Diabetes Metab J.
2022 Nov;46(6):866-878. 10.4093/dmj.2021.0307.
Abnormal Responses in Cognitive Impulsivity Circuits Are Associated with Glycosylated Hemoglobin Trajectories in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Impaired Metabolic Control
- Affiliations
-
- 1PIDFIF, Coimbra Institute for Biomedical Imaging and Translational Research (CIBIT)/Instituto de Ciências Nucleares Aplicadas à Saúde (ICNAS), University of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal
- 2CIBIT/ICNAS, University of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal
- 3Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism Department (SEMD), Coimbra University Hospital, University of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal
- 4Faculty of Psychology and Educational Sciences & Center for Social Studies, University of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal
- KMID: 2536145
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0307
Abstract
- Background
Risky health decisions and impulse control profiles may impact on metabolic control in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). We hypothesize that the neural correlates of cognitive impulsivity and decision-making in T1DM relate to metabolic control trajectories.
Methods
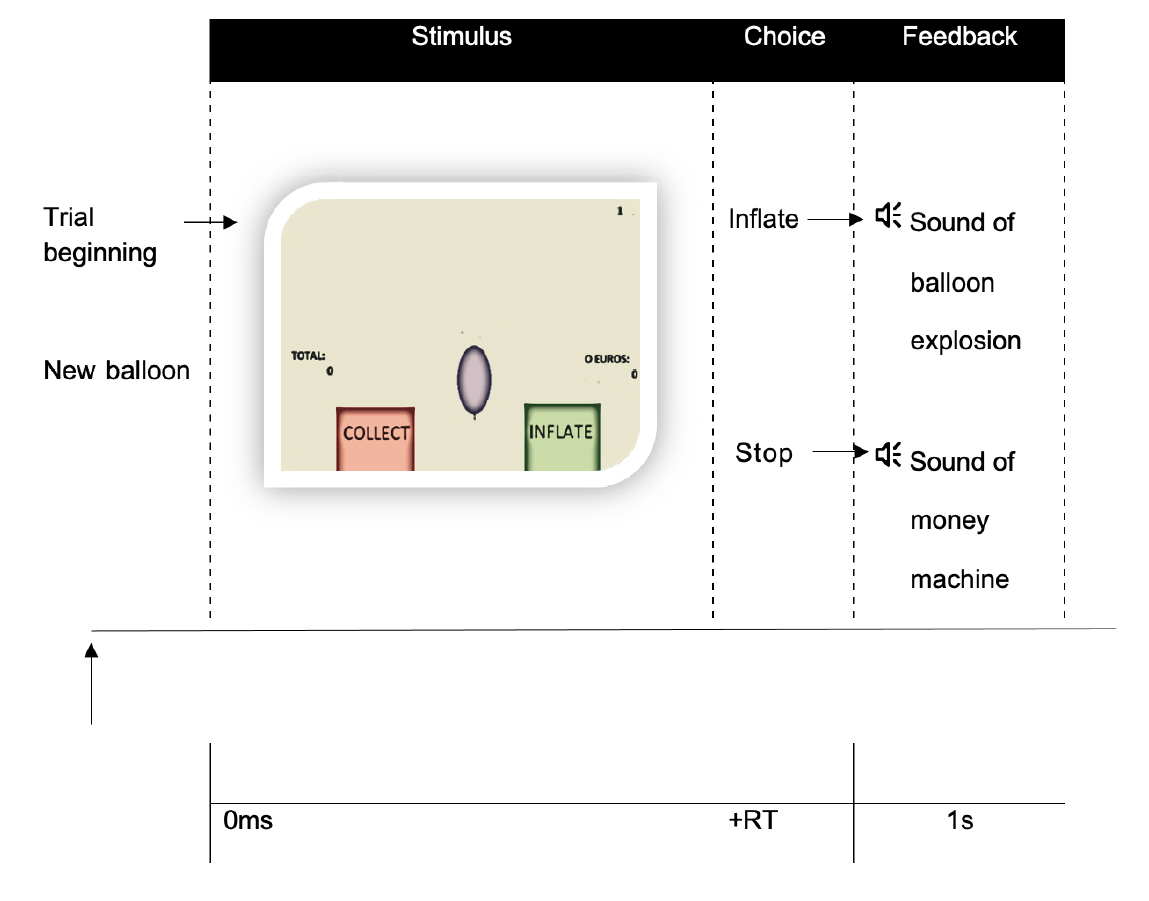
We combined functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), measures of metabolic trajectories (glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c] over multiple time points) and behavioral assessment using a cognitive impulsivity paradigm, the Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART), in 50 participants (25 T1DM and 25 controls).
