guidance? Clin Radiol. 66:840–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.crad.2011.04.003. PMID: 21658688.
Article11. Sakamoto N, Ogawa Y, Tsunoda Y, Fukuma E. 2017; Evaluation of the sonographic visibility and sonographic appearance of the breast biopsy marker (UltraClipⓇ) placed in phantoms and patients. Breast Cancer. 24:585–92. DOI: 10.1007/s12282-016-0741-0. PMID: 27838870.
Article12. Koo JH, Kim EK, Moon HJ, Yoon JH, Park VY, Kim MJ. 2019; Comparison of breast tissue markers for tumor localization in breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ultrasonography. 38:336–44. DOI: 10.14366/usg.19004. PMID: 31378014. PMCID: PMC6769188.
Article13. Rissanen TJ, Mäkäräinen HP, Mattila SI, Karttunen AI, Kiviniemi HO, Kallioinen MJ, et al. 1993; Wire localized biopsy of breast lesions: a review of 425 cases found in screening or clinical mammography. Clin Radiol. 47:14–22. DOI: 10.1016/S0009-9260(05)81207-3. PMID: 8428412.
Article14. Wazir U, Tayeh S, Perry N, Michell M, Malhotra A, Mokbel K. o2020; Wireless breast localization using radio-frequency identification tags: the first reported European experience in breast cancer. In. 34:233–8. DOI: 10.21873/invivo.11765. PMID: 31882483. PMCID: PMC6984090.
Article15. Ruiz-Delgado ML, López-Ruiz JA, Sáiz-López A. 2008; Abnormal mammography and sonography associated with foreign-body giant-cell reaction after stereotactic vacuum-assisted breast biopsy with carbon marking. Acta Radiol. 49:1112–8. DOI: 10.1080/02841850802452075. PMID: 18932053.
Article16. Kang T. Korean Surgical Ultrasound Society. 2021. Ultrasound-guided breast marker insertion. Textbook of Surgical Ultrasound. Koonja Publishing;Paju: p. 252–58.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasound-Guided Intervention for Breast Lesions
- Intraductal Migration of a Breast Tissue Marker Placed under Ultrasound Guidance during COVIDInduced Delay of Surgery
- Evaluating imaging-pathology concordance and discordance after ultrasound-guided breast biopsy
- US-guided Clip Implantation for Tumor Localization in Breast Cancer Patients Who Undergo Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Feasibility Study
- New Metallic Marker Used after Mammotome Biopsy for the Localization of Breast Lesions: Initial Experience