J Surg Ultrasound.
2022 May;9(1):1-7. 10.46268/jsu.2022.9.1.1.
Ultrasound Evaluation of Miscellaneous Neck Masses
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Chonnam National University Medical School, Hwasun, Korea
- KMID: 2536057
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.46268/jsu.2022.9.1.1
Abstract
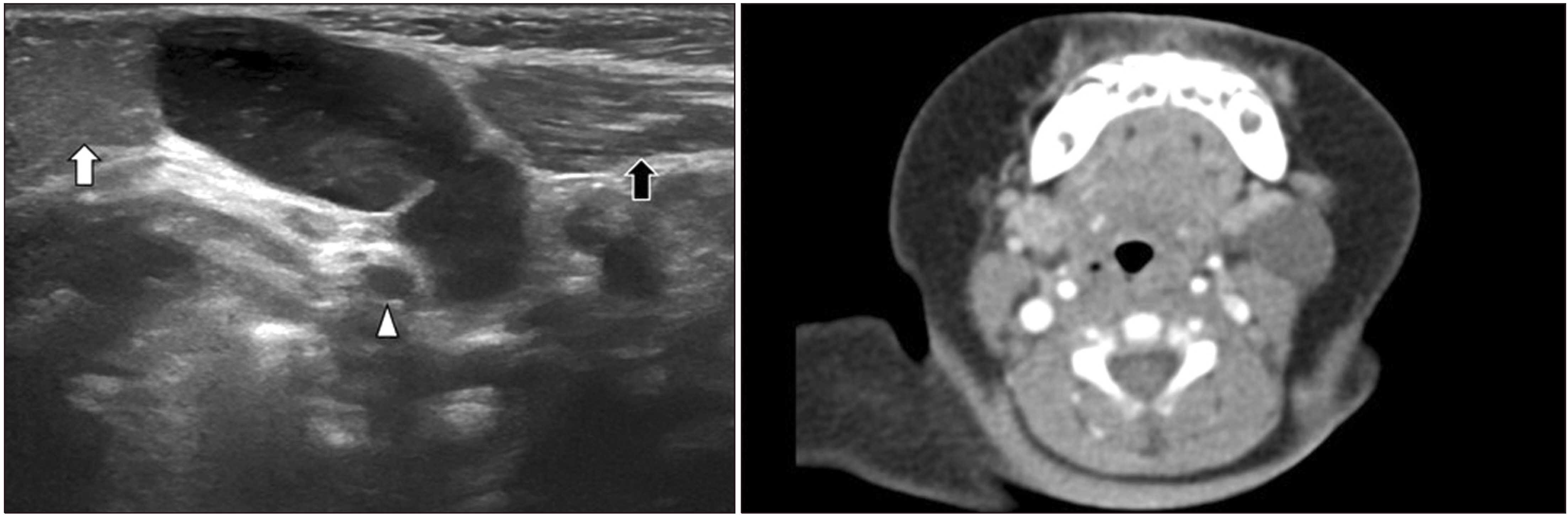
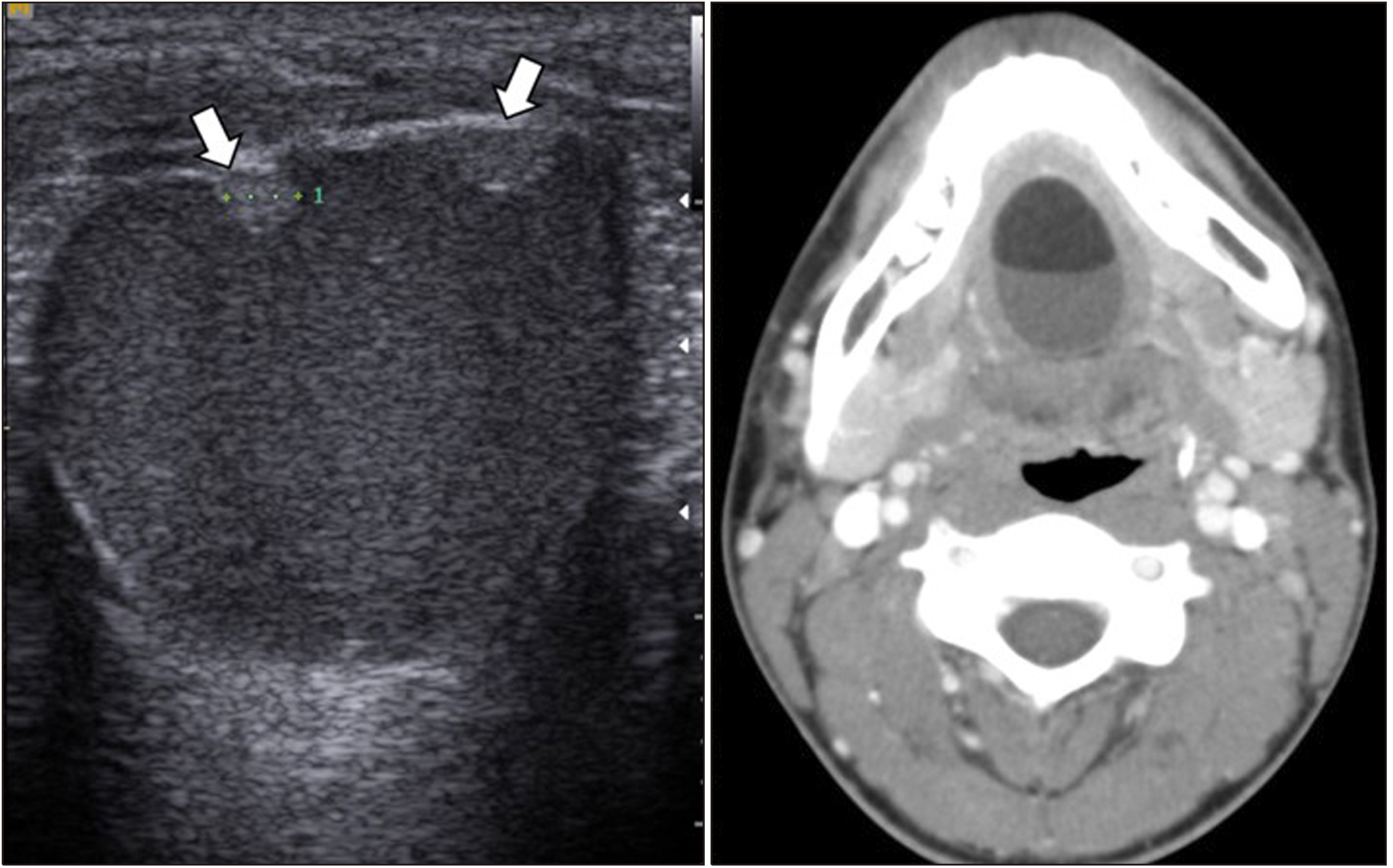
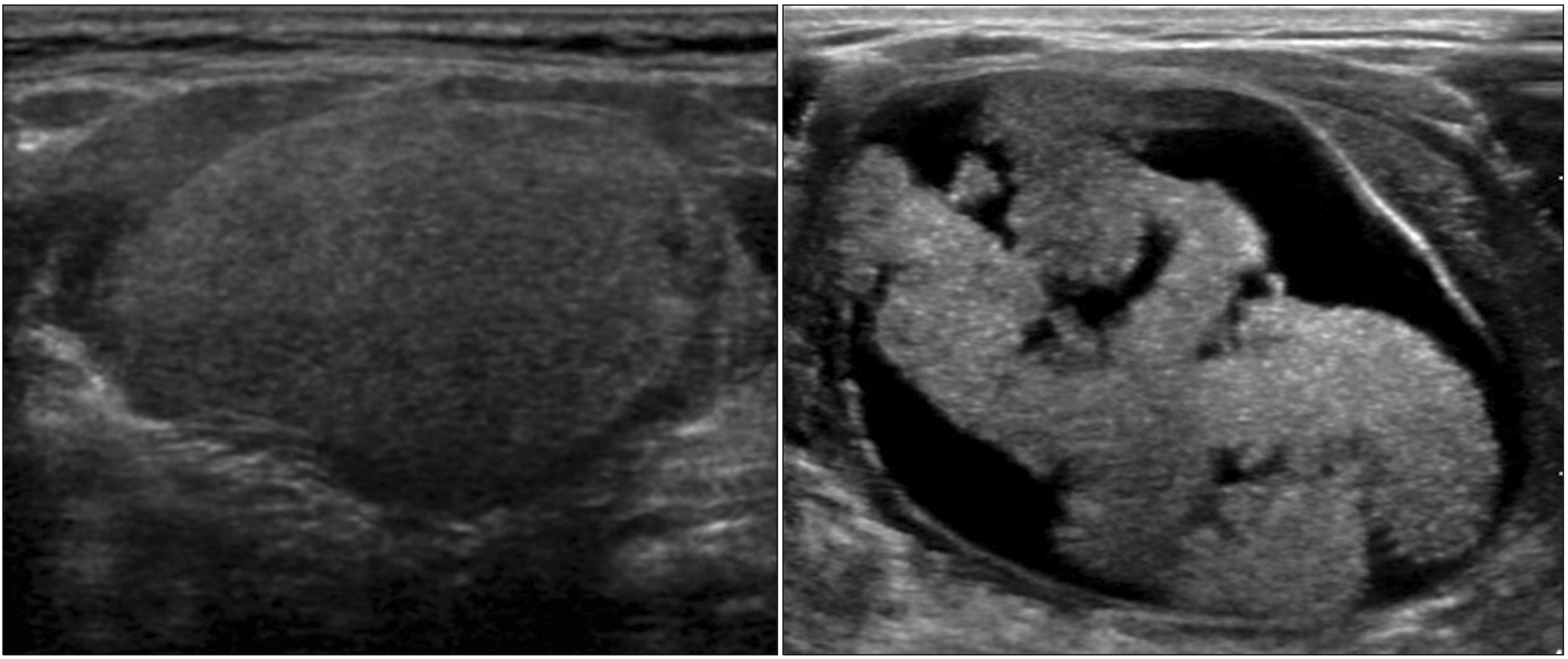
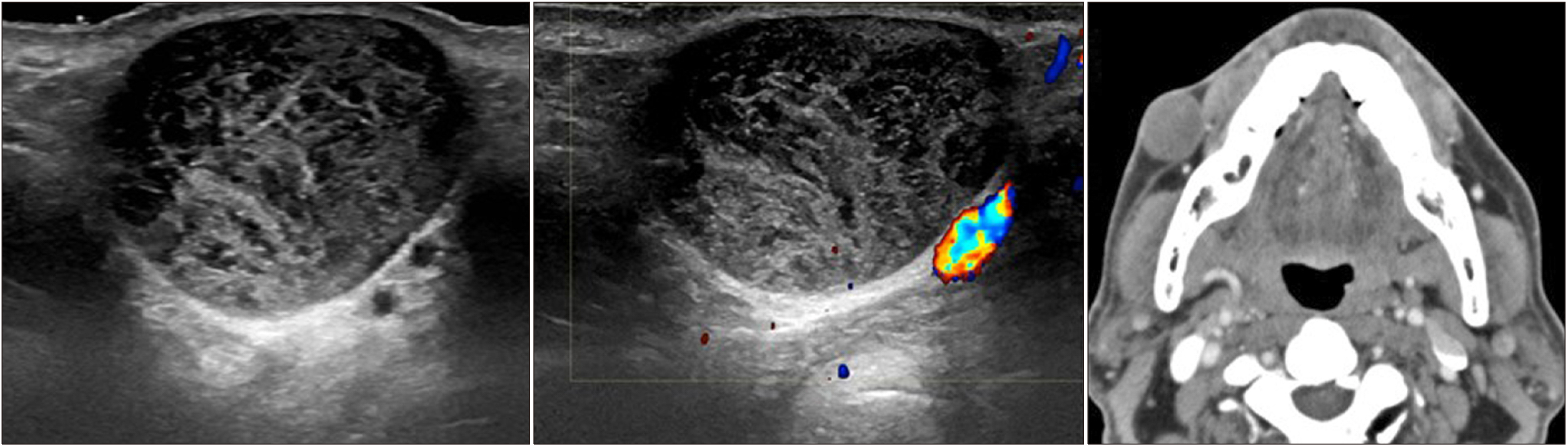
