J Dent Rehabil Appl Sci.
2022 Sep;38(3):150-161. 10.14368/jdras.2022.38.3.150.
A study on the effect of microgroove-fibronectin complex titanium plate on the expression of various cell behavior-related genes in human gingival fibroblasts
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomaterials & Prosthodontics, Kyung Hee University College of Dentistry, Kyung Hee Unoversity Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2535020
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14368/jdras.2022.38.3.150
Abstract
- Purpose
To determine the effects of the microgroove-fibronectin complex surface on the expression of various genes related to cel-lular activity in human gingival fibroblasts.
Materials and Methods
Smooth titanium specimens (NE0), acid-treated titanium speci-mens (E0), microgroove and acid-treated titanium specimens (E60/10), fibronectin-fixed smooth titanium specimens (NE0FN), acidtreated and fibronectin-immobilized titanium specimens (E0FN), and microgroove and acid-treated titanium specimens immobilized with fibronectin (E60/10FN) were prepared. Real-time polymerase chain reaction experiments were conducted on 44 genes related to cell behavior of human gingival fibroblasts.
Results
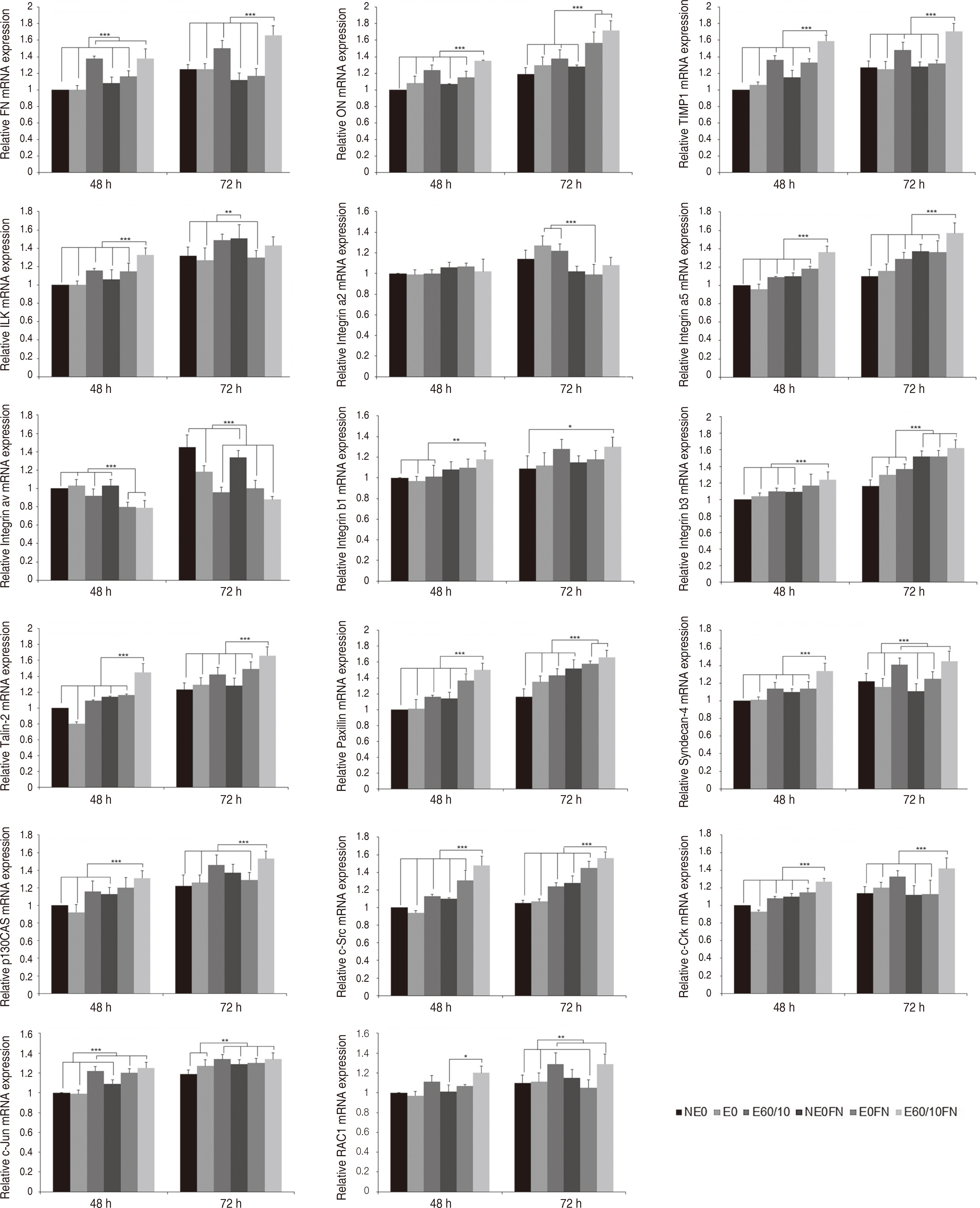
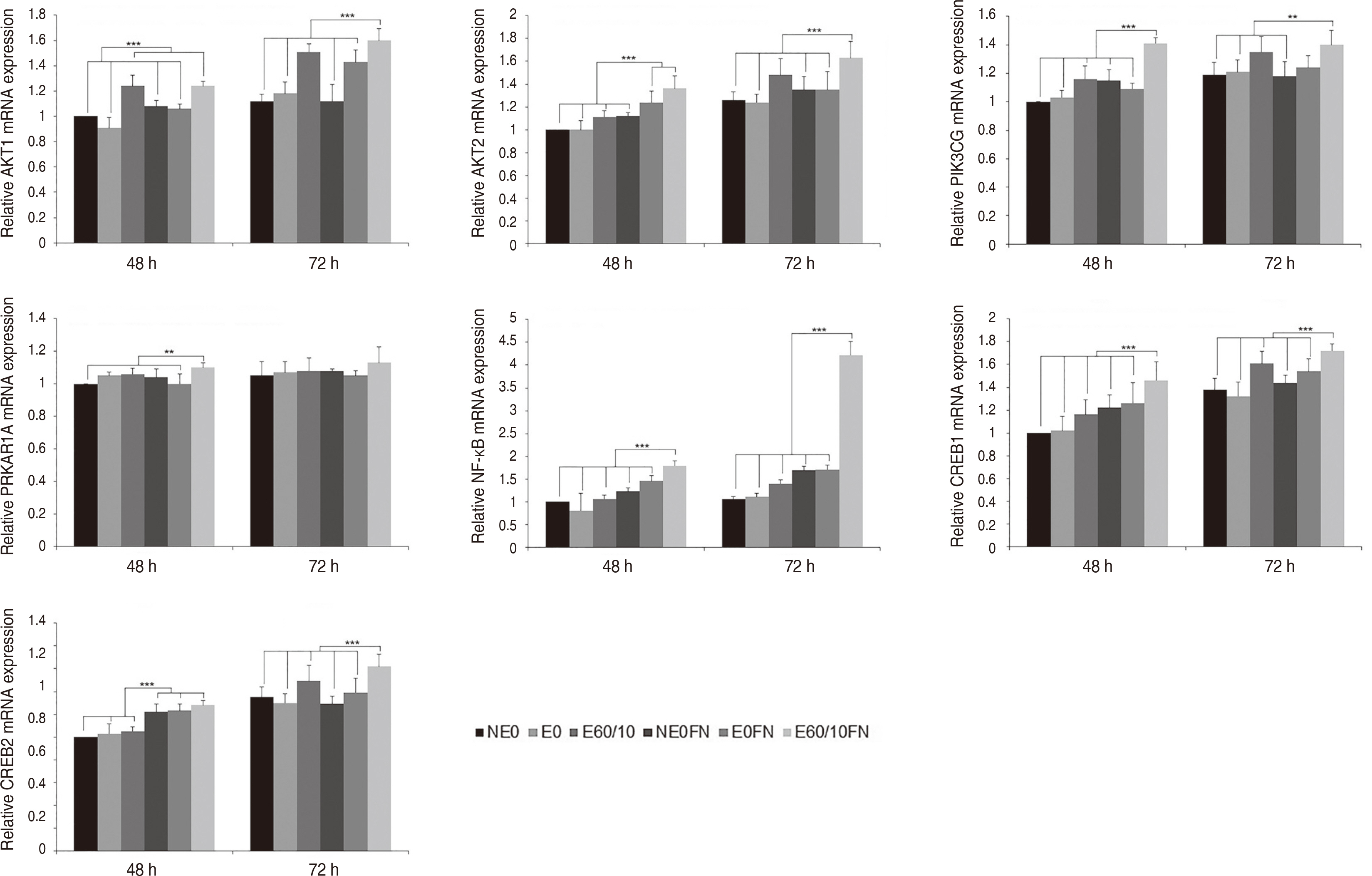
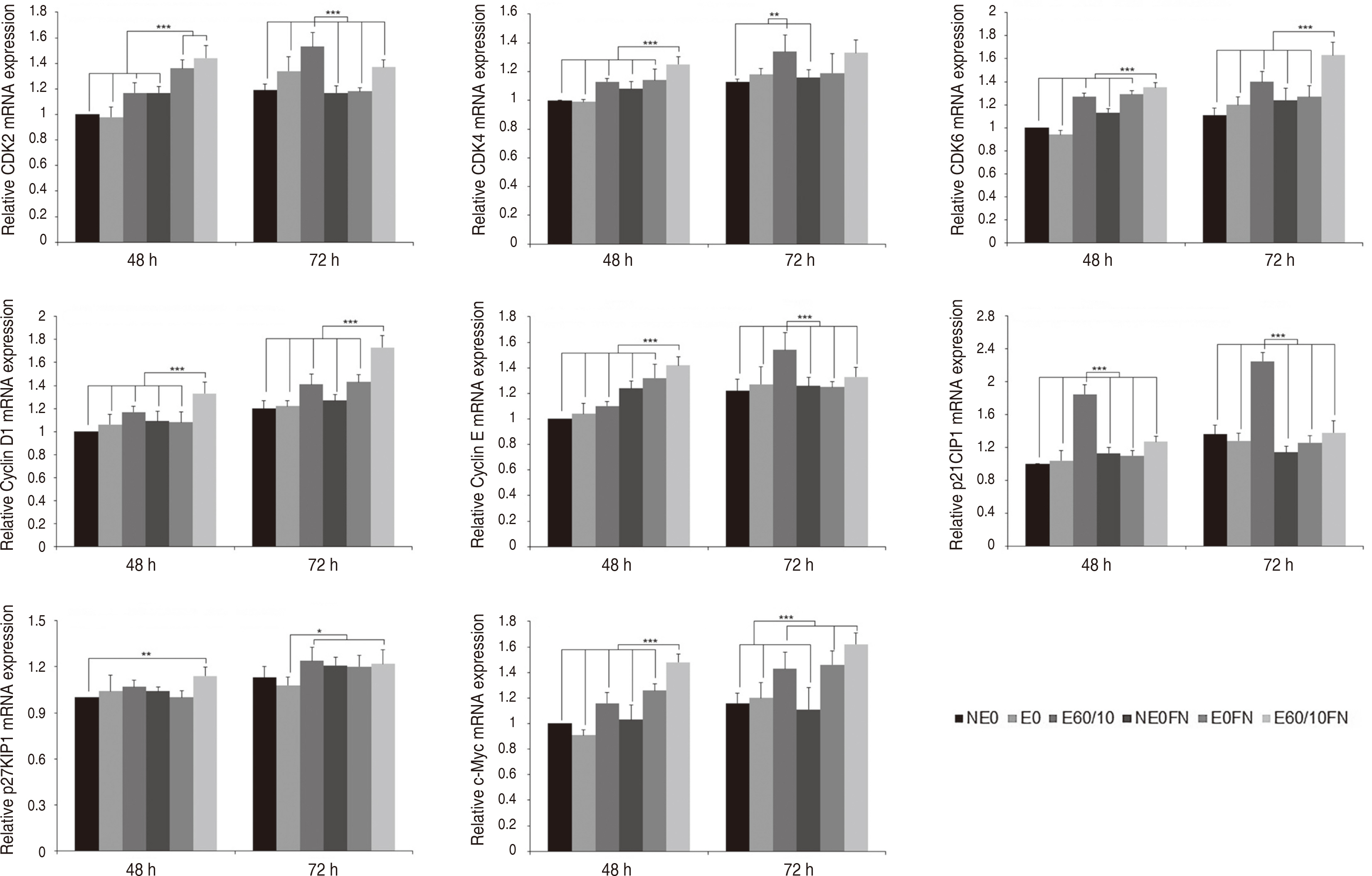
Adhesion and proliferation of human gingival fibroblast on microgroovefibronectin complex titanium were activated through four types of signaling pathway. Integrin α5, Integrin β1, Integrin β3, Talin-2, which belong to the focal adhesion pathway, AKT1, AKT2, NF-κB, which belong to the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway, MEK2, ERK1, ERK2, which belong to the MAPK signaling pathway, and Cyclin D1, CDK4, CDK6 genes belonging to the cell cycle signaling pathway were upregulated on the microgroove-fibronectin complex titanium surface (E60/10FN).
Conclusion
The microgroove-fibronectin complex titanium surface can up-regulate various genes involved in cell behavior.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Rompen E, Domken O, Degidi M, Pontes AE, Piattelli A. 2006; The effect of material characteristics, of surface topography and of implant components and connections on soft tissue integration: a literature review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 17(Suppl 2):55–67. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2006.01367.x. PMID: 16968382.
