J Rhinol.
2022 Nov;29(3):172-175. 10.18787/jr.2022.00413.
A Giant Maxillary Mucocele Presenting Left Cheek Swelling
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Head & Neck Surgery, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2536587
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2022.00413
Abstract
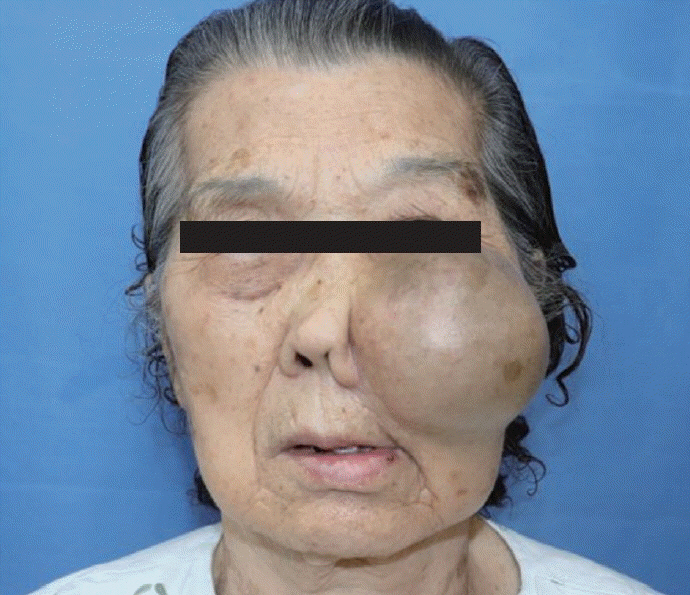
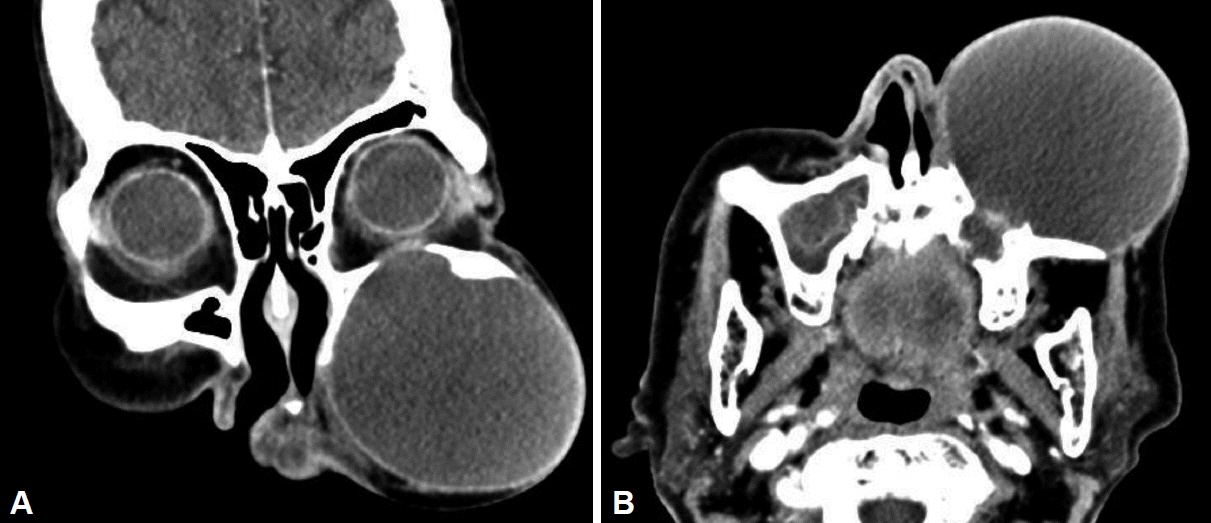
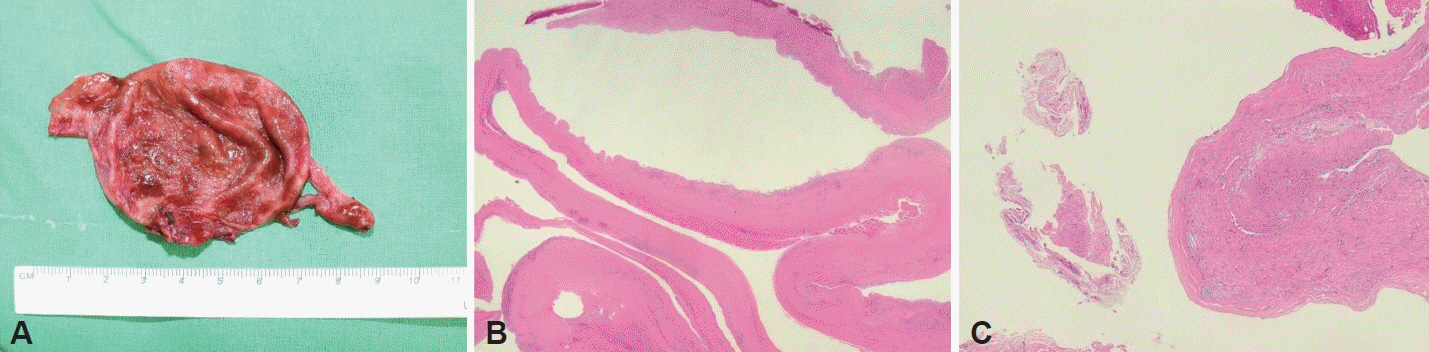
- A paranasal sinus mucocele is an epithelial-lined, mucus-containing sac that completely fills the sinus and forms an expandable cystic structure. It most commonly affects the frontal and ethmoidal sinuses, and rarely the maxillary and sphenoid sinuses. Orbital displacement or external disfigurement resulting from the expansion of the frontal or ethmoid sinuses is common; however, facial asymmetry caused by maxillary bone remodeling is rare. We describe a case of large maxillary sinus mucocele that destroyed the maxillary sinus bony wall, resulting in notable left cheek swelling and disfigurement, and review the relevant literature.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Lee TJ, Li SP, Fu CH, Huang CC, Chang PH, Chen YW, et al. Extensive paranasal sinus mucoceles: a 15-year review of 82 cases. Am J Otolaryngol. 2009; 30(4):234–8.
Article2. Simões JC, Nogueira-Neto FB, Gregório LL, Caparroz FdA, Kosugi EM. Visual loss: a rare complication of maxillary sinus mucocele. Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2015; 81:451–3.
Article3. Shahi S, Devkota A, Bhandari TR, Pantha T, Gautam D. Rare giant maxillay mucocele: a rare case report and literature review. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2019; 43:68–71.
