J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2022 Dec;48(6):390-396. 10.5125/jkaoms.2022.48.6.390.
Surgical correction of cleft lip lower-lip deformity: a report of three cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Seoul National University Dental Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2537566
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2022.48.6.390
Abstract
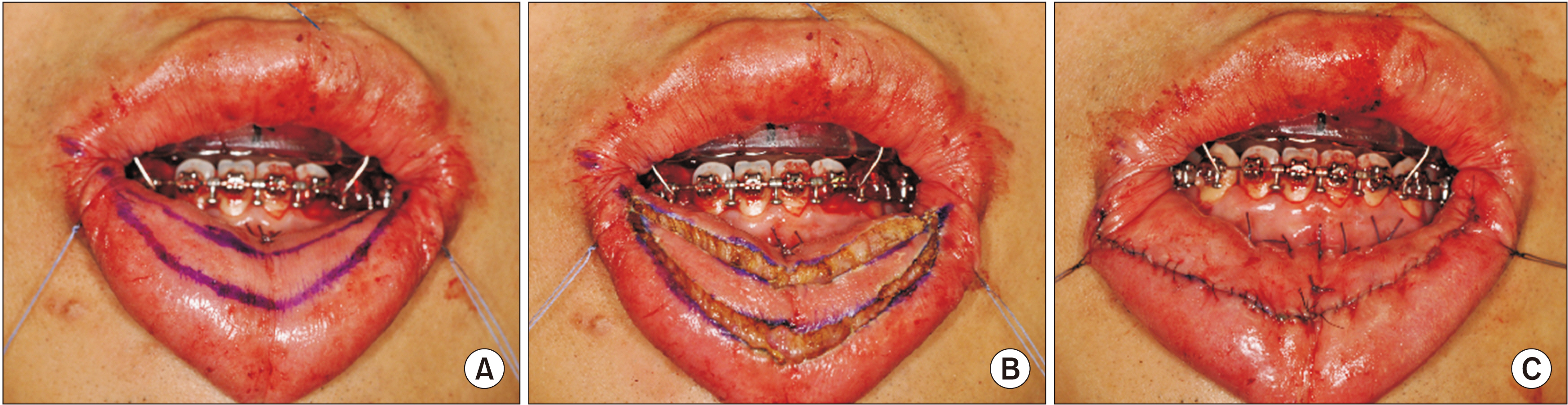
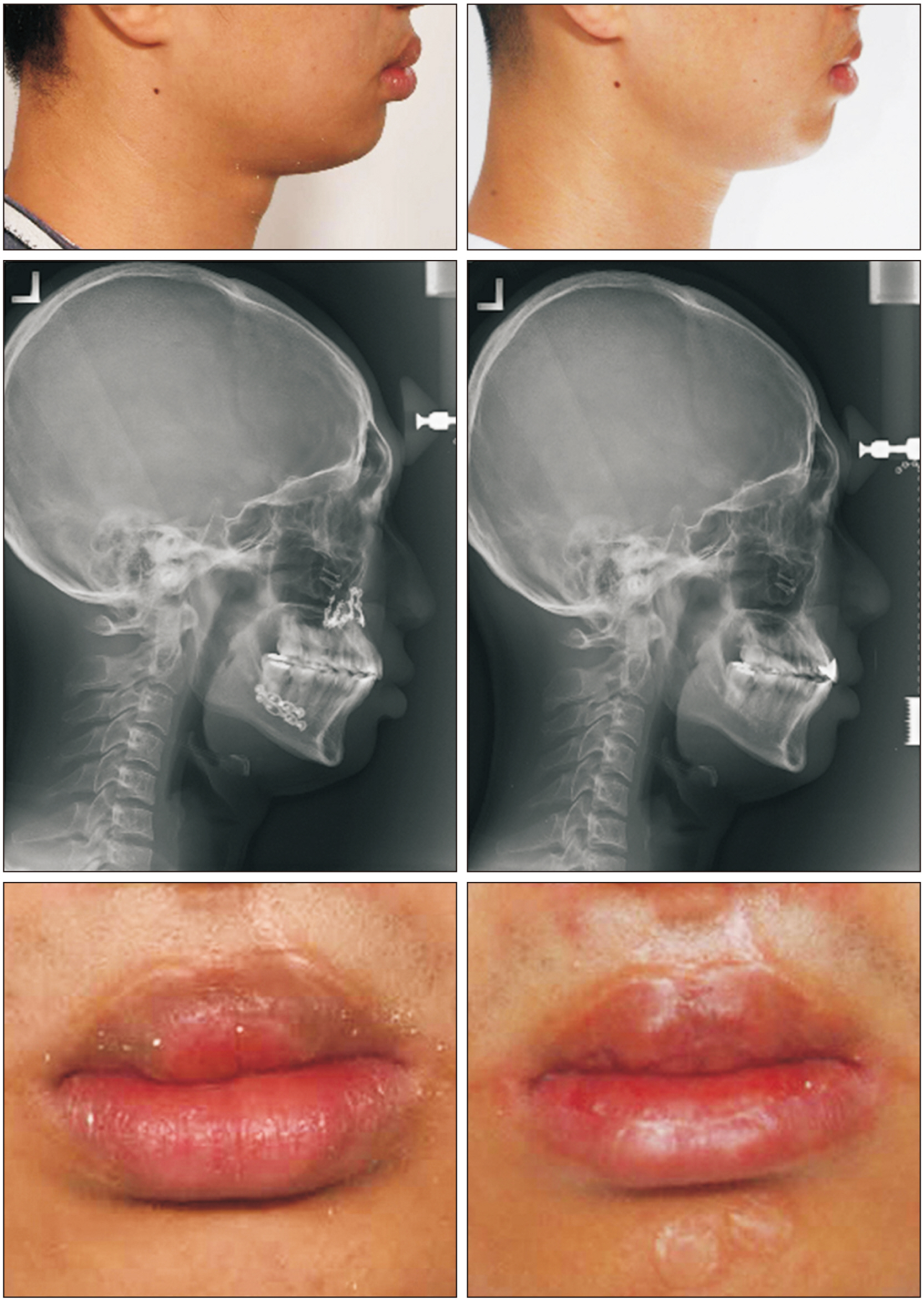
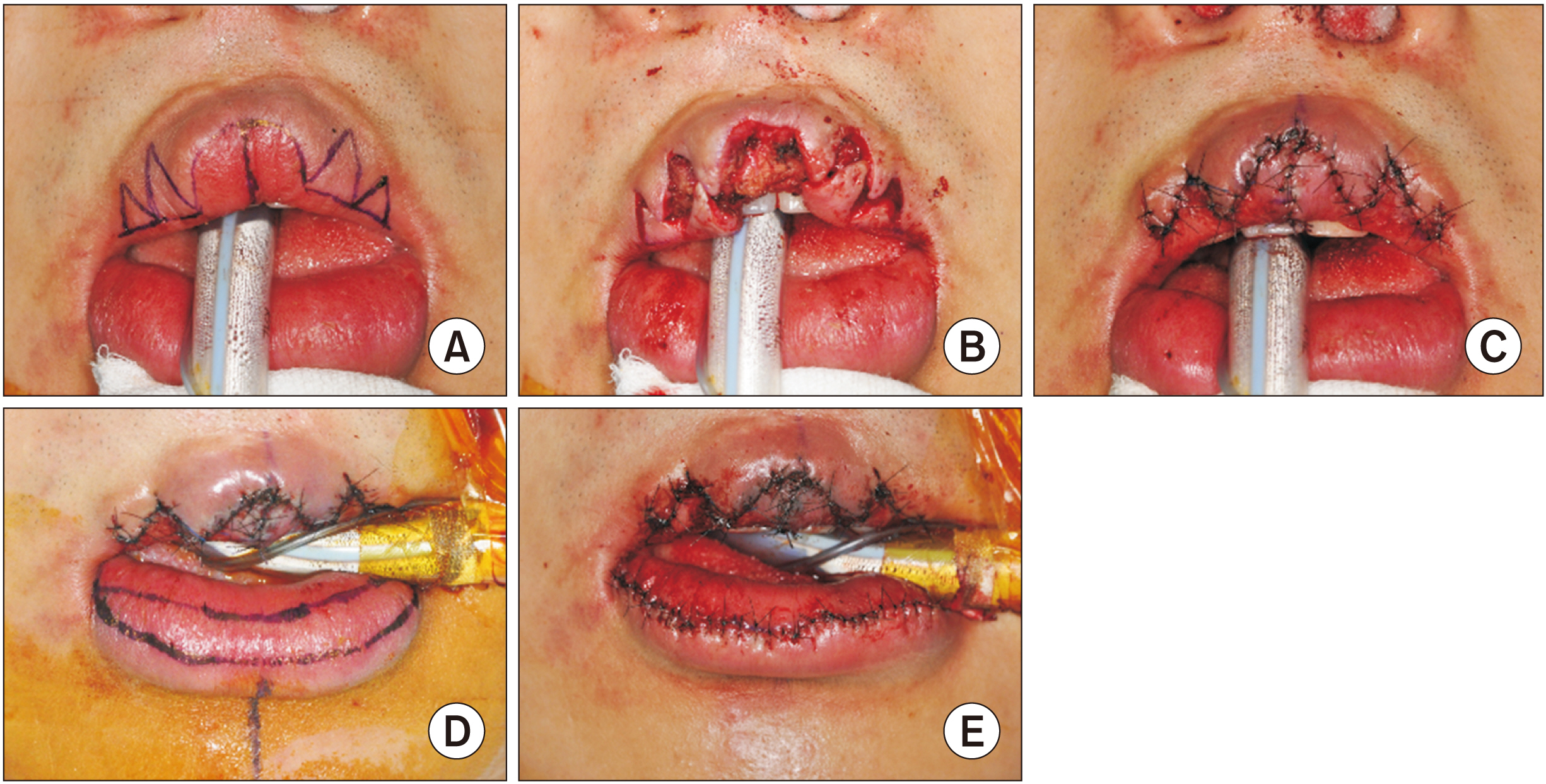
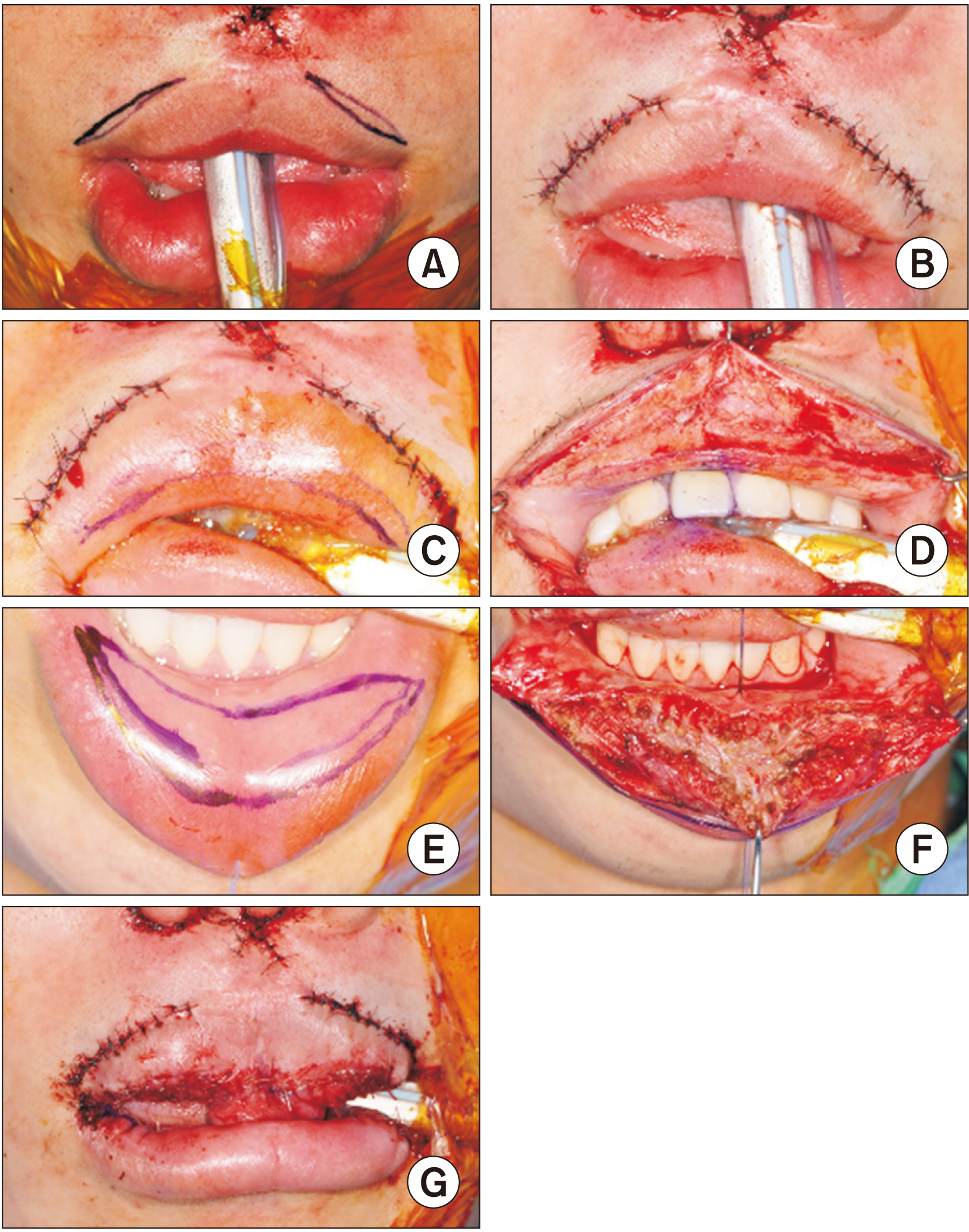
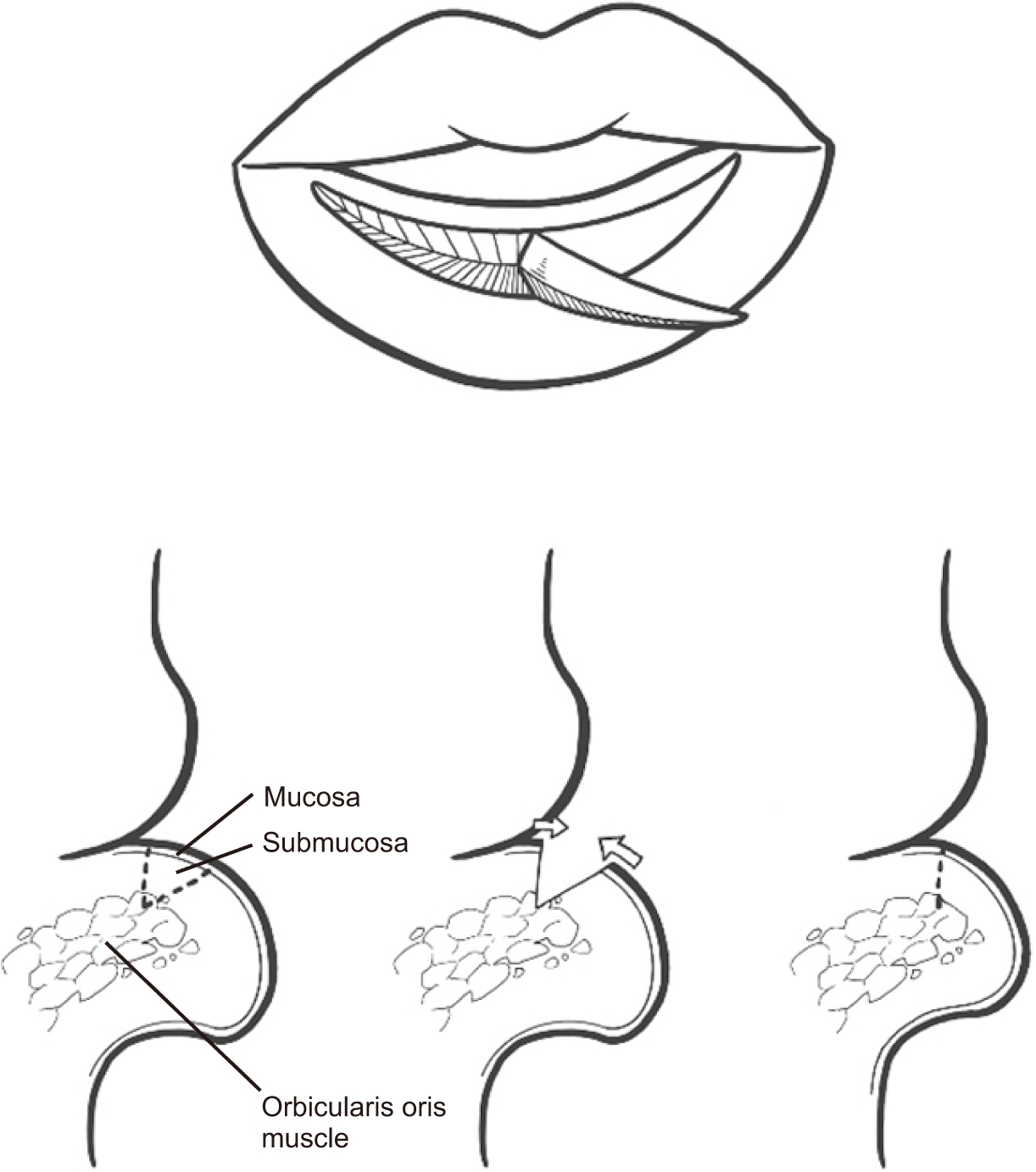
- Cleft lip lower-lip deformity is a secondary deformity in patients who underwent primary cheiloplasty of the upper lip, characterized by an enlarged and anteriorly rotated lower lip. In these cases, soft-tissue imbalances remain even after skeletal correction with orthognathic surgery, and additional soft tissue treatment is required for lip harmony and esthetic facial balance in CLP (cleft lip palate) patients. This study describes three cases of transverse myomucosal excision of the lower lip for correction of cleft lip lower-lip deformity to restore facial esthetic