Korean J Gastroenterol.
2022 Nov;80(5):233-236. 10.4166/kjg.2022.119.
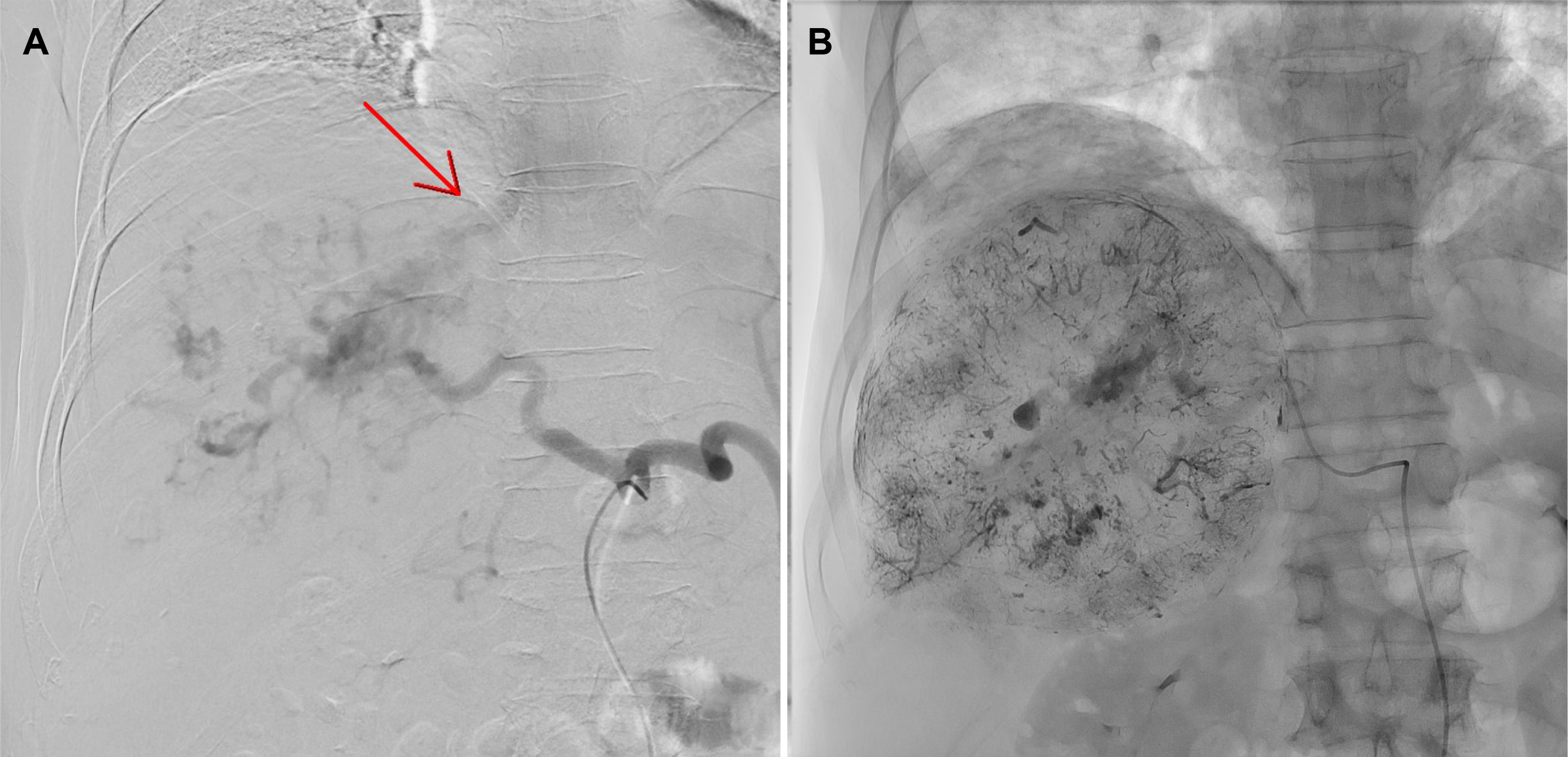
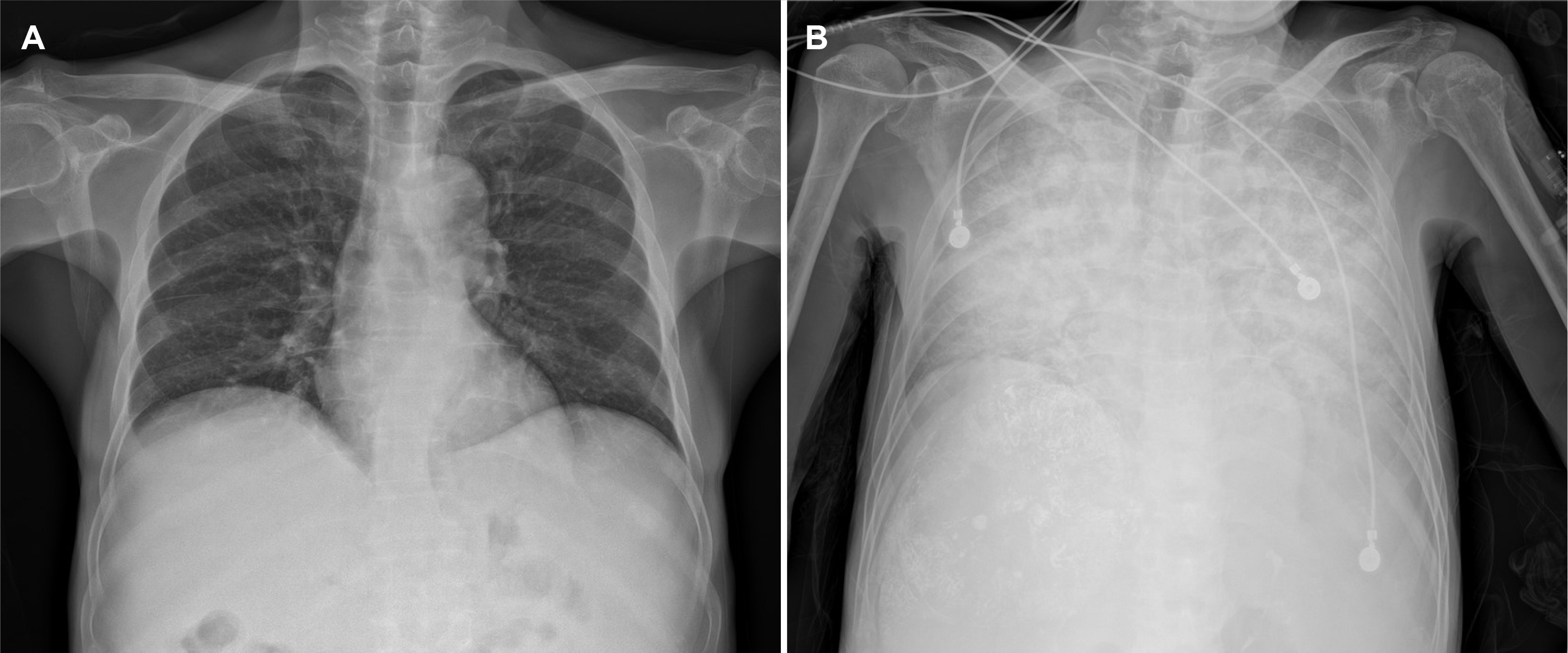
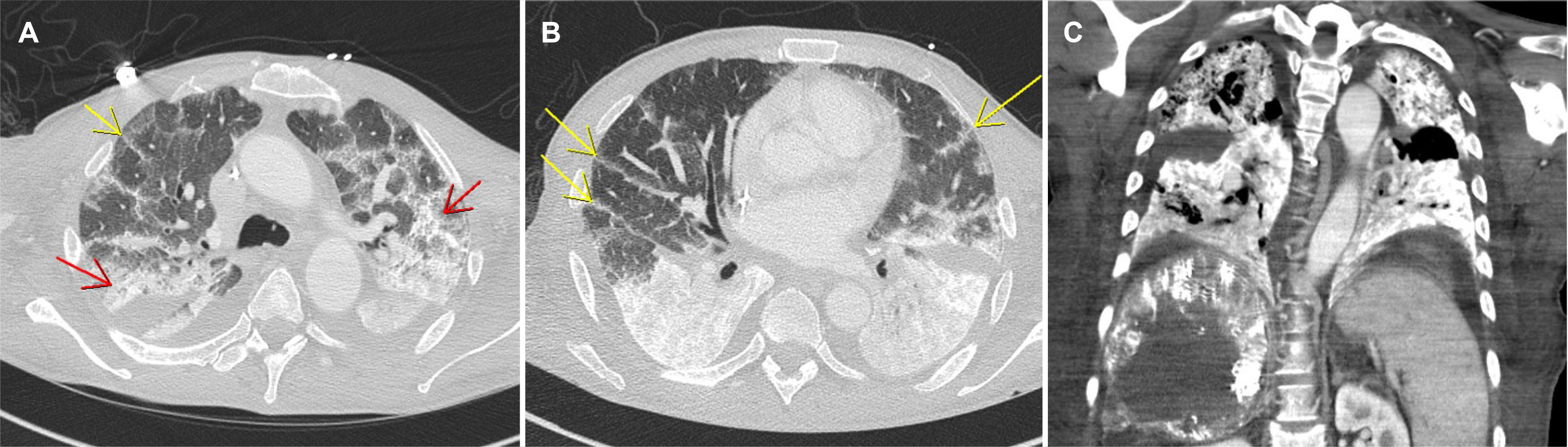
Lipiodol-induced Pneumonitis Following Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Uijeongbu, Korea
- KMID: 2536353
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2022.119
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jouneau S, Vauléon E, Caulet-Maugendre S, et al. 2011; 131I-labeled lipiodol-induced interstitial pneumonia: a series of 15 cases. Chest. 139:1463–1469. DOI: 10.1378/chest.10-1591. PMID: 20947651.2. Kim S, Kim HY, Lee SL, Ku YM, Won YD, Kim CW. 2020; Lipiodol pneumonitis following transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Liver Cancer. 20:60–66. DOI: 10.17998/jlc.20.1.60.
Article3. Youn I, Chong S, Kwak BK, et al. 2011; Pulmonary lipiodol accumulation after transarterial chemoembolization: CT findings and its radiologic outcomes. J Korean Soc Radiol. 65:577–583. DOI: 10.3348/jksr.2011.65.6.577.