Results
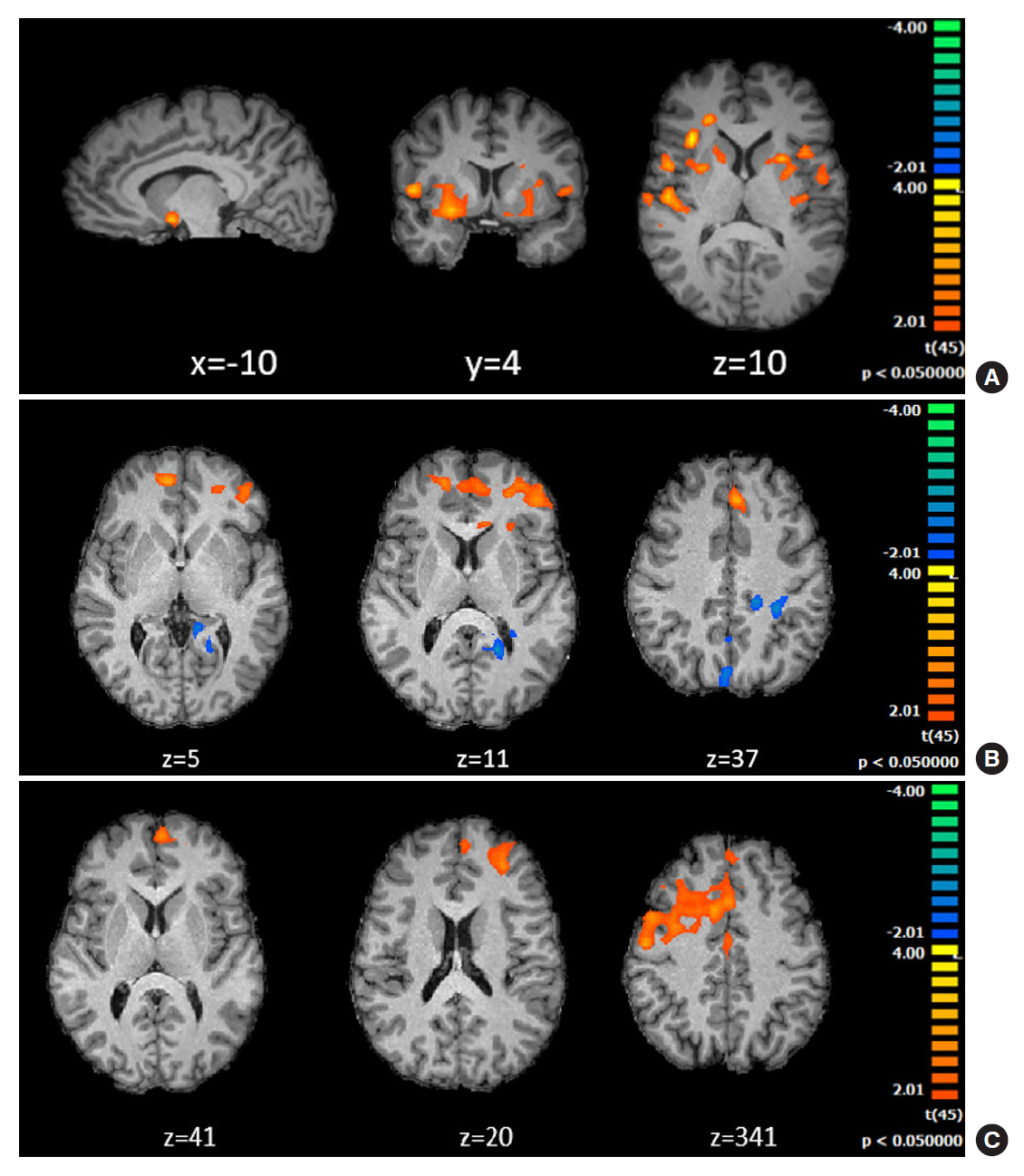
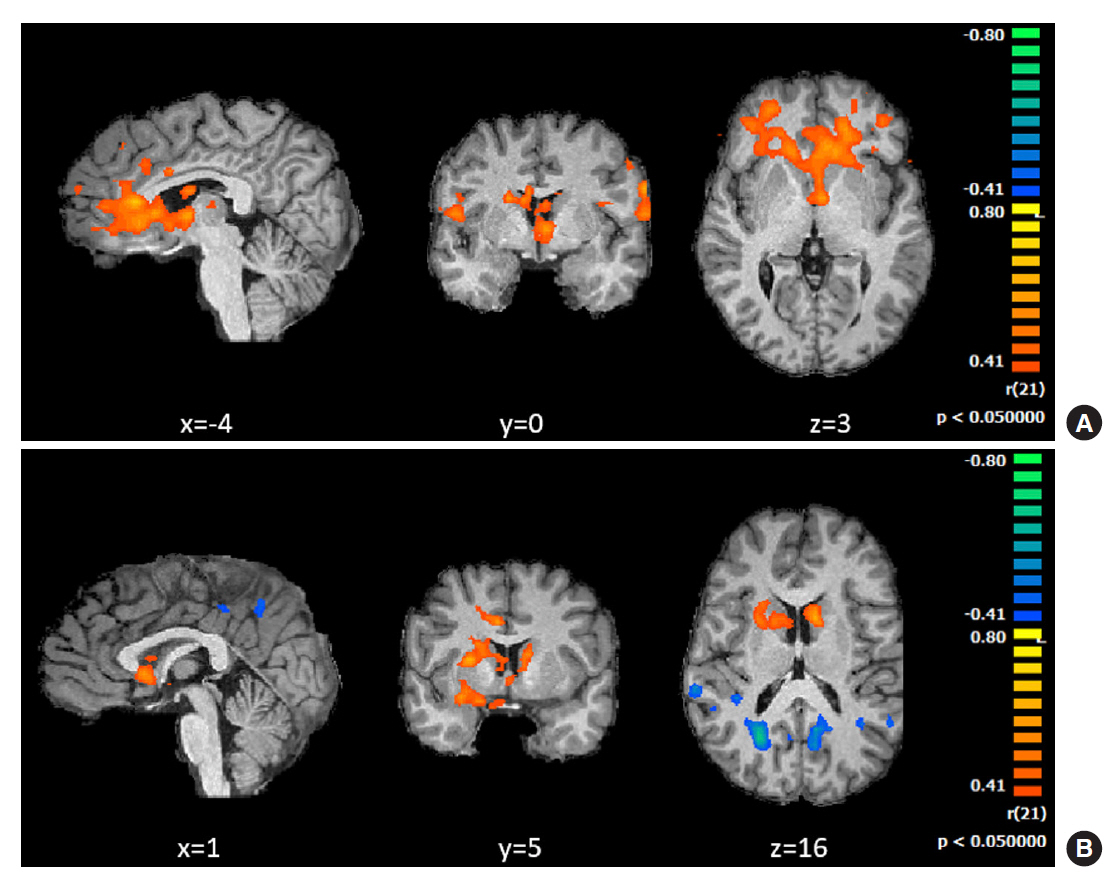
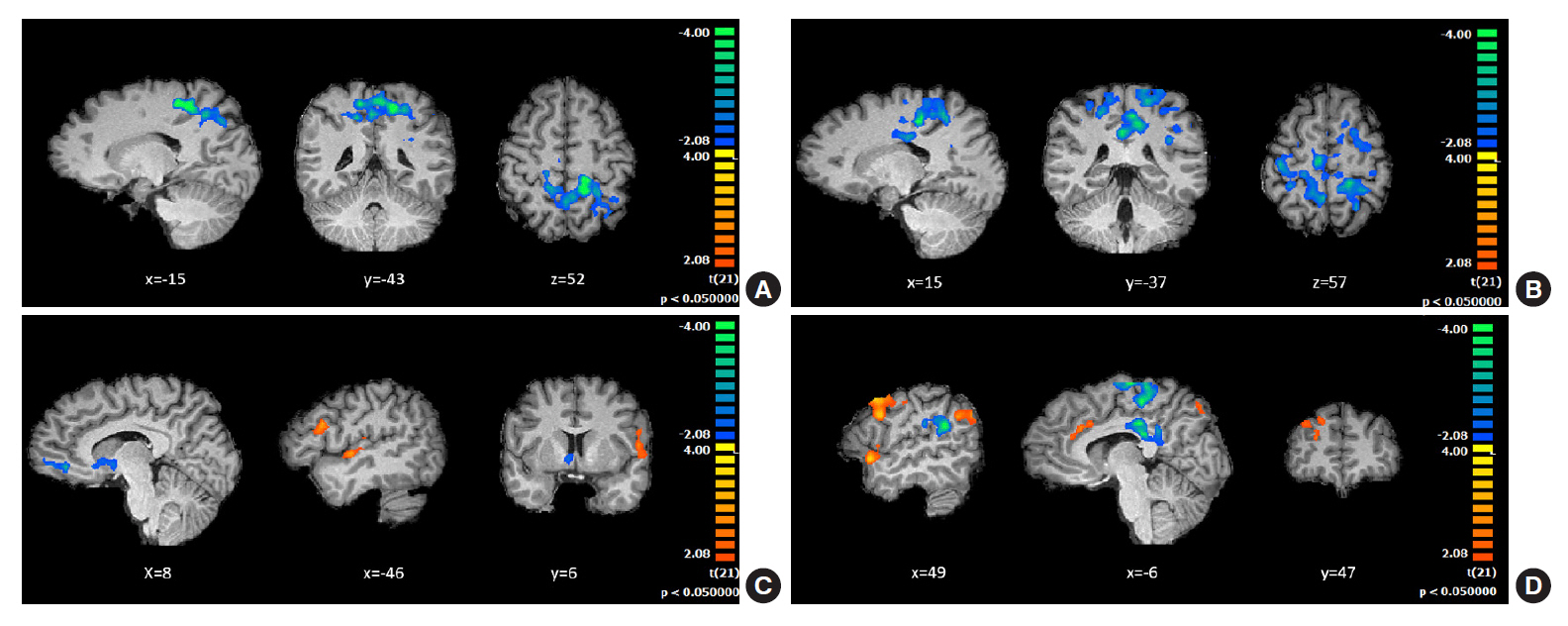
Behavioral results showed that T1DM participants followed a rigid conservative risk strategy along the iterative game. Imaging group comparisons showed that patients showed larger activation of reward related, limbic regions (nucleus accumbens, amygdala) and insula (interoceptive saliency network) in initial game stages. Upon game completion differences emerged in relation to error monitoring (anterior cingulate cortex [ACC]) and inhibitory control (inferior frontal gyrus). Importantly, activity in the saliency network (ACC and insula), which monitors interoceptive states, was related with metabolic trajectories, which was also found for limbic/reward networks. Parietal and posterior cingulate regions activated both in controls and patients with adaptive decision-making, and positively associated with metabolic trajectories.
Conclusion
We found triple converging evidence when comparing metabolic trajectories, patients versus controls or risk averse (non-learners) versus patients who learned by trial and error. Dopaminergic reward and saliency (interoceptive and error monitoring) circuits show a tight link with impaired metabolic trajectories and cognitive impulsivity in T1DM. Activity in parietal and posterior cingulate are associated with adaptive trajectories. This link between reward-saliency-inhibition circuits suggests novel strategies for patient management.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jorge H, Duarte IC, Correia BR, Barros L, Relvas AP, CasteloBranco M. Successful metabolic control in diabetes type 1 depends on individual neuroeconomic and health risk-taking decision endophenotypes: a new target in personalized care. Psychol Med. 2021; Mar. 18. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291721000386.