- A neck mass is a commonly observed clinical finding across all age groups. Neck masses are wide ranging from congenital, and inflammatory to neoplastic lesions. Ultrasound (US) is a convenient and applicable imaging modality for the evaluation of a neck mass in clinical practice. Although US is influenced by the operator’s experience and is not an ideal approach to detect deep structures, it can examine the structure from various angles in real-time and guide tissue sampling while simultaneously explaining about the same to patients. Therefore, US is useful for evaluating all neck masses, involving the lymph nodes, thyroid, parathyroid, and salivary glands. This article aimed to review miscellaneous neck masses and their ultrasonographic features.
Keyword
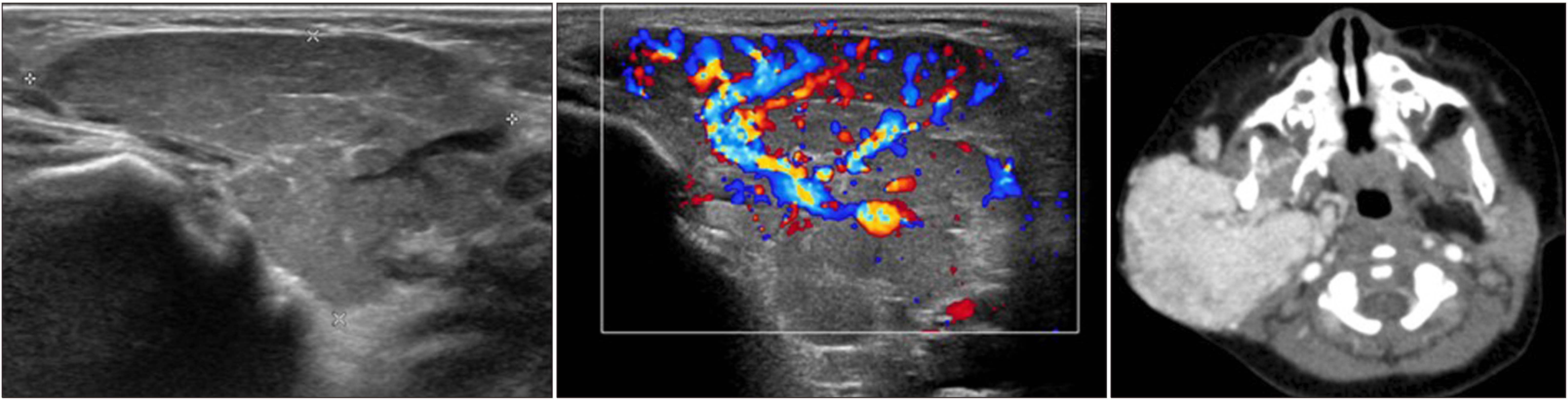
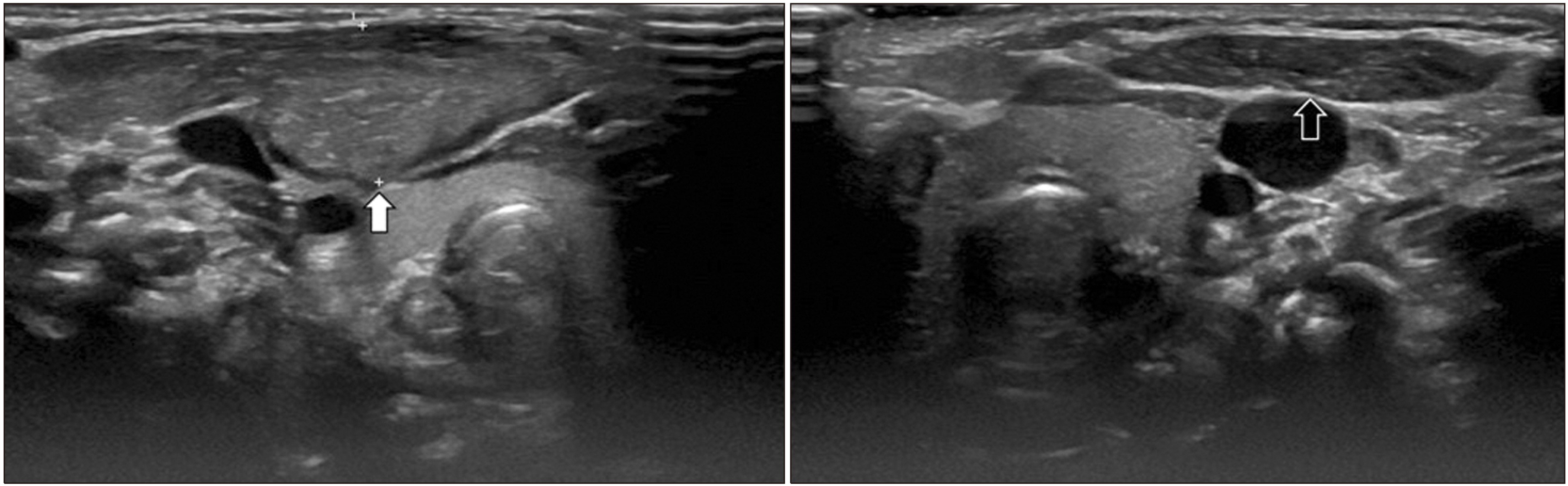
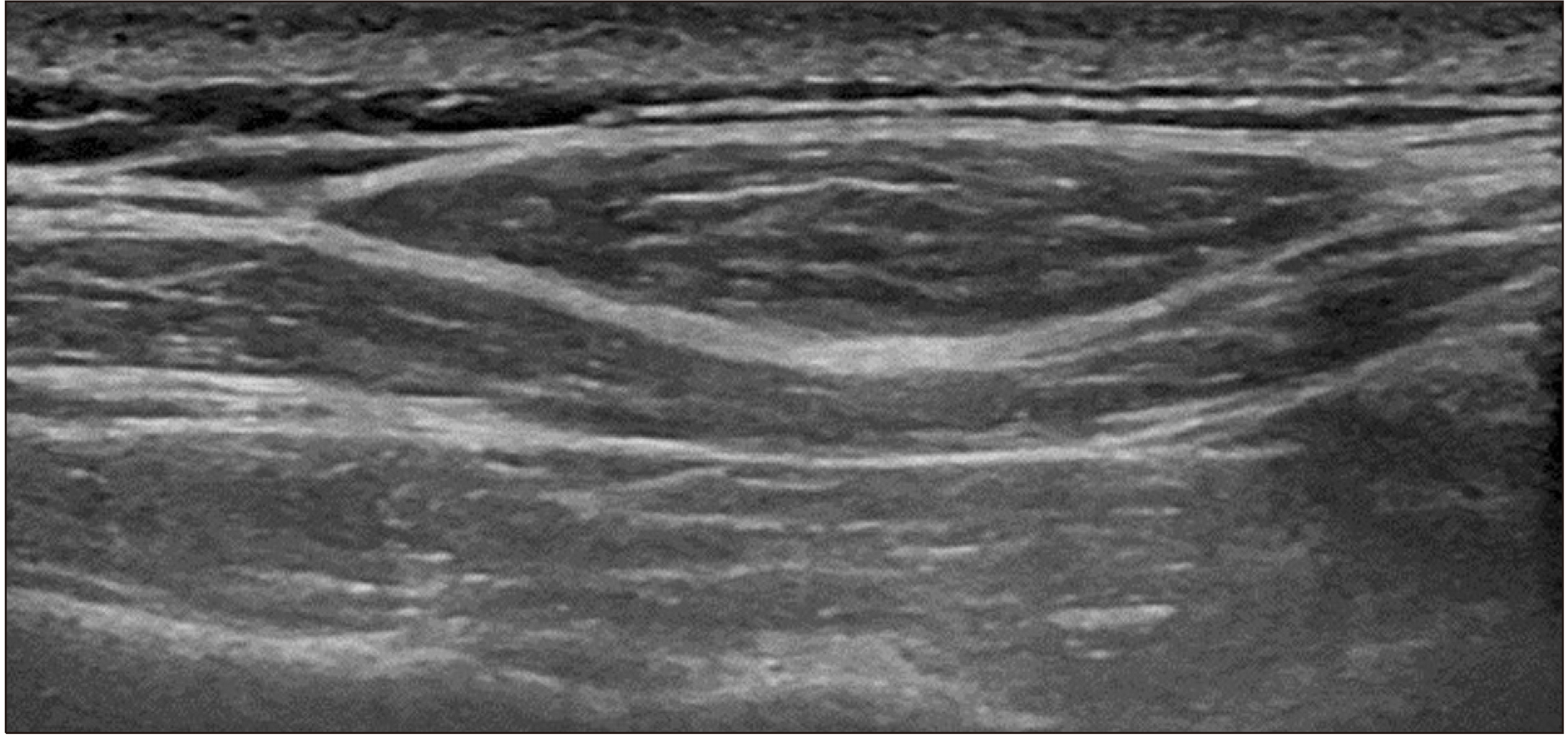
Figure
Reference
-
