J Korean Med Sci.
2023 Jan;38(2):e7. 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e7.
Diagnostic Usefulness of Varicella Zoster Virus-Specific Immunoglobulin (Ig) A and IgG in Patients With Herpes Zoster
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Infectious Diseases, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- 3Department of Infectious Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2537954
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e7
Abstract
- Background
Whether varicella zoster virus (VZV) antibody titer could discriminate patients with herpes zoster (HZ) from healthy controls (HCs) is unclear. We evaluated the diagnostic usefulness of VZV-specific immunoglobulin A (IgA) and immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies in patients with confirmed HZ.
Methods
Study subjects comprised patients with confirmed HZ by salivary VZV DNA positivity and control age- and sex-matched HCs. Saliva was collected and concurrent blood samples were obtained on the first visit day (acute phase) and after 4 weeks (convalescent phase) from 44 HZ patients. All 44 healthy volunteers provided blood and saliva samples once.
Results
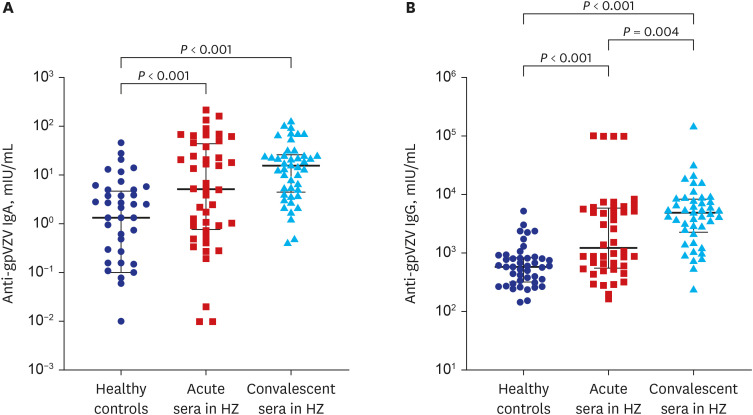
The median VZV IgA titers in acute-phase (5.2 mIU/mL, P < 0.001) and convalescentphase (15.8 mIU/mL, P < 0.001) serum samples from HZ patients were significantly higher than those in HCs (1.35 mIU/mL). VZV IgA positivity was detected in about 20% of acute phase serum and convalescent-phase serum of HZ patients. The median VZV IgG antibody titers of HZ patients during acute (1,471.0 mIU/mL, P < 0.001) and convalescent (4,934.7 mIU/mL, P < 0.001) phases were significantly higher than the median titer reported for HCs (591.6 mIU/mL). A four-fold or higher increase in VZV IgG antibody titer was observed in 36.4% of HZ patients.
Conclusion
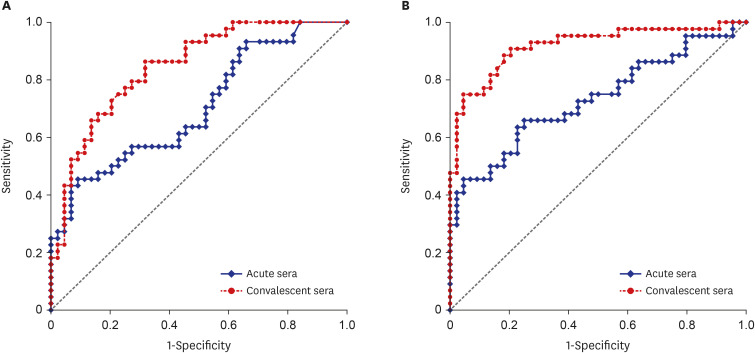
VZV IgA positivity or four-fold or higher increase in VZV IgG antibody titers were not detected in a satisfactory proportion of HZ-infected patients. However, the titer of VZV IgA or IgG antibody particularly in convalescent-phase sera may discriminate HZ patients from HCs.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zerboni L, Sen N, Oliver SL, Arvin AM. Molecular mechanisms of varicella zoster virus pathogenesis. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2014; 12(3):197–210. PMID: 24509782.2. Park SY, Kim JY, Kim JA, Kwon JS, Kim SM, Jeon NY, et al. Diagnostic usefulness of varicella-zoster virus real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis of DNA in saliva and plasma specimens from patients with herpes zoster. J Infect Dis. 2017; 217(1):51–57. PMID: 29029120.3. Leung J, Harpaz R, Baughman AL, Heath K, Loparev V, Vázquez M, et al. Evaluation of laboratory methods for diagnosis of varicella. Clin Infect Dis. 2010; 51(1):23–32. PMID: 20504232.4. Sauerbrei A, Eichhorn U, Schacke M, Wutzler P. Laboratory diagnosis of herpes zoster. J Clin Virol. 1999; 14(1):31–36. PMID: 10548128.5. Mehta SK, Tyring SK, Gilden DH, Cohrs RJ, Leal MJ, Castro VA, et al. Varicella-zoster virus in the saliva of patients with herpes zoster. J Infect Dis. 2008; 197(5):654–657. PMID: 18260763.6. Warren-Gash C, Forbes H, Maple P, Quinlivan M, Breuer J. Viral load and antibody boosting following herpes zoster diagnosis. J Clin Virol. 2018; 103:12–15. PMID: 29602095.7. Dobec M, Bossart W, Kaeppeli F, Mueller-Schoop J. Serology and serum DNA detection in shingles. Swiss Med Wkly. 2008; 138(3-4):47–51. PMID: 18224496.8. Hadar T, Tovi F, Sidi J, Sarov B, Sarov I. Detection of specific IgA antibodies to varicella zoster virus in serum of patients with Ramsay Hunt syndrome. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1990; 99(6 Pt 1):461–465. PMID: 2161635.9. Oladepo DK, Klapper PE, Percival D, Vallely PJ. Serological diagnosis of varicella-zoster virus in sera with antibody-capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of IgM. J Virol Methods. 2000; 84(2):169–173. PMID: 10680966.10. Min SW, Kim YS, Nahm FS, Yoo DH, Choi E, Lee PB, et al. The positive duration of varicella zoster immunoglobulin M antibody test in herpes zoster. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95(33):e4616. PMID: 27537598.11. Cradock-Watson JE, Ridehalgh MK, Bourne MS. Specific immunoglobulin responses after varicella and herpes zoster. J Hyg (Lond). 1979; 82(2):319–336. PMID: 219110.12. Fluss R, Faraggi D, Reiser B. Estimation of the Youden Index and its associated cutoff point. Biom J. 2005; 47(4):458–472. PMID: 16161804.13. Wittek AE, Arvin AM, Koropchak CM. Serum immunoglobulin A antibody to varicella-zoster virus in subjects with primary varicella and herpes zoster infections and in immune subjects. J Clin Microbiol. 1983; 18(5):1146–1149. PMID: 6315766.14. Tovi F, Hadar T, Sidi J, Sarov B, Sarov I. The significance of specific IgA antibodies in the serum in the early diagnosis of zoster. J Infect Dis. 1985; 152(1):230. PMID: 2989386.15. van Loon AM, van der Logt JT, Heessen FW, Heeren MC, Zoll J. Antibody-capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays that use enzyme-labelled antigen for detection of virus-specific immunoglobulin M, A and G in patients with varicella or herpes zoster. Epidemiol Infect. 1992; 108(1):165–174. PMID: 1312479.16. Laing KJ, Ouwendijk WJ, Koelle DM, Verjans GM. Immunobiology of varicella-zoster virus infection. J Infect Dis. 2018; 218(suppl_2):S68–S74. PMID: 30247598.17. Rondaan C, de Haan A, Horst G, Hempel JC, van Leer C, Bos NA, et al. Altered cellular and humoral immunity to varicella-zoster virus in patients with autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014; 66(11):3122–3128. PMID: 25223407.18. Schub D, Assmann G, Sester U, Sester M, Schmidt T. VZV-specific T-cell levels in patients with rheumatic diseases are reduced and differentially influenced by antirheumatic drugs. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018; 20(1):252. PMID: 30413189.19. Champsaur H, Fattal-German M, Arranhado R. Sensitivity and specificity of viral immunoglobulin M determination by indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1988; 26(2):328–332. PMID: 3125220.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Significance of Serum Varicella Zoster Virus Immunoglobulin M and G in Varicella and Herpes Zoster
- A Case of Herpes Zoster in a Normal 3 - Month - Old Infant
- A Study of Cellular and Humoral Immunity in Patients with Herpes Zoster
- A Case of Aseptic Meningitis with Herpes Zoster
- A Case of Herpes Zoster in a 9-month-old Infant