Anat Cell Biol.
2022 Dec;55(4):433-440. 10.5115/acb.22.081.
Geometric morphometric analysis of mandibular symphysis in Class III skeletal base
- Affiliations
-
- 1Orthodontic Discipline, Department of Family Oral Health, Faculty of Dentistry, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
- 2Ministry of Health Malaysia, Putrajaya, Malaysia
- 3School of Health Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Kelantan, Malaysia
- KMID: 2537462
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.22.081
Abstract
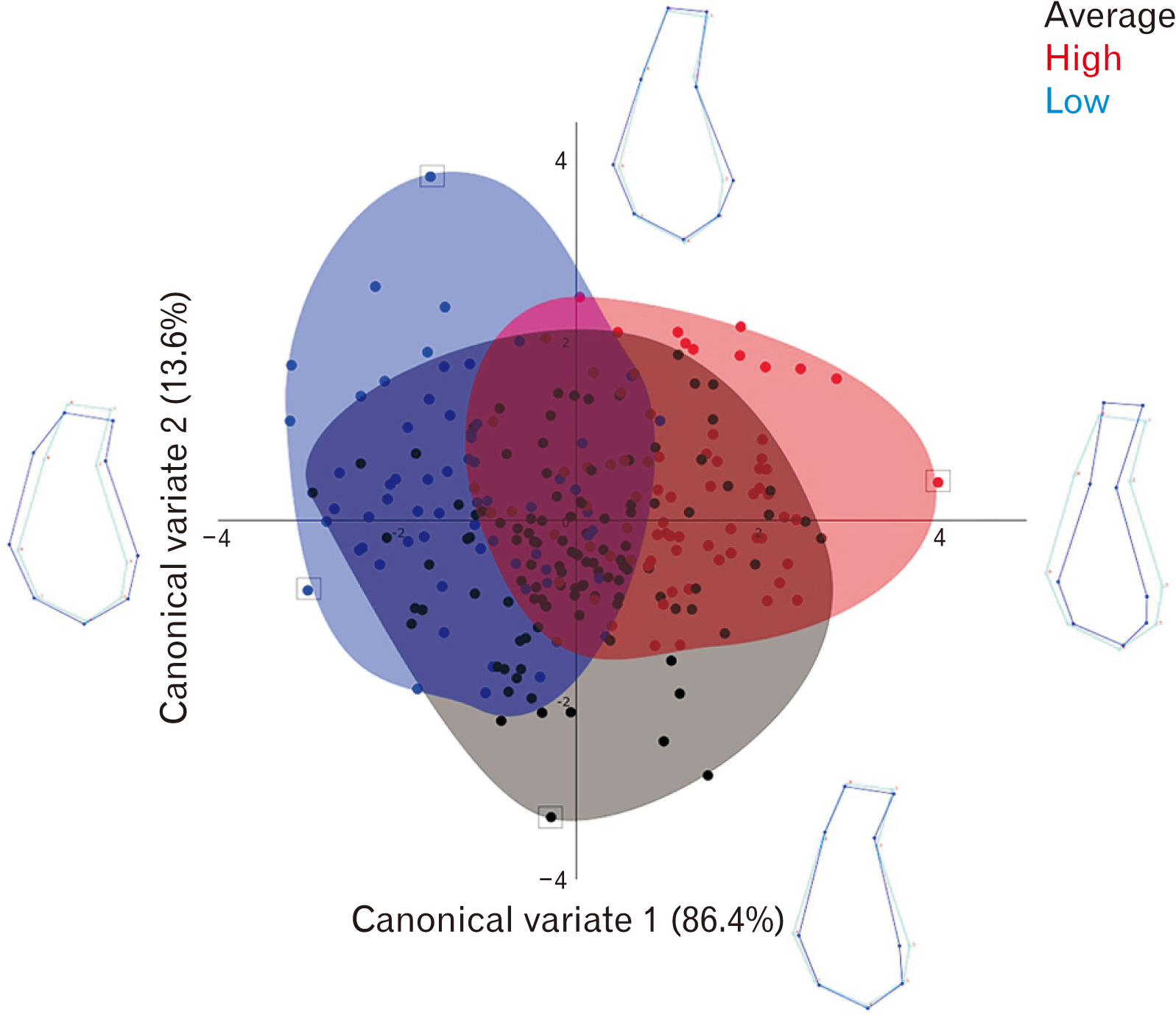
- This study aimed to investigate the general mandibular symphysis (MS) shape variation among Class III skeletal base, using geometric morphometric analysis. Pre-treatment lateral cephalometric radiographs of 254 patients aged 11–40 years old, with Class III skeletal base (ANB <1o ) and lower incisor angle (<99o ) were included. Nine-landmarks with x and y coordinates were identified on MS using TPSDig2 software, then exported into Morpho J for shape and statistical analysis. Principal component analysis showed that three main shape dimensions with a total variance of 74.6% represented the majority variation of samples. Procrustes Anova showed the shape of MS in Class III skeletal base to be mainly influenced by gonial angle, incisor inclination and sex (P<0.0001). Canonical variate analysis showed that high gonial angle groups had significantly narrower and elongated MS whereas low gonial angle groups had wider, bulbous and rounded MS (P<0.0001). The ratio of alveolar part to basal part was 1:5 in low gonial angle and 2:3 in high gonial angle. Males had significantly taller MS with narrower B point area compared to females (P<0.0001). Retroclined incisors exhibited taller and retroclined alveolar parts (P<0.0001). The shape of MS in Class III skeletal base varied at the alveolar part, basal part or both and it is influenced by gonial angle, incisor inclination and sex. Hence, understanding the shape variation of MS is important to aid orthodontic treatment planning.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Yamada C, Kitai N, Kakimoto N, Murakami S, Furukawa S, Takada K. 2007; Spatial relationships between the mandibular central incisor and associated alveolar bone in adults with mandibular prognathism. Angle Orthod. 77:766–72. DOI: 10.2319/072906-309. PMID: 17685772.2. Choi YJ, Chung CJ, Kim KH. 2015; Periodontal consequences of mandibular incisor proclination during presurgical orthodontic treatment in Class III malocclusion patients. Angle Orthod. 85:427–33. DOI: 10.2319/021414-110.1. PMID: 25090134. PMCID: PMC8612433.3. Lee KA, Kim MS, Hong JY, Lee JS, Choi SH, Chai JK, Jung UW. 2014; Anatomical topography of the mandibular symphysis in the Korean population: a computed tomography analysis. Clin Anat. 27:592–7. DOI: 10.1002/ca.22315. PMID: 24343797.4. Chung CJ, Jung S, Baik HS. 2008; Morphological characteristics of the symphyseal region in adult skeletal Class III crossbite and openbite malocclusions. Angle Orthod. 