Article4. Xia J, Ren Z, Ye S, et al. 2006; Study of severe and rare complications of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for liver cancer. Eur J Radiol. 59:407–412. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2006.03.002. PMID: 16621394.
Article5. Chung JW, Park JH, Im JG, Han JK, Han MC. 1993; Pulmonary oil embolism after transcatheter oily chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology. 187:689–693. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.187.3.8388567. PMID: 8388567.
Article6. Tajima T, Honda H, Kuroiwa T, et al. 2002; Pulmonary complications after hepatic artery chemoembolization or infusion via the inferior phrenic artery for primary liver cancer. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 13:893–900. DOI: 10.1016/S1051-0443(07)61772-2. PMID: 12354823.
Article7. Lin MT, Kuo PH. 2010; Pulmonary lipiodol embolism after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. JRSM Short Rep. 1:6. DOI: 10.1258/shorts.2009.090352. PMID: 21103098. PMCID: PMC2984328.
Article8. Lee JH, Won JH, Park SI, Won JY, Lee DY, Kang BC. 2007; Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma with hepatic arteriovenous shunt after temporary balloon occlusion of hepatic vein. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 18:377–382. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvir.2007.01.005. PMID: 17377183.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lipiodol Pneumonitis Following Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- The Suppression Effect of the Intrahepatic Recurrence of Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization with Cisplatin in the Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients: The Comparison of Adriamycin-Lipiodol Emulsion Infusions with Adriamycin-Lipiodol Emulsion Infusions
- A Fatal Case of Pulmonary Embolism after Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Pulmonary Lipiodol Embolism after Transcatheter Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- An A to Z of Lipiodol Beyond the Clinical Practice in the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma