Ann Surg Treat Res.
2022 Nov;103(5):306-311. 10.4174/astr.2022.103.5.306.
Correlation of histological diagnosis and laboratory findings in distinguishing acute appendicitis and lymphoid hyperplasia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Emergency Medicine, Konya Training and Research Hospital, Baskent University, Konya, Turkey
- 2Department of Pathology, Konya Training and Research Hospital, Baskent University, Konya, Turkey
- 3Department of Statistics, Faculty of Science, Selcuk University, Konya, Turkey
- 4Department of Pulmonary Disease, Konya Private Meram Akademi Hospital, Konya, Turkey
- KMID: 2534857
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2022.103.5.306
Abstract
- Purpose
Acute appendicitis (AA) is one of the most frequent causes of abdominal surgery encountered in emergency rooms. However, reactive lymphoid hyperplasia (RLH) is one of the appendicular pathologies often misdiagnosed. It is quite challenging to distinguish between AA and RLH in terms of planning treatment in an emergency. Therefore, this retrospective study aimed to compare the histological and laboratory findings of AA and RLH.
Methods
The retrospective data included in the study were obtained from patients diagnosed with AA. Complete blood count (CBC) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels of patients with AA and RLH were compared before the surgery based on the histological diagnosis of the patients.
Results
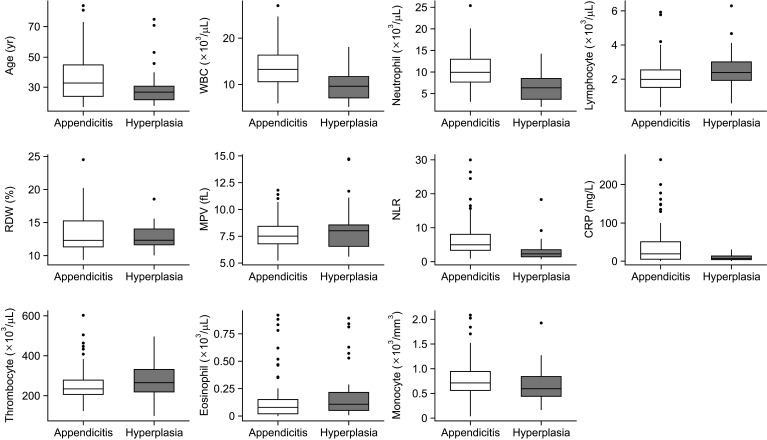
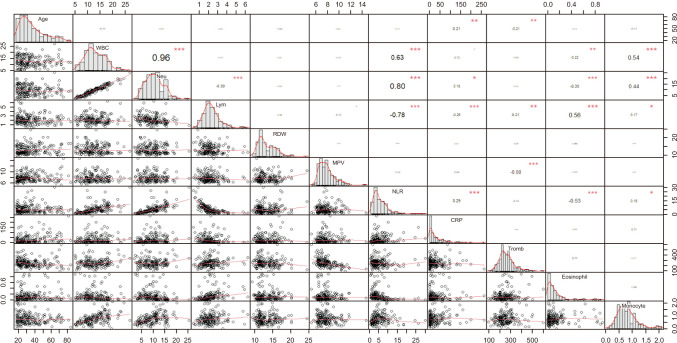
A total of 187 patients who previously underwent appendectomy were included in the study. Histopathological examination revealed that 152 patients (81.3%) were diagnosed with AA, and 35 (18.7%) with RLH. While white blood cell count (P < 0.001), neutrophil (P < 0.001), and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (P < 0.001) were found to be significantly higher in those with AA; lymphocyte (P = 0.003) and eosinophil counts (P = 0.033) were detected to be significantly higher in those with RLH. CRP level was also significantly higher in those with AA (P = 0.002) Conclusion: We consider that CBC and CRP levels may be predictive in distinguishing between AA and RLH. We consider that these parameters may be valuable in making a distinction between patients before surgery.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Andersson RE. Meta-analysis of the clinical and laboratory diagnosis of appendicitis. Br J Surg. 2004; 91:28–37. PMID: 14716790.
