Ann Clin Neurophysiol.
2022;24(2):79-83. 10.14253/acn.2022.24.2.79.
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma presenting as transverse myelitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, School of Medicine, Jeonbuk National University, Jeonju, Korea
- 2Department of Neurology, Jeonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonbuk National University School of Medicine, Jeonju, Korea
- 3Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Jeonbuk National University-Jeonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea
- 4Department of Pathology, Jeonbuk National University School of Medicine, Jeonju, Korea
- KMID: 2535723
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/acn.2022.24.2.79
Abstract
- Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Although progressive lymphadenopathy is a typical feature, extranodal involvement may also occur, including the gastrointestinal tract, skin, bone, thyroid, and testes. Central nervous system invasion is rare, so differentiating it from diseases such as inflammatory demyelinating disorder or infection is essential. DLBCL is therefore a challenge to diagnose, especially when the first findings are neurological symptoms. We report an unusual case of DLBCL that presented as transverse myelitis.
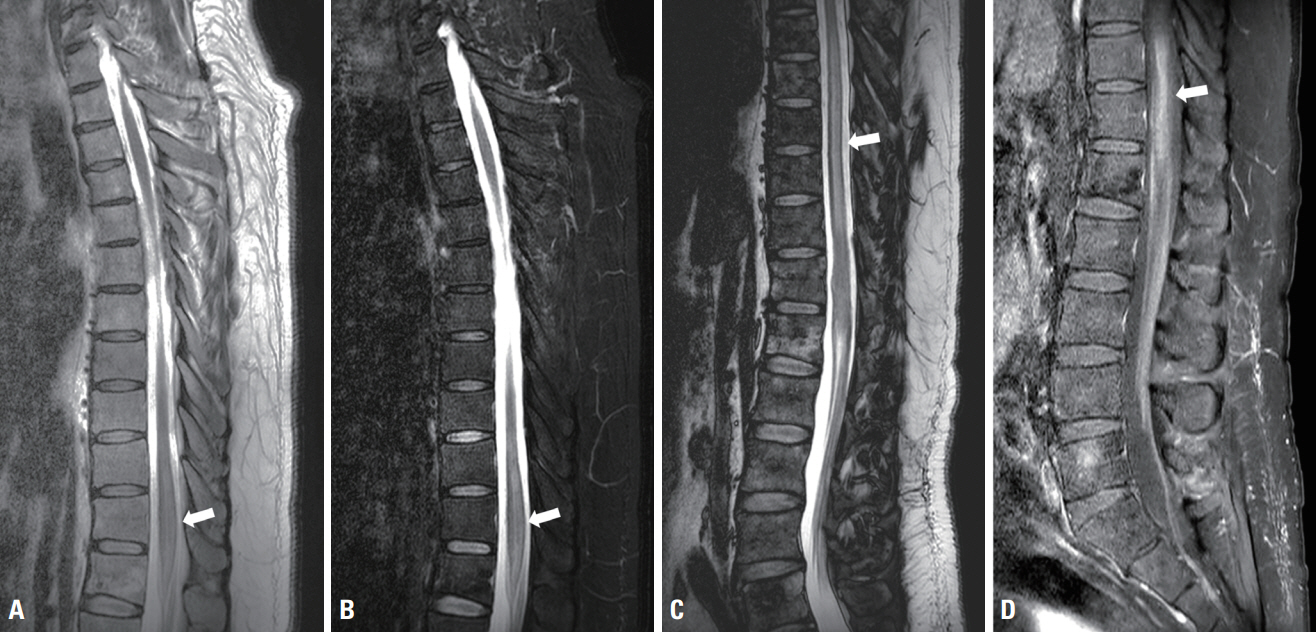
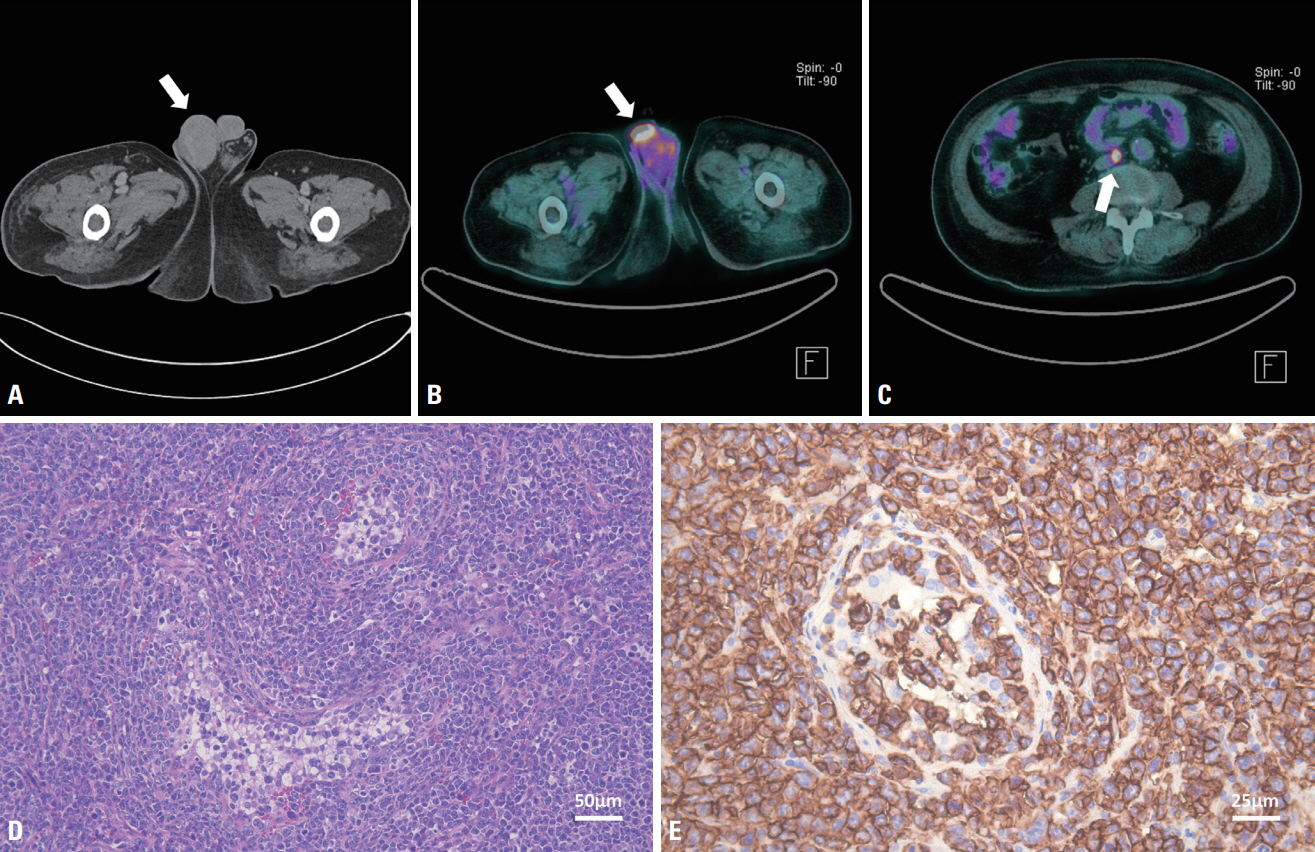
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sehn LH, Salles G. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384:842–858.2. Li S, Young KH, Medeiros LJ. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Pathology. 2018; 50:74–87.3. Shi Y, Han Y, Yang J, Liu P, He X, Zhang C, et al. Clinical features and outcomes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma based on nodal or extranodal primary sites of origin: analysis of 1,085 WHO classified cases in a single institution in China. Chin J Cancer Res. 2019; 31:152–161.4. Chen Y, Lin C, Zhang B. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma with longitudinally extensive transverse myelopathy as the initial symptom: a case report. Front Oncol. 