Article4. Kim DY, Kwon BW, Park DE. Clinical evaluation of paranasal sinus mucocele. J Clin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004; 15(1):93–7.
Article5. Abdel-Aziz M, El-Hoshy H, Azooz K, Naguib N, Hussein A. Maxillary sinus mucocele: predisposing factors, clinical presentations, and treatment. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017; 21(1):55–8.
Article6. Hong SL, Cho KS, Roh HJ. Maxillary sinus retention cysts protruding into the inferior meatus. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2014; 7(3):226–8.
Article7. Mutlu V, Yoruk O, Ozkan O. Destructive giant maxillary sinus mucocele: a case report. Med-Science. 2016; 5(1):306–12.
Article8. Song HM, Park HW, Chung YS, Jang YJ, Lee BJ. Primary mucoceles of the maxillary sinus. Korean J Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surg. 2006; 49(1):47–51.9. Makeieff M, Gardiner Q, Mondain M, Crampette L. Maxillary sinus mucocoeles--10 cases--8 treated endoscopically. Rhinology. 1998; 36(4):192–5.10. Bosmans F, Vanhoenacker F. Giant frontal paranasal mucocele: case report and review of the literature. J Belg Soc Radiol. 2020; 104(1):48.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Maxillary Sinus Mucocele Secondary to Organized Hematoma
- Maxillary Sinus Mucocele as a Late Complication in a Patient Underwent Lefort I Procedure
- A Case of Giant Mucocele at Frontal Sinus
- Rare complication of acute maxillary sinusitis: Abscess of inferior turbinate and nasal Dorsum
- Mucocele in the maxillary sinus involving the orbit: A report of 2 cases