Article2. McGowan DR, Sims HM, Zia K, Uheba M, Shaikh IA. The value of biochemical markers in predicting a perforation in acute appendicitis. ANZ J Surg. 2013; 83:79–83. PMID: 23231057.
Article3. Sengupta A, Bax G, Paterson-Brown S. White cell count and C-reactive protein measurement in patients with possible appendicitis. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2009; 91:113–115. PMID: 19102827.
Article4. Sheridan AD, Ehrlich L, Morotti RA, Goodman TR. Sonographic distinction between acute suppurative appendicitis and viral appendiceal lymphoid hyperplasia (“pink appendix”) with pathological correlation. Ultrasound Q. 2015; 31:95–98. PMID: 25945725.
Article5. Swischuk LE, Chung DH, Hawkins HK, Jadhav SP, Radhakrishnan R. Non-fecalith-induced appendicitis: etiology, imaging, and pathology. Emerg Radiol. 2015; 22:643–649. PMID: 26293120.
Article6. Bhangu A, Søreide K, Di Saverio S, Assarsson JH, Drake FT. Acute appendicitis: modern understanding of pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Lancet. 2015; 386:1278–1287. PMID: 26460662.
Article7. Stewart B, Khanduri P, McCord C, Ohene-Yeboah M, Uranues S, Vega Rivera F, et al. Global disease burden of conditions requiring emergency surgery. Br J Surg. 2014; 101:e9–e22. PMID: 24272924.
Article8. Stringer MD. Acute appendicitis. J Paediatr Child Health. 2017; 53:1071–1076. PMID: 29044790.
Article9. Carr NJ. The pathology of acute appendicitis. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2000; 4:46–58. PMID: 10684382.
Article10. Xu Y, Jeffrey RB, DiMaio MA, Olcott EW. Lymphoid hyperplasia of the appendix: a potential pitfall in the sonographic diagnosis of appendicitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016; 206:189–194. PMID: 26700351.
Article11. Rabah R. Pathology of the appendix in children: an institutional experience and review of the literature. Pediatr Radiol. 2007; 37:15–20. PMID: 17031635.
Article12. Goldin AB, Khanna P, Thapa M, McBroom JA, Garrison MM, Parisi MT. Revised ultrasound criteria for appendicitis in children improve diagnostic accuracy. Pediatr Radiol. 2011; 41:993–999. PMID: 21409546.
Article13. Kaya A, Karaman K, Aziret M, Ercan M, Köse E, Kahraman YS, et al. The role of hematological parameters in distinguishing acute appendicitis from lymphoid hyperplasia. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2022; 28:434–439. PMID: 35485518.
Article14. Yilmaz M, Akbulut S, Kutluturk K, Sahin N, Arabaci E, Ara C, et al. Unusual histopathological findings in appendectomy specimens from patients with suspected acute appendicitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:4015–4022. PMID: 23840147.
Article15. Markar SR, Karthikesalingam A, Falzon A, Kan Y. The diagnostic value of neutrophil: lymphocyte ratio in adults with suspected acute appendicitis. Acta Chir Belg. 2010; 110:543–547. PMID: 21158332.
Article16. Kahramanca S, Ozgehan G, Seker D, Gökce EI, Seker G, Tunç G, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of acute appendicitis. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2014; 20:19–22. PMID: 24639310.
Article17. Goodman DA, Goodman CB, Monk JS. Use of the neutrophil:lymphocyte ratio in the diagnosis of appendicitis. Am Surg. 1995; 61:257–259. PMID: 7887542.18. Hallan S, Asberg A, Edna TH. Additional value of biochemical tests in suspected acute appendicitis. Eur J Surg. 1997; 163:533–538. PMID: 9248988.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasound Findings of Lymphoid Hyperplasia of the Appendix in Children: Differentiation from Acute Appendicitis
- A Case of Acute Appendicitis following Diagnostic Colonoscopy
- Appendicitis – Is a Clinical Diagnosis Enough?
- Radiologic diagnosis of acute appendicitis
- CT Findings of Acute Appendicitis in Children