Clin Endosc.
2022 Nov;55(6):784-792. 10.5946/ce.2021.244.
The feasibility of percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder aspiration for acute cholecystitis after self-expandable metallic stent placement for malignant biliary obstruction: a 10-year retrospective analysis in a single center
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Clinical Research Institute, National Hospital Organization Kyushu Medical Center, Fukuoka, Japan
- 2Department of Medicine and Bioregulatory Science, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan
- KMID: 2536079
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2021.244
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Patients with acute cholecystitis (AC) after metallic stent (MS) placement for malignant biliary obstruction (MBO) have a high surgical risk. We performed percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder aspiration (PTGBA) as the first treatment for AC. We aimed to identify the risk factors for AC after MS placement and the poor response factors of PTGBA.
Methods
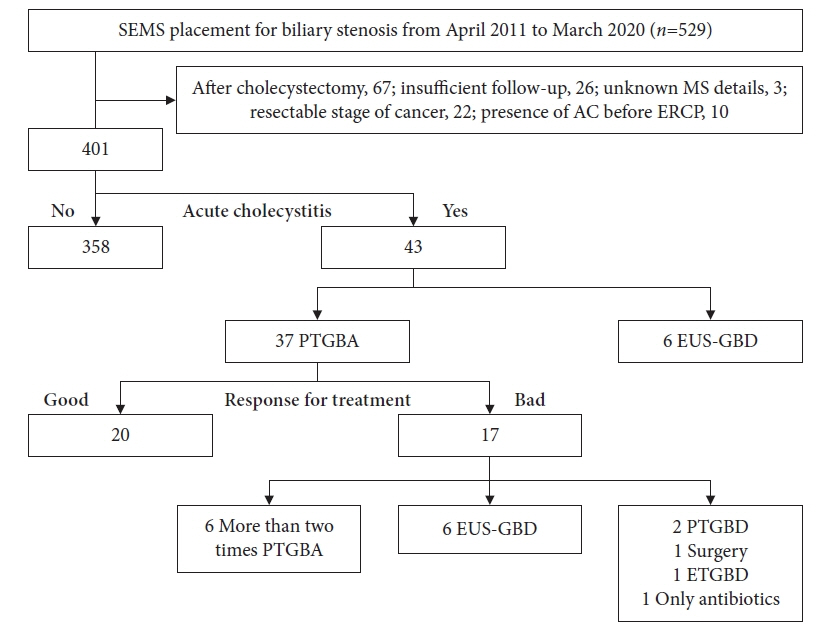
We enrolled 401 patients who underwent MS placement for MBO between April 2011 and March 2020. The incidence of AC was 10.7%. Of these 43 patients, 37 underwent PTGBA as the first treatment. The patients’ responses to PTGBA were divided into good and poor response groups.
Results
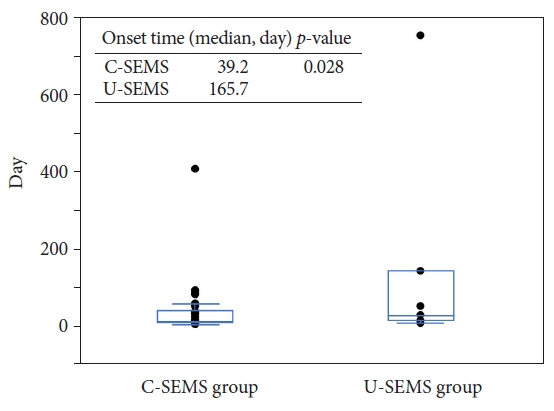
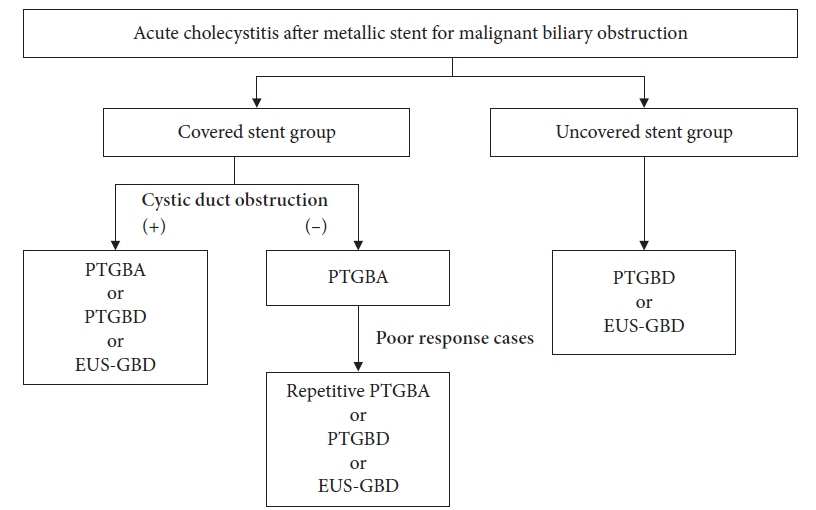
There were 20 patients in good response group and 17 patients in poor response group. Risk factors for cholecystitis after MS placement included cystic duct obstruction (p<0.001) and covered MS (p<0.001). Cystic duct obstruction (p=0.003) and uncovered MS (p=0.011) demonstrated significantly poor responses to PTGBA. Cystic duct obstruction is a risk factor for cholecystitis and poor response factor for PTGBA, whereas covered MS is a risk factor for cholecystitis and an uncovered MS is a poor response factor of PTGBA for cholecystitis.
Conclusions
The onset and poor response factors of AC after MS placement were different between covered and uncovered MS. PTGBA can be a viable option for AC after MS placement, especially in patients with covered MS.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