78:38–43. DOI: 10.2319/101606-427.1. PMID: 18193946.5. Guerino P, Marquezan M, Mezomo MB, Antunes KT, Grehs RA, Ferrazzo VA. 2017; Tomographic evaluation of the lower incisor's bone limits in mandibular symphysis of orthodontically untreated adults. Biomed Res Int. 2017:9103749. DOI: 10.1155/2017/9103749. PMID: 29181407. PMCID: PMC5664189.6. Arruda KEM, Neto JV, de Araújo Almeida G. 2012; Assessment of the mandibular symphysis of Caucasian Brazilian adults with well-balanced faces and normal occlusion: the influence of gender and facial type. Dent Press J Orthod. 17:40–50. DOI: 10.1590/S2176-94512012000300012.7. Gracco A, Luca L, Bongiorno MC, Siciliani G. 2010; Computed tomography evaluation of mandibular incisor bony support in untreated patients. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 138:179–87. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2008.09.030. PMID: 20691359.8. Handelman CS. 1996; The anterior alveolus: its importance in limiting orthodontic treatment and its influence on the occurrence of iatrogenic sequelae. Angle Orthod. 66:246. DOI: 10.1043/0003-3219(1996)066<0095:TAAIII>2.3.CO;2. PMID: 8712499.9. Mangla R, Singh N, Dua V, Padmanabhan P, Khanna M. 2011; Evaluation of mandibular morphology in different facial types. Contemp Clin Dent. 2:200–6. DOI: 10.4103/0976-237X.86458. PMID: 22090764. PMCID: PMC3214527.10. Molina-Berlanga N, Llopis-Perez J, Flores-Mir C, Puigdollers A. 2013; Lower incisor dentoalveolar compensation and symphysis dimensions among Class I and III malocclusion patients with different facial vertical skeletal patterns. Angle Orthod. 83:948–55. DOI: 10.2319/011913-48.1. PMID: 23758599. PMCID: PMC8722832.11. Bangar C, Wagh S, Murthy K, Parhad S. 2015; Compensatory cephalometric changes in mandibular symphysis with different anteroposterior jaw relationships. Int J Oral Health Med Res. 2:3–7.12. Nor MM, Manan M, Mohamed AM, Rosli TI, Hafiz A. 2020; Lower incisor inclination and bony support in class II skeletal pattern patients-CBCT study. J Res Med Dent Sci. 8:85–93.13. Yu Q, Pan XG, Ji GP, Shen G. 2009; The association between lower incisal inclination and morphology of the supporting alveolar bone--a cone-beam CT study. Int J Oral Sci. 1:217–23. DOI: 10.4248/IJOS09047. PMID: 20690425. PMCID: PMC3733600.14. Fukase H. 2007; Functional significance of bone distribution in the human mandibular symphysis. Anthropol Sci. 115:55–62. DOI: 10.1537/ase.060329.15. Proffit WR, Fields HW. 1983; Occlusal forces in normal- and long-face children. J Dent Res. 62:571–4. DOI: 10.1177/00220345830620051301. PMID: 6573374.16. Swasty D, Lee J, Huang JC, Maki K, Gansky SA, Hatcher D, Miller AJ. 2011; Cross-sectional human mandibular morphology as assessed in vivo by cone-beam computed tomography in patients with different vertical facial dimensions. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 139(4 Suppl):e377–89. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2009.10.039. PMID: 21435546.17. Maniyar M, Kalia A, Hegde A, Gautam RG, Mirdehghan N. 2014; Lower incisor dentoalveolar compensation and symphysis dimensions in class II and class III patients. Int J Dent Med Spec. 1:20–4. DOI: 10.5958/2394-4196.2014.00005.3.18. Moshfeghi M, Nouri M, Mirbeigi S, Baghban AA. 2014; Correlation between symphyseal morphology and mandibular growth. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 11:375–9. DOI: 10.4103/1735-3327.135915. PMID: 25097649. PMCID: PMC4119372.19. Aki T, Nanda RS, Currier GF, Nanda SK. 1994; Assessment of symphysis morphology as a predictor of the direction of mandibular growth. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 106:60–9. DOI: 10.1016/S0889-5406(94)70022-2. PMID: 8017351.20. Pan JY, Chou ST, Chang HP, Liu PH. 2006; Morphometric analysis of the mandible in subjects with Class III malocclusion. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 22:331–8. DOI: 10.1016/S1607-551X(09)70319-5. PMID: 16849101.21. Woon CK, Jamal NAA, Noor MNIM, Abdullah SM, Mohamed Ibrahim N, Norman NH, Alias A. 2019; Geometric morphometric analysis of malocclusion on lateral cephalograms in Malaysian population. Anat Cell Biol. 52:397–405. Erratum in: Anat Cell Biol 2020;53:378. DOI: 10.5115/acb.19.118. PMID: 31949978. PMCID: PMC6952698.22. Rohlf FJ, Marcus LF. 1993; A revolution morphometrics. Trends Ecol Evol. 8:129–32. DOI: 10.1016/0169-5347(93)90024-J. PMID: 21236128.23. Mitteroecker P, Gunz P. 2009; Advances in geometric morphometrics. Evol Biol. 36:235–47. DOI: 10.1007/s11692-009-9055-x.24. Cocos A, Halazonetis DJ. 2017; Craniofacial shape differs in patients with tooth agenesis: geometric morphometric analysis. Eur J Orthod. 39:345–51. DOI: 10.1093/ejo/cjw049. PMID: 27464525.25. Katsadouris A, Halazonetis DJ. 2017; Geometric morphometric analysis of craniofacial growth between the ages of 12 and 14 in normal humans. Eur J Orthod. 39:386–94. DOI: 10.1093/ejo/cjw070. PMID: 27940444.26. Cardini A, Seetah K, Barker G. 2015; How many specimens do I need? Sampling error in geometric morphometrics: testing the sensitivity of means and variances in simple randomized selection experiments. Zoomorphology. 134:149–63. DOI: 10.1007/s00435-015-0253-z.27. Izard G. 1927; The goniomandibular angle in dentofacial orthopedia. Int J Orthod Oral Surg Radiogr. 13:578–81. DOI: 10.1016/S0099-6963(27)90110-0.28. Rohlf FJ. 2005. tpsDig, digitize landmarks and outlines, version 2.05. State University of New York at Stony Brook;Stony Brook: DOI: 10.1016/s0099-6963(27)90110-0.29. Bookstein FL. Bookstein FL, editor. 1992. Chapter 3: landmarks. Morphometric Tools for Landmark Data: Geometry and Biology. Cambridge University Press;Cambridge: p. 55–87. DOI: 10.1017/CBO9780511573064.004.30. Klingenberg CP. 2011; MorphoJ: an integrated software package for geometric morphometrics. Mol Ecol Resour. 11:353–7. DOI: 10.1111/j.1755-0998.2010.02924.x. PMID: 21429143.31. Zelditch M, Swiderski D, Sheets H, Fink W. Zelditch M, Swiderski D, Sheets H, Fink W, editors. 2004. Simple size and shape variables: Bookstein shape coordinates. Geometric Morphometrics for Biologists: A Primer. Academic Press;London: p. 51–72. DOI: 10.1016/B978-012778460-1/50005-3.32. García-Morales P, Buschang PH, Throckmorton GS, English JD. 2003; Maximum bite force, muscle efficiency and mechanical advantage in children with vertical growth patterns. Eur J Orthod. 