Clin Endosc.
2022 Nov;55(6):742-750. 10.5946/ce.2022.141.
Outcomes of thin versus thick-wire snares for cold snare polypectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Nizam’s Institute of Medical Sciences, Hyderabad, India
- 2Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India
- 3Seth GS Medical College and KEM Hospital, Mumbai, India
- 4Department of Digestive Diseases and Clinical Nutrition, TATA Memorial Hospital, Mumbai, India
- KMID: 2536071
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2022.141
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Cold snare polypectomy (CSP) is commonly used for the resection of colorectal polyps ≤10 mm. Data regarding the influence of snare type on CSP effectiveness are conflicting. Hence, this meta-analysis aimed to compare the outcomes and safety of thin- and thick-wire snares for CSP.
Methods
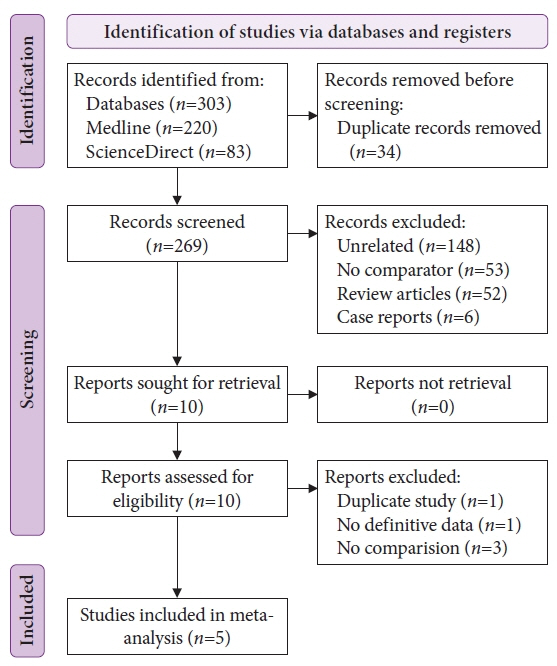
A comprehensive search of the literature published between 2000 and 2021 was performed of various databases for comparative studies evaluating the outcomes of thin- versus thick-wire snares for CSP.
Results
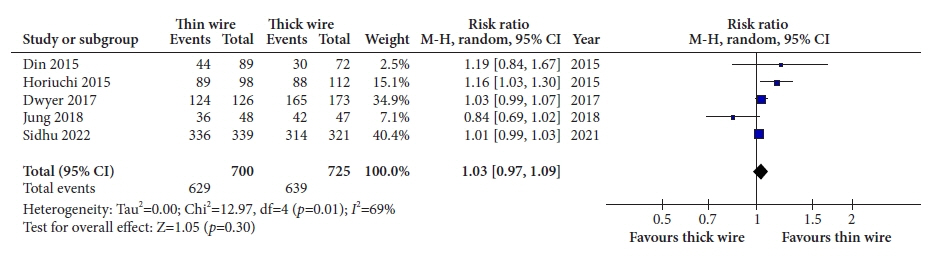
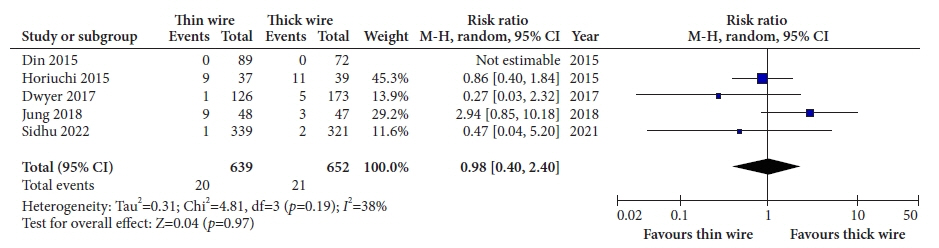
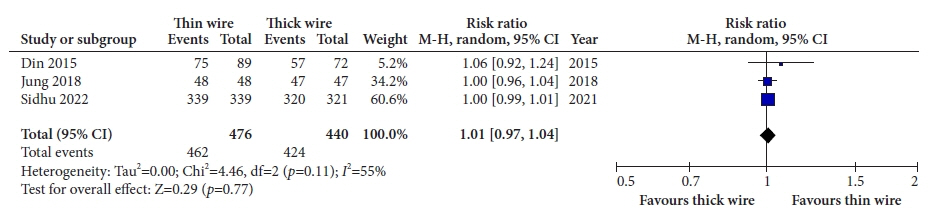
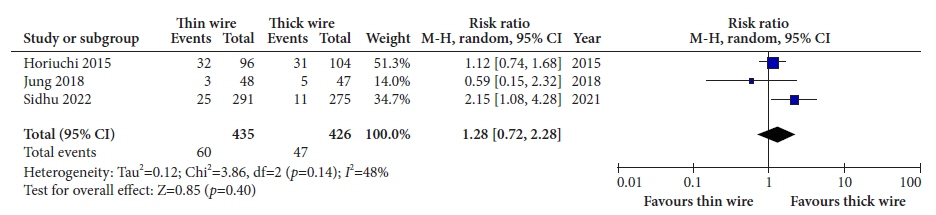
Five studies with data on 1,425 polyps were included in the analysis. The thick-wire snare was comparable to the thin-wire snare with respect to complete histological resection (risk ratio [RR], 1.03; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.97–1.09), overall bleeding (RR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.40–2.40), polyp retrieval (RR, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.97–1.04), and involvement of submucosa in the resection specimen (RR, 1.28; 95% CI, 0.72–2.28). There was no publication bias and a small study effect, and the relative effects remained the same in the sensitivity analysis.
Conclusions
CSP using a thin-wire snare has no additional benefit over thick-wire snares in small colorectal polyps. Factors other than snare design may play a role in improving CSP outcomes.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zauber AG, Winawer SJ, O’Brien MJ, et al. Colonoscopic polypectomy and long-term prevention of colorectal-cancer deaths. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:687–696.
Article2. Lowenfels AB, Williams JL, Holub JL, et al. Determinants of polyp size in patients undergoing screening colonoscopy. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011; 11:101.