Article2. Hadj-Abo A, Enge S, Rose J, Kunte H, Fleischhauer M. Individual differences in impulsivity and need for cognition as potential risk or resilience factors of diabetes self-management and glycemic control. PLoS One. 2020; 15:e0227995.
Article3. Canario N, Sousa M, Moreira F, Duarte IC, Oliveira F, Januario C, et al. Impulsivity across reactive, proactive and cognitive domains in Parkinson’s disease on dopaminergic medication: evidence for multiple domain impairment. PLoS One. 2019; 14:e0210880.
Article4. Probst CC, van Eimeren T. The functional anatomy of impulse control disorders. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2013; 13:386.
Article5. Muthukrishnan AV, Wathieu L, Xu AJ. Ambiguity aversion and the preference for established brands. Manag Sci. 2009; 55:1933–41.
Article6. Congdon E, Bato AA, Schonberg T, Mumford JA, Karlsgodt KH, Sabb FW, et al. Differences in neural activation as a function of risk-taking task parameters. Front Neurosci. 2013; 7:173.
Article7. Hsu M, Bhatt M, Adolphs R, Tranel D, Camerer CF. Neural systems responding to degrees of uncertainty in human decision-making. Science. 2005; 310:1680–3.
Article8. Taya F. Seeking ambiguity: a review on neuroimaing studies on decision making under ambiguity. Louvain Econ Rev. 2012; 78:85–100.9. Fukunaga R, Brown JW, Bogg T. Decision making in the Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART): anterior cingulate cortex signals loss aversion but not the infrequency of risky choices. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2012; 12:479–90.
Article10. Schonberg T, Fox CR, Mumford JA, Congdon E, Trepel C, Poldrack RA. Decreasing ventromedial prefrontal cortex activity during sequential risk-taking: an FMRI investigation of the balloon analog risk task. Front Neurosci. 2012; 6:80.
Article11. Helfinstein SM, Schonberg T, Congdon E, Karlsgodt KH, Mumford JA, Sabb FW, et al. Predicting risky choices from brain activity patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014; 111:2470–5.
Article12. Lamichhane B, Adhikari BM, Dhamala M. The activity in the anterior insulae is modulated by perceptual decision-making difficulty. Neuroscience. 2016; 327:79–94.
Article13. Rao H, Korczykowski M, Pluta J, Hoang A, Detre JA. Neural correlates of voluntary and involuntary risk taking in the human brain: an fMRI Study of the Balloon Analog Risk Task (BART). Neuroimage. 2008; 42:902–10.
Article14. Heilbronner SR, Hayden BY. Dorsal anterior cingulate cortex: a bottom-up view. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2016; 39:149–70.
Article15. Korucuoglu O, Harms MP, Kennedy JT, et al. Adolescent decision-making under risk: neural correlates and sex differences. Cereb Cortex. 2020; 30:2690–706.
Article16. Peters SK, Dunlop K, Downar J. Cortico-striatal-thalamic loop circuits of the salience network: a central pathway in psychiatric disease and treatment. Front Syst Neurosci. 2016; 10:104.
Article17. Rajmohan V, Mohandas E. The limbic system. Indian J Psychiatry. 2007; 49:132–9.
Article18. Arias-Carripn O, Stamelou M, Murillo-Rodriguez E, Menendez-Gonzalez M, Poppel E. Dopaminergic reward system: a short integrative review. Int Arch Med. 2010; 3:24.
Article19. Daw ND, Doya K. The computational neurobiology of learning and reward. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2006; 16:199–204.
Article20. Japee S, Holiday K, Satyshur MD, Mukai I, Ungerleider LG. A role of right middle frontal gyrus in reorienting of attention: a case study. Front Syst Neurosci. 2015; 9:23.