balance. Each patient underwent orthognathic surgery, rhinoplasty, or upper lip revision cheiloplasty according to condition. Postoperatively, volume of the lower lip decreased and lip harmony was improved in all three patients. The surgeon should fully understand the anatomical structure around the lips and be able to evaluate overall harmony of the soft tissue. When a lower lip deformity is present, careful surgical planning and execution are important for each patient.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Park JS, Koh KS, Choi JW. 2015; Lower lip deformity in patients with cleft and non-cleft class III malocclusion before and after orthognathic surgery. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 43:1638–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2015.07.029. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcms.2015.07.029. PMID: 26315274.2. Yilmaz H, Demirkaya AA. Gülşen A, editor. 2020. Orthognathic surgery in cleft lip and palate patients. Current treatment of cleft lip and palate. IntechOpen;London: p. 63–82. DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.89556.3. Smahel Z, Polivková H, Skvarilová B, Horák I. 1992; Configuration of facial profile in adults with cleft lip with or without cleft palate. Acta Chir Plast. 34:190–203.4. Semb G, Brattström V, Mølsted K, Prahl-Andersen B, Zuurbier P, Rumsey N, et al. 2005; The Eurocleft study: intercenter study of treatment outcome in patients with complete cleft lip and palate. Part 4: relationship among treatment outcome, patient/parent satisfaction, and the burden of care. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 42:83–92. https://doi.org/10.1597/02-119.4.1. DOI: 10.1597/02-119.4.1. PMID: 15643921.5. Ferrari Júnior FM, Ayub PV, Capelozza Filho L, Pereira Lauris JR, Garib DG. 2015; Esthetic evaluation of the facial profile in rehabilitated adults with complete bilateral cleft lip and palate. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 73:169.e1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2014.09.012. DOI: 10.1016/j.joms.2014.09.012. PMID: 25511967.6. Pensler JM, Mulliken JB. 1988; The cleft lip lower-lip deformity. Plast Reconstr Surg. 82:602–10. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-198810000-00007. DOI: 10.1097/00006534-198810000-00007. PMID: 3420181.7. Brown JB, McDowell F. 1941; Secondary repair of cleft lips and their nasal deformities. Ann Surg. 114:101–17. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-194107000-00012. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-194107000-00012. PMID: 17857848. PMCID: PMC1385792.8. Langeveld M, Bruun RA, Koudstaal MJ, Padwa BL. 2019; Etiology of cleft lip lower lip deformity: use of an objective analysis to measure severity. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 56:1333–9. https://doi.org/10.1177/1055665619853373. DOI: 10.1177/1055665619853373. PMID: 31610716.9. Zhu NW, Senewiratne S, Pigott RW. 1994; Lip posture and mouth width in children with unilateral cleft lip. Br J Plast Surg. 47:301–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/0007-1226(94)90086-8. DOI: 10.1016/0007-1226(94)90086-8. PMID: 8087366.10. Duffy S, Noar JH, Evans RD, Sanders R. 2000; Three-dimensional analysis of the child cleft face. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 37:137–44. https://doi.org/10.1597/1545-1569_2000_037_0137_tdaotc_2.3.co_2. DOI: 10.1597/1545-1569_2000_037_0137_tdaotc_2.3.co_2. PMID: 10749054.11. Oyama T, Yoshimura Y, Onoda M, Hosokawa K. 2010; One-stage vermilion switch flap procedure for the correction of thin lips in patients with bilateral cleft lips. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 63:e248–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2009.06.004. DOI: 10.1016/j.bjps.2009.06.004. PMID: 19577526.12. Kawamoto HK Jr. 1979; Correction of major defects of the vermilion with a cross-lip vermilion flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 64:315–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-197909000-00005. DOI: 10.1097/00006534-197909000-00005. PMID: 472041.13. Wintsch K, Ortiz Monasterio F. 1990; Contour correction of the vermilion of the upper lip by island flap of the lower lip. Plast Reconstr Surg. 86:768–72. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199010000-00031. DOI: 10.1097/00006534-199010000-00031. PMID: 2217596.14. Chung KH, Lo LJ. 2017; A new method for reconstruction of vermilion deficiency in cleft lip deformity: the bi-winged myomucosa switch flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 140:1251–5. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000003889. DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000003889. PMID: 28820844.15. Ohtsuka H. 1985; One-stage lip-switch operation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 76:613–5. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-198510000-00025. DOI: 10.1097/00006534-198510000-00025. PMID: 4034780.16. Niamtu J 3rd. 2010; Lip reduction surgery (reduction cheiloplasty). Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 18:79–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2009.11.007. DOI: 10.1016/j.fsc.2009.11.007. PMID: 20206092.17. Anvar BA, Evans BCD, Evans GRD. 2007; Lip reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 120:57e–64e. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000278056.41753.ce. DOI: 10.1097/01.prs.0000278056.41753.ce. PMID: 17805106.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Treatment of Microform Cleft Lip Patients According to the Classification
- Orthodontic consideration of cleft lip and palate (Report 1)
- Columellar Lengthening Using V-Y Advancement Flap or Central Lip Flap in Secondary Correction of Bilateral Cleft Lip Nose Deformity
- Surgical Correction for Minimal Cleft Lip
- Corrective Rhinoplasty with Combined Use of Autogenous Auricular Cartilage and Porcine Dermal Collagen in Cleft Lip Nose Deformity