Article3. Lieberman DA, Holub JL, Moravec MD, et al. Prevalence of colon polyps detected by colonoscopy screening in asymptomatic black and white patients. JAMA. 2008; 300:1417–1422.
Article4. Burgess NG, Metz AJ, Williams SJ, et al. Risk factors for intraprocedural and clinically significant delayed bleeding after wide-field endoscopic mucosal resection of large colonic lesions. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014; 12:651–661.
Article5. Kaltenbach T, Anderson JC, Burke CA, et al. Endoscopic removal of colorectal lesions-recommendations by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020; 91:486–519.
Article6. Ferlitsch M, Moss A, Hassan C, et al. Colorectal polypectomy and endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR): European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Clinical Guideline. Endoscopy. 2017; 49:270–297.
Article7. Takamaru H, Saito Y, Hammoud GM, et al. Comparison of postpolypectomy bleeding events between cold snare polypectomy and hot snare polypectomy for small colorectal lesions: a large-scale propensity score-matched analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022; 95:982–989.
Article8. Brenner H, Chang-Claude J, Jansen L, et al. Colorectal cancers occurring after colonoscopy with polyp detection: sites of polyps and sites of cancers. Int J Cancer. 2013; 133:1672–1679.
Article9. Humphris JL, Tippett J, Kwok A, et al. Cold snare polypectomy for diminutive polyps: an assessment of the risk of incomplete removal of small adenomas. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69:AB207.
Article10. Gonzalez I, Riley DE, Ho SB, et al. Quality colonoscopy: midterm results of a qualitative comparison of cold snare versus cold biopsy forceps for the resection of colonic polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:AB244.11. de Benito Sanz M, Hernández L, Garcia Martinez MI, et al. Efficacy and safety of cold versus hot snare polypectomy for small (5-9 mm) colorectal polyps: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Endoscopy. 2022; 54:35–44.
Article12. Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, et al. Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016; 5:210.
Article13. Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011; 343:d5928.
Article14. Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, et al. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ. 2016; 355:i4919.
Article15. Puhan MA, Schünemann HJ, Murad MH, et al. A GRADE Working Group approach for rating the quality of treatment effect estimates from network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2014; 349:g5630.