Article2. Corvino E, Pesce P, Mura R, Marcano E, Canullo L. 2020; Influence of modified titanium abutment surface on peri-implant soft tissue behavior: a systematic review of in vitro studies. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 35:503–19. DOI: 10.11607/jomi.8110. PMID: 32406646.
Article3. Lai Y, Chen J. 2015; Comparative study on contact guidance activity of human gingival fibroblasts on microgroove surfaces. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 50:33–7. PMID: 25779073.4. Chou L, Firth JD, Uitto VJ, Brunette DM. 1995; Substratum surface topography alters cell shape and regulates fibronectin mRNA level, mRNA stability, secretion and assembly in human fibroblasts. J Cell Sci. 108:1563–73. DOI: 10.1242/jcs.108.4.1563. PMID: 7615675.
Article5. Kim SY, Oh N, Lee MH, Kim SE, Leesungbok R, Lee SW. 2009; Surface microgrooves and acid-etching on titanium substrata alter various cell behaviors of cultured human gingival fibroblasts. Clin Oral Implants Res. 20:262–72. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2008.01652.x. PMID: 19397638.6. Leiss M, Beckmann K, Girós A, Costell M, Fässler R. 2008; The role of integrin binding sites in fibronectin matrix assembly in vivo. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 20:502–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.06.001. PMID: 18586094.
Article7. Missirlis D, Haraszti T, Kessler H, Spatz JP. 2017; Fibronectin promotes directional persistence in fibroblast migration through interactions with both its cell-binding and heparin-binding domains. Sci Rep. 7:3711. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-03701-0. PMID: 28623309. PMCID: PMC5473823. PMID: f05ac0fbbf9a498f9e9f5b297e6e308e.
Article8. Mao Y, Schwarzbauer JE. 2005; Fibronectin fibrillogenesis, a cell-mediated matrix assembly process. Matrix Biol. 24:389–99. DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2005.06.008. PMID: 16061370.
Article9. Kim EC, Lee DY, Lee MH, Lee HJ, Kim KH, Leesungbok R, Ahn SJ, Park SJ, Yoon JH, Jee YJ, Lee SC, Lee SW. 2018; The effect of fibronectin-immobilized microgrooved titanium substrata on cell proliferation and expression of genes and proteins in human gingival fibroblasts. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 15:615–27. DOI: 10.1007/s13770-018-0153-7. PMID: 30603583. PMCID: PMC6171696.