How should a therapeutic strategy be constructed for acute cholecystitis after self-expanding metal stent placement for malignant biliary obstruction?
Mamoru Takenaka, Masatoshi Kudo
Clin Endosc. 2022;55(6):757-759. doi: 10.5946/ce.2022.275.The writing on the wall: self-expandable stents for endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy?
Hyung Ku Chon, Shayan Irani, Tae Hyeon Kim
Clin Endosc. 2023;56(6):741-743. doi: 10.5946/ce.2023.207.
Reference
-
1. Isayama H, Komatsu Y, Tsujino T, et al. A prospective randomised study of “covered” versus “uncovered” diamond stents for the management of distal malignant biliary obstruction. Gut. 2004; 53:729–734.
Article2. Fumex F, Coumaros D, Napoleon B, et al. Similar performance but higher cholecystitis rate with covered biliary stents: results from a prospective multicenter evaluation. Endoscopy. 2006; 38:787–792.
Article3. Minami Y, Kudo M. Hepatocellular carcinoma with obstructive jaundice: endoscopic and percutaneous biliary drainage. Dig Dis. 2012; 30:592–597.
Article4. Kim GH, Ryoo SK, Park JK, et al. Risk factors for pancreatitis and cholecystitis after endoscopic biliary stenting in patients with malignant extrahepatic bile duct obstruction. Clin Endosc. 2019; 52:598–605.
Article5. Kanno Y, Koshita S, Ogawa T, et al. Inside plastic stents versus metal stents for treating unresectable malignant perihilar biliary obstructions: a retrospective comparative study. Clin Endosc. 2020; 53:735–742.
Article6. Lee TH, Kim TH, Moon JH, et al. Bilateral versus unilateral placement of metal stents for inoperable high-grade malignant hilar biliary strictures: a multicenter, prospective, randomized study (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 86:817–827.
Article7. Huffman JL, Schenker S. Acute acalculous cholecystitis: a review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 8:15–22.
Article8. Chopra S, Dodd GD 3rd, Mumbower AL, et al. Treatment of acute cholecystitis in non-critically ill patients at high surgical risk: comparison of clinical outcomes after gallbladder aspiration and after percutaneous cholecystostomy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001; 176:1025–1031.
Article9. Imai Y, Hasegawa T, Sato Y, et al. Management of acute cholecystitis after biliary stenting for malignant obstruction: comparison of percutaneous gallbladder drainage and aspiration. Jpn J Radiol. 2019; 37:719–726.
Article10. Teoh AYB, Kitano M, Itoi T, et al. Endosonography-guided gallbladder drainage versus percutaneous cholecystostomy in very high-risk surgical patients with acute cholecystitis: an international randomised multicentre controlled superiority trial (DRAC 1). Gut. 2020; 69:1085–1091.
Article11. Komatsu S, Tsuchida S, Tsukamoto T, et al. Current role of percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder aspiration: from palliative to curative management for acute cholecystitis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2016; 23:708–714.
Article12. Yokoe M, Hata J, Takada T, et al. Tokyo Guidelines 2018: diagnostic criteria and severity grading of acute cholecystitis (with videos). J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2018; 25:41–54.13. Yokoe M, Takada T, Strasberg SM, et al. New diagnostic criteria and severity assessment of acute cholecystitis in revised Tokyo Guidelines. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2012; 19:578–585.
Article14. Jang S, Stevens T, Parsi M, et al. Association of covered metallic stents with cholecystitis and stent migration in malignant biliary stricture. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018; 87:1061–1070.
Article15. Cao J, Peng C, Ding X, et al. Risk factors for post-ERCP cholecystitis: a single-center retrospective study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2018; 18:128.
Article16. Isayama H, Nakai Y, Toyokawa Y, et al. Measurement of radial and axial forces of biliary self-expandable metallic stents. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 70:37–44.
Article17. Shimizu S, Naitoh I, Nakazawa T, et al. Predictive factors for pancreatitis and cholecystitis in endoscopic covered metal stenting for distal malignant biliary obstruction. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 28:68–72.
Article18. Nakai Y, Isayama H, Kawakubo K, et al. Metallic stent with high axial force as a risk factor for cholecystitis in distal malignant biliary obstruction. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014; 29:1557–1562.
Article19. Isayama H, Kawabe T, Nakai Y, et al. Cholecystitis after metallic stent placement in patients with malignant distal biliary obstruction. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006; 4:1148–1153.
Article20. Suk KT, Kim HS, Kim JW, et al. Risk factors for cholecystitis after metal stent placement in malignant biliary obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 64:522–529.
Article21. Fukasawa M, Takano S, Shindo H, et al. Endoscopic biliary stenting for unresectable malignant hilar obstruction. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2017; 10:485–490.
Article22. Naitoh I, Hayashi K, Nakazawa T, et al. Side-by-side versus stent-in-stent deployment in bilateral endoscopic metal stenting for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Dig Dis Sci. 2012; 57:3279–3285.
Article23. Gwon DI, Ko GY, Yoon HK, et al. Prospective evaluation of a newly designed T-configured stent graft system for palliative treatment of advanced hilar malignant biliary obstructions. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010; 21:1410–1418.
Article24. Ito K, Fujita N, Noda Y, et al. Percutaneous cholecystostomy versus gallbladder aspiration for acute cholecystitis: a prospective randomized controlled trial. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004; 183:193–196.
Article25. Itoi T, Takada T, Hwang TL, et al. Percutaneous and endoscopic gallbladder drainage for acute cholecystitis: international multicenter comparative study using propensity score-matched analysis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2017; 24:362–368.
Article26. Takinami M, Murohisa G, Yoshizawa Y, et al. Risk factors for cholecystitis after stent placement in patients with distal malignant biliary obstruction. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2020; 27:470–476.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Ultrasonography-Guided Gallbladder Drainage as a Treatment Option for Acute Cholecystitis after Metal Stent Placement in Malignant Biliary Strictures
- Percutaneous Transhepatic Gallbladder Stenting for Acute Cholecystitis after Palliative Metallic Biliary Stenting
- Prophylactic endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder stenting to prevent acute cholecystitis induced after metallic stent placement for malignant biliary strictures: a retrospective study in Japan
- Cholecystitis after Placement of Covered Self-Expandable Metallic Stents in Patients with Distal Malignant Biliary Obstructions
- Multiple metallic stents placement for malignant hilar biliary obstruction: Perspective of a radiologist