25:265–72. DOI: 10.1093/ejo/25.3.265. PMID: 12831216.33. Grünheid T, Langenbach GE, Korfage JA, Zentner A, van Eijden TM. 2009; The adaptive response of jaw muscles to varying functional demands. Eur J Orthod. 31:596–612. DOI: 10.1093/ejo/cjp093. PMID: 19656804.34. Ueda HM, Miyamoto K, Saifuddin M, Ishizuka Y, Tanne K. 2000; Masticatory muscle activity in children and adults with different facial types. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 118:63–8. DOI: 10.1067/mod.2000.99142. PMID: 10893474.35. Sella-Tunis T, Pokhojaev A, Sarig R, O'Higgins P, May H. 2018; Human mandibular shape is associated with masticatory muscle force. Sci Rep. 8:6042. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-24293-3. PMID: 29662127. PMCID: PMC5902585.36. Karlsen AT. 1995; Craniofacial growth differences between low and high MP-SN angle males: a longitudinal study. Angle Orthod. 65:341–50. DOI: 10.1043/0003-3219(1995)065<0341:CGDBLA>2.0.CO;2. PMID: 8526293.37. Richardson ME. 2002; Late lower arch crowding: the aetiology reviewed. Dent Update. 29:234–8. DOI: 10.12968/denu.2002.29.5.234. PMID: 12096382.38. Wennström JL. 1996; Mucogingival considerations in orthodontic treatment. Semin Orthod. 2:46–54. DOI: 10.1016/S1073-8746(96)80039-9. PMID: 9161283.39. Uysal T, Yagci A, Ozer T, Veli I, Ozturk A. 2012; Mandibular anterior bony support and incisor crowding: is there a relationship? Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 142:645–53. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2012.05.017. PMID: 23116505.40. Dempsey PJ, Townsend GC, Martin NG, Neale MC. 1995; Genetic covariance structure of incisor crown size in twins. J Dent Res. 74:1389–98. DOI: 10.1177/00220345950740071101. PMID: 7560390.41. Ursi WJ, Trotman CA, McNamara JA Jr, Behrents RG. 1993; Sexual dimorphism in normal craniofacial growth. Angle Orthod. 63:47–56. DOI: 10.1043/0003-3219(1993)063<0047:SDINCG>2.0.CO;2. PMID: 8507031.42. Osborn J, Mao J. 1993; A thin bite-force transducer with three-dimensional capabilities reveals a consistent change in bite-force direction during human jaw-muscle endurance tests. Arch Oral Biol. 38:139–44. DOI: 10.1016/0003-9969(93)90198-U. PMID: 8476343.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Morphology of mandibular symphysis and positioning of lower incisors in the skeletal Class III malocclusions
- A study of morphoiogy of mandibular symphysis and location of lower incisor under the influence of the craniofacial skeleton in skeletal Class III malocclusion
- A study on the relationship of the mandibular symphysis and anterior alveolar and skeletal morphology according to the rotational growth pattern of mandible in skeletal Class III malocclusion
- A study on the morphological changes of lower incisor and symphysis during surgical-orthodontic treatment in skeletal class III malocclusion
- Comparison of cranial base morphology between the mandibular prognathism and maxillary retrognathism in skeletal class III patients