1. Choi SS, Zalzal GH. 1995; Branchial anomalies: a review of 52 cases. Laryngoscope. 105(9 Pt 1):909–13. DOI: 10.1288/00005537-199509000-00007. PMID: 7666723.
Article2. Lee DH, Yoon TM, Lee JK, Lim SC. 2018; Clinical study of second branchial cleft anomalies. J Craniofac Surg. 29:e557–60. DOI: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000004540. PMID: 29608472.
Article3. Cooc A, Chong I, Wang KY, Jiang K, Lincolns CM. 2020; Papillary thyroid carcinoma metastasis to a branchial cleft cyst: a case report and review of imaging. Clin Imaging. 64:1–6. Erratum in: Clin Imaging 2021;70:142. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2020.09.001. PMID: 32958362.
Article4. Taha A, Enodien B, Frey DM, Taha-Mehlitz S. 2022; Thyroglossal duct cyst, a case report and literature review. Diseases. 10:7. DOI: 10.3390/diseases10010007. PMID: 35225860. PMCID: PMC8883879.
Article5. Inarejos Clemente E, Oyewumi M, Propst EJ, Ngan BY, Greer ML. 2017; Thyroglossal duct cysts in children: Sonographic features every radiologist should know and their histopathological correlation. Clin Imaging. 46:57–64. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2017.07.002. PMID: 28732244.
Article6. Rayess HM, Monk I, Svider PF, Gupta A, Raza SN, Lin HS. 2017; Thyroglossal duct cyst carcinoma: a systematic review of clinical features and outcomes. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 156:794–802. DOI: 10.1177/0194599817696504. PMID: 28322121.