Article10. Pankov R, Yamada KM. 2002; Fibronectin at a glance. J Cell Sci. 115:3861–3. DOI: 10.1242/jcs.00059. PMID: 12244123.
Article11. Hynes RO. 2002; Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 110:673–87. DOI: 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00971-6. PMID: 12297042.12. Burridge K, Connell L. 1983; A new protein of adhesion plaques and ruffling membranes. J Cell Biol. 97:359–67. DOI: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.359. PMID: 6684120. PMCID: PMC2112532.
Article13. Turner CE, Glenney JR Jr, Burridge K. 1990; Paxillin: a new vinculin-binding protein present in focal adhesions. J Cell Biol. 111:1059–68. DOI: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1059. PMID: 2118142. PMCID: PMC2116264.
Article14. Carey DJ. 1997; Syndecans: multifunctional cell-surface co-receptors. Biochem J. 327:1–16. DOI: 10.1042/bj3270001. PMID: 9355727. PMCID: PMC1218755.
Article15. Song G, Ouyang G, Bao S. 2005; The activation of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival. J Cell Mol Med. 9:59–71. DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2005.tb00337.x. PMID: 15784165. PMCID: PMC6741304.
Article16. Vanhaesebroeck B, Alessi DR. 2000; The PI3K-PDK1 connection: more than just a road to PKB. Biochem J. 346:561–76. DOI: 10.1042/bj3460561. PMID: 10698680. PMCID: PMC1220886.
Article17. Orton RJ, Sturm OE, Vyshemirsky V, Calder M, Gilbert DR, Kolch W. 2005; Computational modelling of the receptor-tyrosine-kinase-activated MAPK pathway. Biochem J. 392:249–61. DOI: 10.1042/BJ20050908. PMID: 16293107. PMCID: PMC1316260.
Article18. Avruch J, Khokhlatchev A, Kyriakis JM, Luo Z, Tzivion G, Vavvas D, Zhang XF. 2001; Ras activation of the Raf kinase: tyrosine kinase recruitment of the MAP kinase cascade. Recent Prog Horm Res. 56:127–55. DOI: 10.1210/rp.56.1.127. PMID: 11237210.
Article19. Monje P, Hernández-Losa J, Lyons RJ, Castellone MD, Gutkind JS. 2005; Regulation of the transcriptional activity of c-Fos by ERK. A novel role for the prolyl isomerase PIN1. J Biol Chem. 280:35081–4. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.C500353200. PMID: 16123044.20. Xiong Y, Hannon GJ, Zhang H, Casso D, Kobayashi R, Beach D. 1993; p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature. 366:701–4. DOI: 10.1038/366701a0. PMID: 8259214.
Article21. Lee SW, Kim SY, Rhyu IC, Chung WY, Leesungbok R, Lee KW. 2009; Influence of microgroove dimension on cell behavior of human gingival fibroblasts cultured on titanium substrata. Clin Oral Implants Res. 20:56–66. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2008.01597.x. PMID: 19133333.
Article22. Huang NF, Lee RJ, Li S. 2010; Engineering of aligned skeletal muscle by micropatterning. Am J Transl Res. 2:43–55. PMID: 20182581. PMCID: PMC2826821.23. Bretones G, Delgado MD, León J. 2015; Myc and cell cycle control. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1849:506–16. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.03.013. PMID: 24704206.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Surface microgrooves of thirty micrometers in width on titanium substrata enhance proliferation and alter gene expression of cultured human gingival fibroblasts
- Regulation of human gingival fibroblast gene expression on microgrooves: A DNA microarray study
- Micropatterned grooves and acid-etching on titanium substrata alter viability and gene expression of adhered human gingival fibroblasts: A pilot study
- Attachment of Human Gingival Fibroblasts to Commercially Pure Titanium Surfaces with Different Instruments: A comparative Study in Vitro
- Screening of genes differentially expressed in cultured human periodontal ligament cells and human gingival fibroblasts