2019; 9:266.5. Kim HS, Kim KK, Kim OJ. A case of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma presenting as transverse myelopathy. J Neurocrit Care. 2008; 1:177–180.6. Kumar N, Keegan BM, Rodriguez FJ, Hammack JE, Kantarci OH. Intravascular lymphoma presenting as a longitudinally-extensive myelitis: diagnostic challenges and etiologic clues. J Neurol Sci. 2011; 303:146–149.7. Ferreri AJ, Campo E, Seymour JF, Willemze R, Ilariucci F, Ambrosetti A, et al. Intravascular lymphoma: clinical presentation, natural history, management and prognostic factors in a series of 38 cases, with special emphasis on the ‘cutaneous variant’. Br J Haematol. 2004; 127:173–183.8. Frohman EM, Wingerchuk DM. Clinical practice. Transverse myelitis. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:564–572.9. Tolvaj B, Hahn K, Nagy Z, Vadvári Á, Csomor J, Gelpi E, et al. Life threatening rare lymphomas presenting as longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis: a diagnostic challenge. Ideggyogy Sz. 2020; 73:275–285.10. Yunoki M, Suzuki K, Uneda A, Yoshino K. A case of intravascular lymphoma presenting as myelopathy diagnosed with a skin biopsy. Surg Neurol Int. 2015; 6(Suppl 13):S367–S370.11. Merino A. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma presenting as transverse myelitis. Minn Med. 2015; 98:46.12. Shea L, Zhao Y, Reddy V, Yacoubian T, Mehta A. Primary bone marrow diffuse large B-cell lymphoma presenting as transverse myelitis. Am J Med Sci. 2018; 356:561–566.13. Kim H, Nam TS, Levy M, Lee KH, Kim J, Lee SJ. Primary central nervous system lymphoma with intramedullary spinal cord involvement mimicking inflammatory demyelinating disease. J Neurocrit Care. 2019; 12:55–63.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Occurring in Thyroid Gland
- A Case of Acute Transverse Myelitis with Hepatitis B Virus Infection
- Relapse of Ocular Lymphoma following Primary Testicular Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
- Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma presenting with cholecystitis-like symptoms
- A Case of Transverse Myelitis as a First Manifestation of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus