Int J Thyroidol.
2022 Nov;15(2):116-120. 10.11106/ijt.2022.15.2.116.
Transoral Robotic Lingual Thyroidectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2536497
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11106/ijt.2022.15.2.116
Abstract
- Base of tongue is the most common location of ectopic thyroid. Conservative management is the mainstay of treatment, but surgical treatment is required when complications occur due to the airway obstruction, dysphagia, or hemorrhage. An 18-year-old male with dyspnea and voice change was diagnosed with lingual thyroid, and the symptoms were refractory after several months of thyroid hormone replacement. The lingual thyroid gland was surgically excised using transoral robotic surgery (TORS). Although there are many surgical approaches for the resection of the lingual thyroid, TORS has advantages of using the natural orifice, and leaving no scar on the cervical area. Herein, we report a case of TORS-assisted lingual thyroidectomy with a literature review.
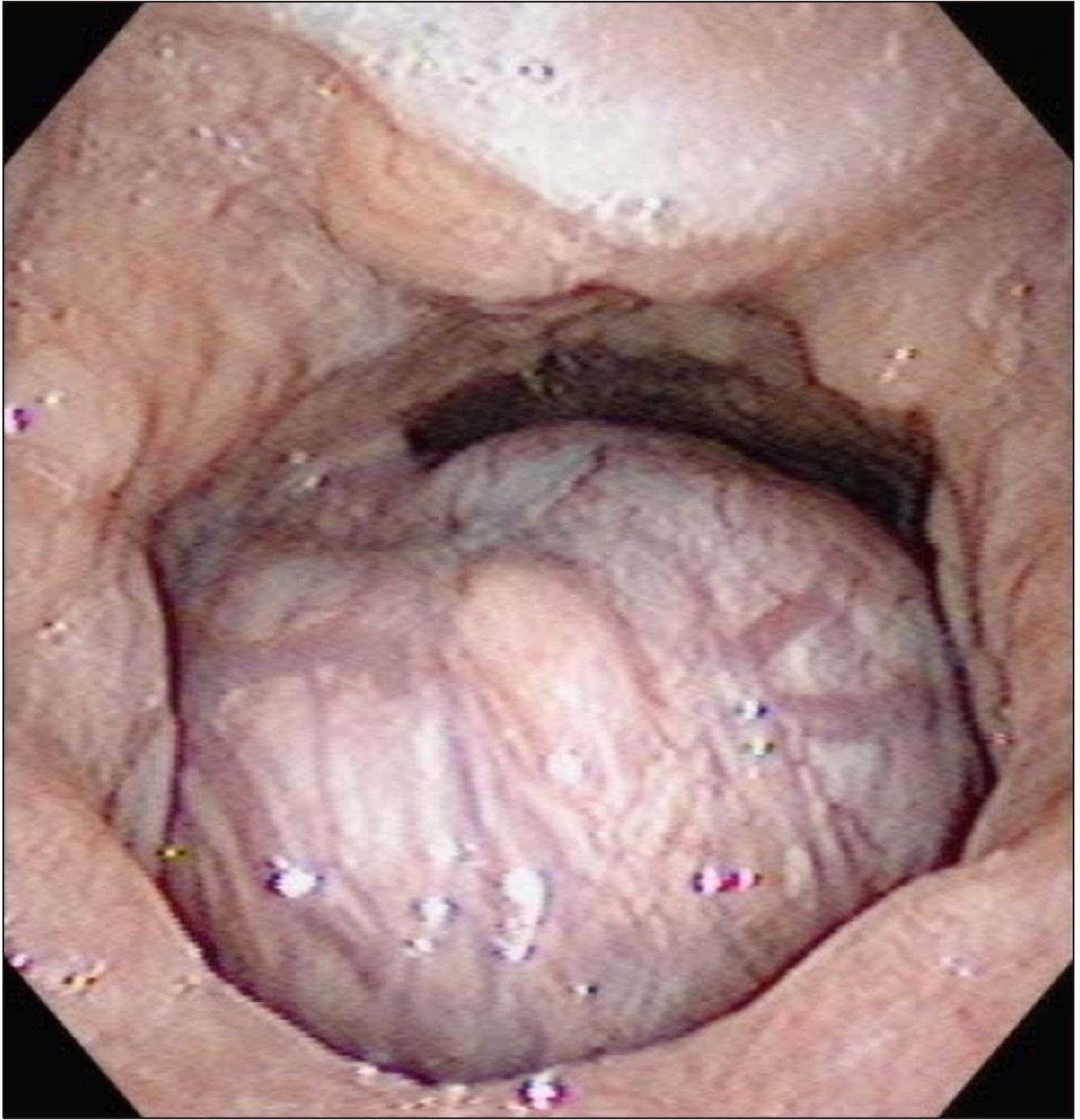
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Thomas G, Hoilat R, Daniels JS, Kalagie W. 2003; Ectopic lingual thyroid: a case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 32(2):219–21. DOI: 10.1054/ijom.2002.0311. PMID: 12729787.
Article2. Goode A, McKellar C, Carter M, Skelly L, Greene L, Roy G, et al. 2015; Incidental lingual thyroid informs surgery. J Nucl Med Technol. 43(1):66–7. DOI: 10.2967/jnmt.114.142075. PMID: 25190734.
Article3. Kumar SS, Kumar DM, Thirunavukuarasu R. 2013; Lingual thyroid-conservative management or surgery? A case report. Indian J Surg. 75(Suppl 1):118–9. DOI: 10.1007/s12262-012-0518-4. PMID: 24426535. PMCID: PMC3693310.
Article4. Toso A, Colombani F, Averono G, Aluffi P, Pia F. 2009; Lingual thyroid causing dysphagia and dyspnoea. Case reports and review of the literature. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 29(4):213–7.5. Prisman E, Patsias A, Genden EM. 2015; Transoral robotic excision of ectopic lingual thyroid: case series and literature review. Head Neck. 37(8):E88–91. DOI: 10.1002/hed.23757. PMID: 24816912.
Article6. Teo EH, Toh ST, Tay HN, Han HJ. 2013; Transoral robotic resection of lingual thyroid: case report. J Laryngol Otol. 127(10):1034–7. DOI: 10.1017/S0022215113002156. PMID: 24125062.
Article7. Huang TS, Chen HY. 2007; Dual thyroid ectopia with a normally located pretracheal thyroid gland: case report and literature review. Head Neck. 29(9):885–8. DOI: 10.1002/hed.20604. PMID: 17358039.
Article8. Fiaschetti V, Claroni G, Scarano AL, Schillaci O, Floris R. 2016; Diagnostic evaluation of a case of lingual thyroid ectopia. Radiol Case Rep. 11(3):165–70. DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2016.04.004. PMID: 27594942. PMCID: PMC4996909.
Article9. Ballard DP, Patel P, Schild SD, Ferzli G, Gordin E. 2018; Ectopic thyroid presenting as supraclavicular mass: a case report and literature review. J Clin Transl Endocrinol:. Case Reports. 10:17–20. DOI: 10.1016/j.jecr.2018.09.001.
Article10. Rahbar R, Yoon MJ, Connolly LP, Robson CD, Vargas SO, McGill TJ, et al. 2008; Lingual thyroid in children: a rare clinical entity. Laryngoscope. 118(7):1174–9. DOI: 10.1097/MLG.0b013e31816f6922. PMID: 18418276.
Article11. Noussios G, Anagnostis P, Goulis DG, Lappas D, Natsis K. 2011; Ectopic thyroid tissue: anatomical, clinical, and surgical implications of a rare entity. Eur J Endocrinol. 165(3):375–82. DOI: 10.1530/EJE-11-0461. PMID: 21715415.
Article12. Sood A, Sood V, Sharma DR, Seam RK, Kumar R. 2008; Thyroid scintigraphy in detecting dual ectopic thyroid: a review. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 35(4):843–6. DOI: 10.1007/s00259-007-0672-2. PMID: 18175113.
Article13. Basaria S, Westra WH, Cooper DS. 2001; Ectopic lingual thyroid masquerading as thyroid cancer metastases. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 86(1):392–5. DOI: 10.1210/jcem.86.1.7130. PMID: 11232030.
Article14. Kobayashi H, Tashita H, Hara H, Hasegawa Y. 2005; Utility of computed tomography in identifying an ectopic thyroid in infants and pre-school children. Endocr J. 52(2):189–92. DOI: 10.1507/endocrj.52.189. PMID: 15863946.
Article15. Ohnishi H, Sato H, Noda H, Inomata H, Sasaki N. 2003; Color Doppler ultrasonography: diagnosis of ectopic thyroid gland in patients with congenital hypothyroidism caused by thyroid dysgenesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 88(11):5145–9. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2003-030743. PMID: 14602741.
Article16. Gallo A, Leonetti F, Torri E, Manciocco V, Simonelli M, DeVincentiis M. 2001; Ectopic lingual thyroid as unusual cause of severe dysphagia. Dysphagia. 16(3):220–3. DOI: 10.1007/s00455-001-0067-7. PMID: 11453571.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Robotic Transoral Thyroidectomy: Right Thyroidectomy and Ipsilateral Central Neck Dissection with da Vinci Si Surgical System
- Transoral Robotic Thyroidectomy
- Robotic transoral thyroidectomy for papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Transoral Robotic Thyroidectomy: The Overview and Suggestions for Future Research in New Minimally Invasive Thyroid Surgery
- Transoral Thyroidectomy: Advantages and Disadvantages