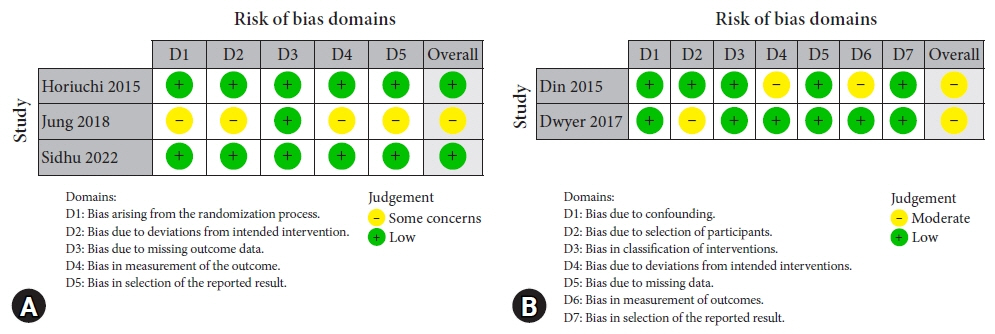
Article16. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021; 372:n71.17. Din S, Ball AJ, Riley SA, et al. Cold snare polypectomy: does snare type influence outcomes? Dig Endosc. 2015; 27:603–608.
Article18. Horiuchi A, Hosoi K, Kajiyama M, et al. Prospective, randomized comparison of 2 methods of cold snare polypectomy for small colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 82:686–692.
Article19. Dwyer JP, Tan JY, Urquhart P, et al. A prospective comparison of cold snare polypectomy using traditional or dedicated cold snares for the resection of small sessile colorectal polyps. Endosc Int Open. 2017; 5:E1062–E1068.
Article20. Jung Y, Chun AR, Han SJ, et al. Comparison of the clinical efficacy of the cold snare polypectomy using a thin wire mini-snare and thick wire mini-snare for small sized colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018; 87:AB366.21. Sidhu M, Forbes N, Tate DJ, et al. A randomized controlled trial of cold snare polypectomy technique: technique matters more than snare wire diameter. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022; 117:100.
Article22. Pohl H, Srivastava A, Bensen SP, et al. Incomplete polyp resection during colonoscopy-results of the complete adenoma resection (CARE) study. Gastroenterology. 2013; 144:74–80.
Article23. Lee SP, Sung IK, Kim JH, et al. Risk factors for incomplete polyp resection during colonoscopic polypectomy. Gut Liver. 2015; 9:66–72.
Article24. Pedersen IB, Bretthauer M, Kalager M, et al. Incomplete endoscopic resection of colorectal polyps: a prospective quality assurance study. Endoscopy. 2021; 53:383–391.
Article25. Saito S, Tajiri H, Ikegami M. Serrated polyps of the colon and rectum: endoscopic features including image enhanced endoscopy. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 7:860–871.
Article26. Pohl H, Anderson JC, Aguilera-Fish A, et al. Recurrence of colorectal neoplastic polyps after incomplete resection. Ann Intern Med. 2021; 174:1377–1384.
Article27. ASGE Technology Committee, Abu Dayyeh BK, Thosani N, et al. ASGE Technology Committee systematic review and meta-analysis assessing the ASGE PIVI thresholds for adopting real-time endoscopic assessment of the histology of diminutive colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 81:502.
Article28. Bendall O, James J, Pawlak KM, et al. Delayed bleeding after endoscopic resection of colorectal polyps: identifying high-risk patients. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2021; 14:477–492.
Article29. Jung YS, Park CH, Nam E, et al. Comparative efficacy of cold polypectomy techniques for diminutive colorectal polyps: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 2018; 32:1149–1159.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of the clinical efficacy of cold snare polypectomy using a thin-wire snare and thick-wire snare for small colorectal polyps
- Endoscopic Instruments and Electrosurgical Unit for Colonoscopic Polypectomy
- A Review of the 2017 European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Guideline for Polypectomy and Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
- Cold snare polypectomy versus cold endoscopic mucosal resection for small colorectal polyps: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Endoscopic Management of Post-Polypectomy Bleeding