Ann Clin Neurophysiol.
2022;24(2):68-72. 10.14253/acn.2022.24.2.68.
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome associated with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Changwon, Korea
- 2Department of Neurology, Gyeongsang Institute of Health Science, College of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea
- KMID: 2535721
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/acn.2022.24.2.68
Abstract
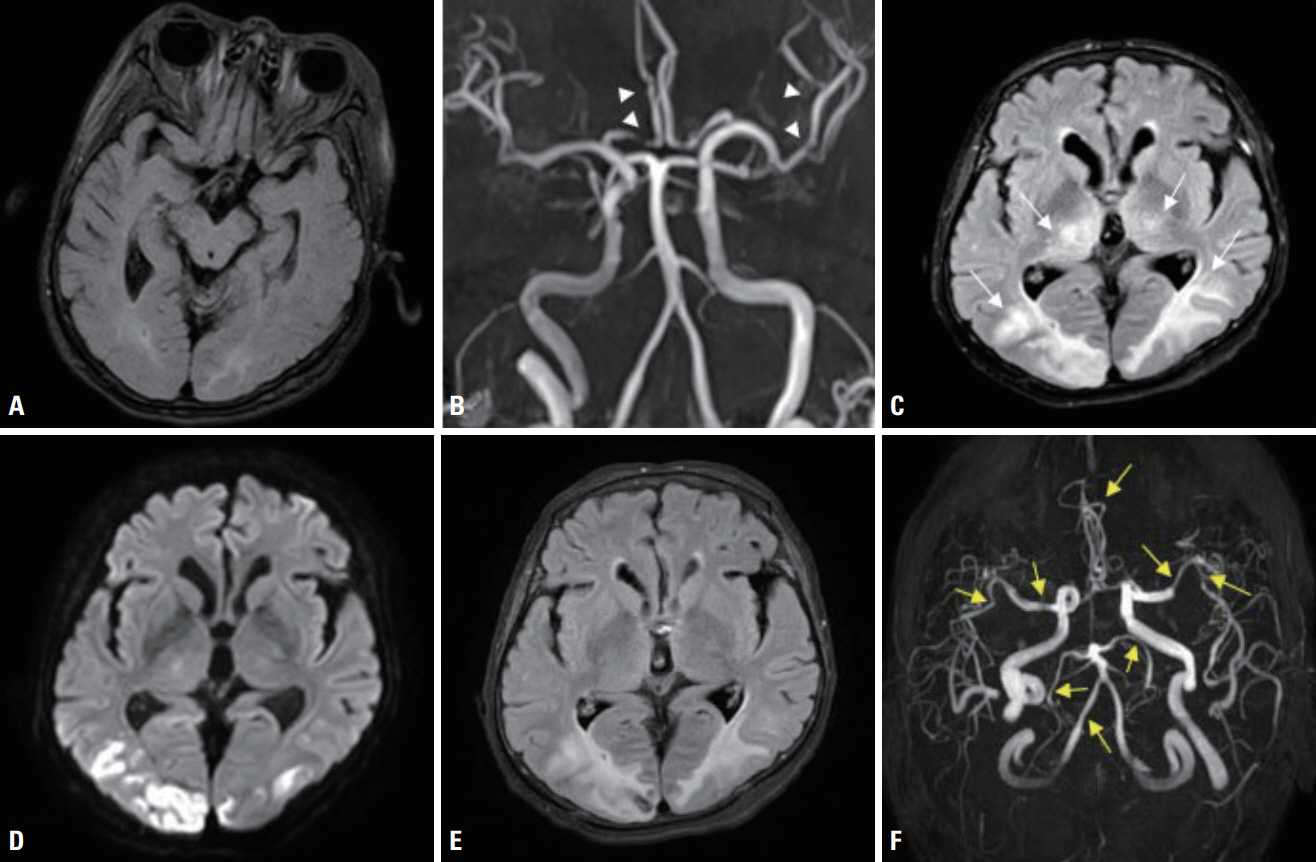
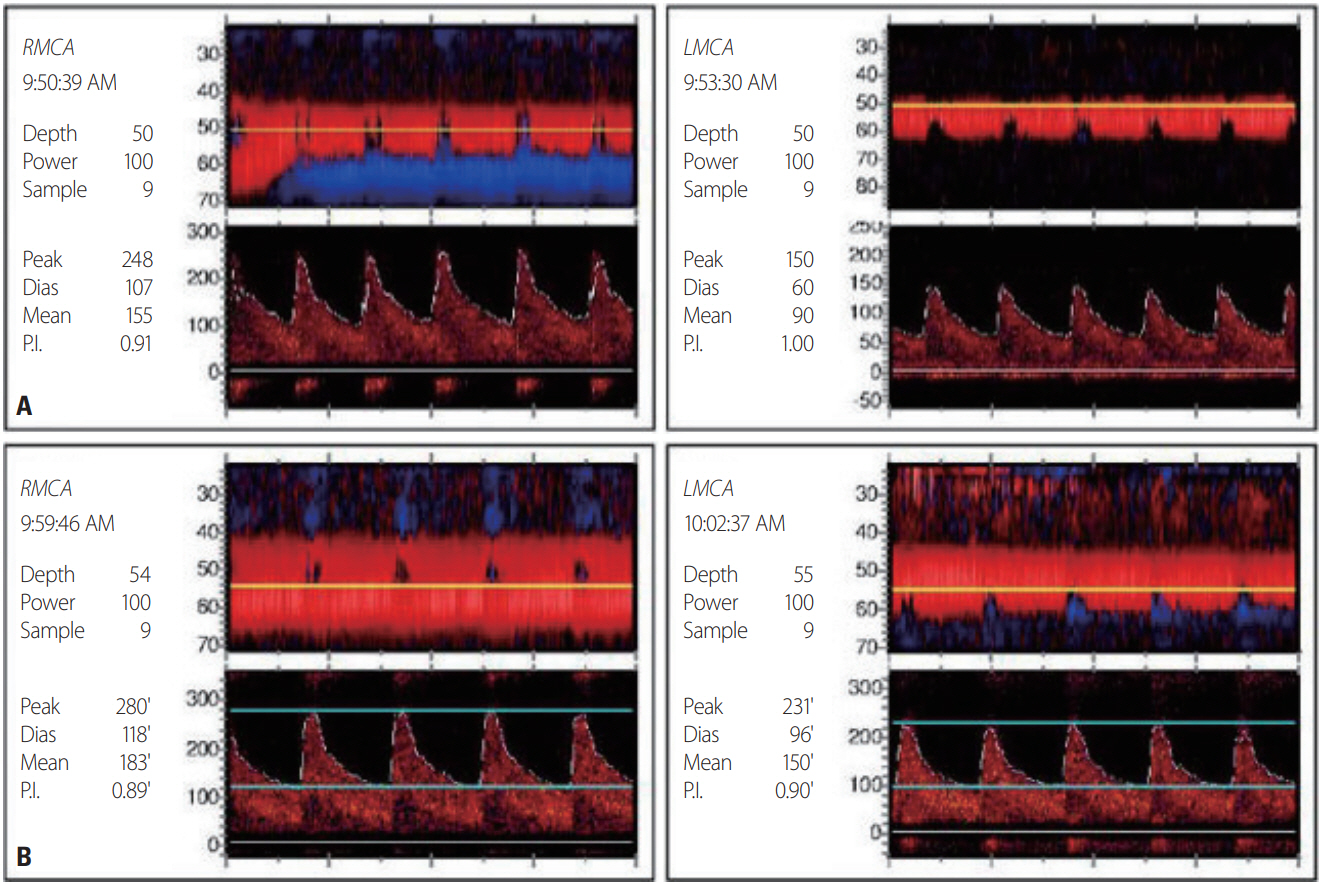
- Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) and reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome (RCVS) are relatively uncommon neurological disorders. These two independent syndromes can be concurrent as a part of a continuum process; however, the specific mechanism is not well known. Although the relationship between RCVS and PRES is currently unclear, they could share a common pathophysiology. This case report aimed to determine the pathophysiology underlying the co-occurrence of PRES and RCVS in a patient with an acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Valencia-Mendoza M, Ramírez-Rodríguez N, Vargas-Avila N, Peña-Ortiz A, Corzo-Villamizar M, Serna-Ramírez L, et al. Fatal reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: a systematic review of case series and case reports. J Clin Neurosci. 2019; 70:183–188.2. Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, Breen J, Pao L, Wang A, et al. A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1996; 334:494–500.3. Dardis C, Craciun R, Schell R. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in the setting of COPD: proposed pathogenesis. Med Hypotheses. 2013; 80:197–200.4. Khanal S, Acharya SP. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in association with exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a case report. BMC Neurol. 2018; 18:1–3.5. Gupta H, Alrohimi A, Nathoo N, Nowacki T, Siddiqi ZA. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome due to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Can J Neurol Sci. 2020; 47:569–571.6. Dietvorst S, Lambert J, Demeestere J, Lemmens R. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in a patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Acta Neurol Belg. 2020; 120:163–165.7. Sattar A, Manousakis G, Jensen MB. Systematic review of reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2010; 8:1417–1421.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome Combined with Posterior Encephalopathy Syndrome, and Transient Splenial Lesion after Delivery
- Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome and Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Presenting with Deep Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Young Women
- Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome in a Professional Rugby Player: A Case Report
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient with Intoxication of Arisaema amurense
- Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome Induced by Blood Transfusion