Article21. Schultz W. Neuronal reward and decision signals: from theories to data. Physiol Rev. 2015; 95:853–951.
Article22. Blais AR, Weber EU. A domain-specific risk-taking (DOSPERT) scale for adult populations. Judgm Decis Mak. 2006; 1:33–47.23. Silva JP. Risk profiling and the DOSPERT scale: an approach using prospect theory [master’s thesis]. Lisboa: University of Lisbon;2012. Available from: https://www.repository.utl.pt/bitstream/10400.5/10351/1/DM-RJCPS-2012.pdf.24. Cruz AR, Barbosa F: European Portuguese Version of BIS-11 for research. Available from: https://www.impulsivity.org/measurement/bis11-translations/bis-11-portuguese-versions (cited 2022 Feb 10).25. Fernandes DAR. Estudos de validação da escala de impulsividade BIS-11 de Barratt para uma amostra da população portuguesa [Validation studies of Barratt Impulsivity Scale BIS-11-for Portuguese population] [master thesis]. Coimbra: University of Coimbra;2014. Available from: https://estudogeral.uc.pt/handle/10316/28357.26. Castro-Fonseca A, Eysenck SB, Simoes A. Um estudo intercultural da personalidade: Comparação de adultos portugueses e ingleses no EPQ. Rev Port Pedagog. 1991; 25:187–203.27. Van Strien T, Frijters JE, Bergers GP, Defares PB. The Dutch Eating Behavior Questionnaire (DEBQ) for assessment of restrained, emotional, and external eating behavior. Int J Eat Disord. 1986; 5:295–315.
Article28. Viana V, Sinde S: Estilo alimentar: adaptação e validação do questionário holandês do comportamento alimentar [Eating style: adaptation and validation of the Dutch eating behavior questionnaire]. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/236649218_ESTILO_ALIMENTAR_Adaptacao_e_validacao_do_Questionario_Holandes_do_Comportamento_Alimentar (cited 2022 Feb 10).29. Mannella F, Gurney K, Baldassarre G. The nucleus accumbens as a nexus between values and goals in goal-directed behavior: a review and a new hypothesis. Front Behav Neurosci. 2013; 7:135.
Article30. Wise RA. Dopamine, learning and motivation. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004; 5:483–94.
Article31. Knutson B, Greer SM. Anticipatory affect: neural correlates and consequences for choice. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2008; 363:3771–86.
Article32. Brevers D, Noel X. Pathological gambling and the loss of willpower: a neurocognitive perspective. Socioaffect Neurosci Psychol. 2013; 3:21592.
Article33. Sohn SY, Kang JI, Namkoong K, Kim SJ. Multidimensional measures of impulsivity in obsessive-compulsive disorder: cannot wait and stop. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e111739.
Article34. Waugh CE, Lemus MG, Gotlib IH. The role of the medial frontal cortex in the maintenance of emotional states. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2014; 9:2001–9.
Article35. Peterson A, Thome J, Frewen P, Lanius RA. Resting-state neuroimaging studies: a new way of identifying differences and similarities among the anxiety disorders? Can J Psychiatry. 2014; 59:294–300.
Article36. Rauch SL, Shin LM, Phelps EA. Neurocircuitry models of posttraumatic stress disorder and extinction: human neuroimaging research: past, present, and future. Biol Psychiatry. 2006; 60:376–82.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Combination of Fasting Plasma Glucose and Glycosylated Hemoglobin as a Predictor for Type 2 Diabetes in Korean Adults (Korean Diabetes J 33(4):306-314, 2009)
- The Combination of Fasting Plasma Glucose and Glycosylated Hemoglobin as a Predictor for Type 2 Diabetes in Korean Adults (Korean Diabetes J 33(4):306-314, 2009)
- Diabetes Camp as Continuing Education for Diabetes Self-Management in Middle-Aged and Elderly People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Hemoglobin Camperdown [β104Arg→Ser] Detection During Hemoglobin A(1c) Measurement via Capillary Electrophoresis
- Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368-78)