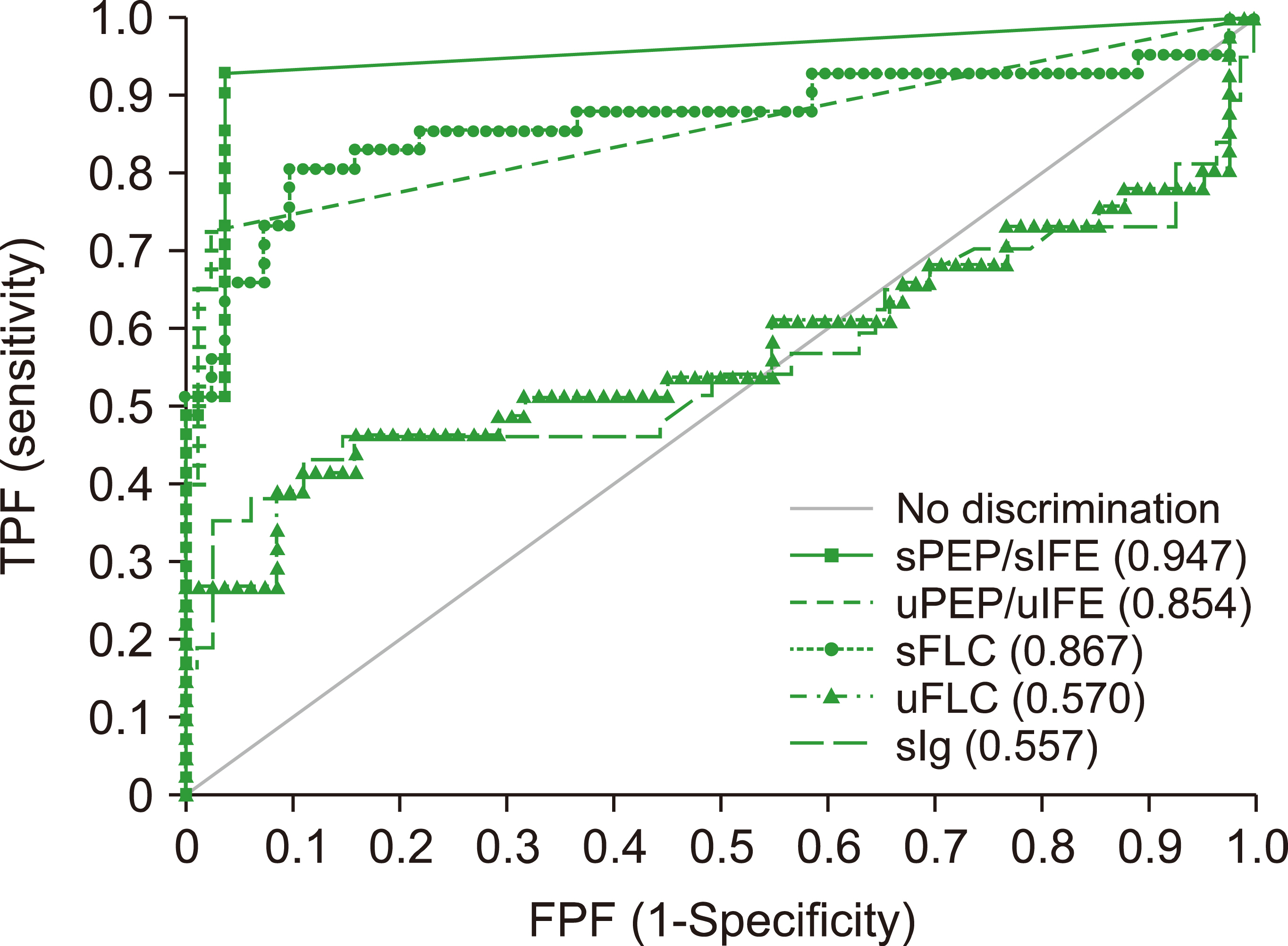
Blood Res.