Article7. Baliga M, Shenoy N, Poojary D, Mohan R, Naik R. 2014; Epidermoid cyst of the floor of the mouth. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 5:79–83. DOI: 10.4103/0975-5950.140185. PMID: 25298725. PMCID: PMC4178364.
Article8. Choi HI, Choi YH, Cheon JE, Kim WS, Kim IO. 2018; Ultrasono-graphic features differentiating thyroglossal duct cysts from dermoid cysts. Ultrasonography. 37:71–7. DOI: 10.14366/usg.17027. PMID: 28658734. PMCID: PMC5769948.
Article9. Paltiel HJ, Burrows PE, Kozakewich HP, Zurakowski D, Mulliken JB. 2000; Soft-tissue vascular anomalies: utility of US for diagnosis. Radiology. 214:747–54. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.214.3.r00mr21747. PMID: 10715041.
Article10. Dubois J, Soulez G, Oliva VL, Berthiaume MJ, Lapierre C, Therasse E. 2001; Soft-tissue venous malformations in adult patients: imaging and therapeutic issues. Radiographics. 21:1519–31. DOI: 10.1148/radiographics.21.6.g01nv031519. PMID: 11706222.
Article11. Li J, Zhong W, Geng X, Liu X, Zhang X, Wang Y, et al. 2020; Ultrasonographic diagnosis, classification, and treatment of cervical lymphatic malformation in paediatric patients: a retrospective study. BMC Pediatr. 20:441. DOI: 10.1186/s12887-020-02337-w. PMID: 32950065. PMCID: PMC7501610.
Article12. de Serres LM, Sie KC, Richardson MA. 1995; Lymphatic malformations of the head and neck. A proposal for staging. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 121:577–82. DOI: 10.1001/archotol.1995.01890050065012. PMID: 7727093.
Article13. Lowry KC, Estroff JA, Rahbar R. 2010; The presentation and management of fibromatosis colli. Ear Nose Throat J. 89:E4–8. DOI: 10.1177/014556131008900902. PMID: 20859860.
Article14. Giovagnorio F, Martinoli C. 2001; Sonography of the cervical vagus nerve: normal appearance and abnormal findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 176:745–9. DOI: 10.2214/ajr.176.3.1760745. PMID: 11222217.15. Roll W, Müther M, Sporns PB, Zinnhardt B, Suero Molina E, Seifert R, et al. 2020; Somatostatin receptor-targeted radioligand therapy in head and neck paraganglioma. World Neurosurg. 143:e391–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.wneu.2020.07.165. PMID: 32745642.
Article16. Burgess A, Calderon M, Jafif-Cojab M, Jorge D, Balanza R. 2017; Bilateral carotid body tumor resection in a female patient. Int J Surg Case Rep. 41:387–91. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2017.11.019. PMID: 29545998. PMCID: PMC5697994.
Article17. Pacini P, Polti G, Faggiano A, Giannetta E, Tarsitano MG, Cantisani V. 2021; Multiparametric ultrasound evaluation of a case of bilateral carotid body tumor. J Ultrasound. 24:311–5. DOI: 10.1007/s40477-021-00581-z. PMID: 33999368. PMCID: PMC8363686.
Article18. Rahmani G, McCarthy P, Bergin D. 2017; The diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography for soft tissue lipomas: a systematic review. Acta Radiol Open. 6:2058460117716704. DOI: 10.1177/2058460117716704. PMID: 28717519. PMCID: PMC5502938.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of ovarian masses with color doppler sonography
- Comparison of ultrasound and radionuclide imaging in the evaluation of hepatic masses
- Ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy for benign non-thyroid cystic mass in the neck
- Prenatal Diagnosis and Outcome of Congenital Lung Mass
- Ultrasound of Head and Neck: Anatomy