2022 Dec;57(4):284-289. 10.5045/br.2022.2022187.
Comparison of serum and urine free light chain analysis in clinical diagnosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Wonju Severance Christian Hospital, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea
- KMID: 2537553
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2022.2022187
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sasson SC, McGill K, Wienholt L, et al. 2015; Comparison of the Freelite serum free light chain (SFLC) assay with serum and urine electrophoresis/immunofixation and the N Latex FLC assay. Pathology. 47:564–9. DOI: 10.1097/PAT.0000000000000316. PMID: 26352111.2. Wijeratne N, Tate JR, Wienholt L, Mollee P. 2019; Report of the survey conducted by RCPAQAP on current practice for paraprotein and serum free light chain measurement and reporting: a need for harmonisation. Clin Biochem Rev. 40:31–42. PMID: 30828118. PMCID: PMC6370284.3. Bradwell AR, Carr-Smith HD, Mead GP, et al. 2001; Highly sensitive, automated immunoassay for immunoglobulin free light chains in serum and urine. Clin Chem. 47:673–80. DOI: 10.1093/clinchem/47.4.673. PMID: 11274017.4. Campos ML, Barbosa-de Carvalho NM, Martín-Reyes G. 2012; The value of serum free light chain assay in patients with monoclonal gammopathies and renal failure. Nefrologia. 32:15–9. DOI: 10.3265/Nefrologia.pre2011.Nov.11098. PMID: 22294000.5. Bhole MV, Sadler R, Ramasamy K. 2014; Serum-free light-chain assay: clinical utility and limitations. Ann Clin Biochem. 51:528–42. DOI: 10.1177/0004563213518758. PMID: 24489083.6. Nowrousian MR, Brandhorst D, Sammet C, et al. 2005; Serum free light chain analysis and urine immunofixation electrophoresis in patients with multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res. 11:8706–14. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0486. PMID: 16361557.7. Lobe M, Pasquale D. 2017; Freelite for measurement of urine-free light chains in monoclonal gammopathies. Am J Hematol Oncol. 12:9–13.8. Snyder MR, Clark R, Bryant SC, Katzmann JA. 2008; Quantification of urinary light chains. Clin Chem. 54:1744–6. DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2008.107599. PMID: 18824580.9. Katzmann JA, Clark RJ, Abraham RS, et al. 2002; Serum reference intervals and diagnostic ranges for free kappa and free lambda immunoglobulin light chains: relative sensitivity for detection of monoclonal light chains. Clin Chem. 48:1437–44. DOI: 10.1093/clinchem/48.9.1437. PMID: 12194920.10. Erdem BK, Davran F, Yilmaz VT, Çetinkaya R, Akbas H. 2015; The association of serum-free light-chain levels with markers of renal function. Ren Fail. 37:1057–60. DOI: 10.3109/0886022X.2015.1052980. PMID: 26056734.11. Katzmann JA, Kyle RA, Benson J, et al. 2009; Screening panels for detection of monoclonal gammopathies. Clin Chem. 55:1517–22. DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2009.126664. PMID: 19520758. PMCID: PMC3773468.12. Abraham RS, Clark RJ, Bryant SC, et al. 2002; Correlation of serum immunoglobulin free light chain quantification with urinary Bence Jones protein in light chain myeloma. Clin Chem. 48:655–7. DOI: 10.1093/clinchem/48.4.655. PMID: 11901068.13. Singhal S, Stein R, Vickrey E, Mehta J. 2007; The serum-free light chain assay cannot replace 24-hour urine protein estimation in patients with plasma cell dyscrasias. Blood. 109:3611–2. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-11-060368. PMID: 17409349.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Discrimination of Monoclonal Gammopathy Using Immunoassay for Free Light Chains
- Evaluation of laboratory diagnostic tests for light-chain clonality and bone marrow findings in AL amyloidosis
- Serum Free Light Chains for Diagnosis and Follow-up of Multiple Myeloma
- Screening Tests for Early Diagnosis of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Disorders
- A Case of Mature B-cell Neoplasm with Light Chain Clonality Confirmed by Cytoplasmic Light Chain Expression Using Flow Cytometry