J Korean Med Sci.
2022 Oct;37(43):e311. 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e311.
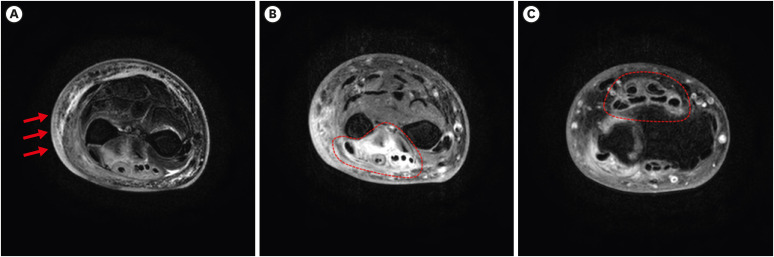
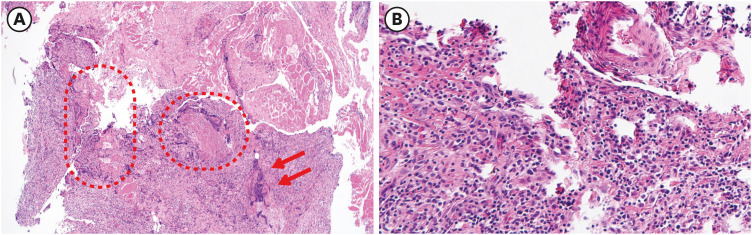
Case 4: A 70-Year-Old Man With Painful Swelling of Left Forearm Unresponsive to Antibiotics
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Vincent’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Korea
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, St. Vincent’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Korea
- 3Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, St. Vincent’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Korea
- KMID: 2534825
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e311
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. Philadelphia, PA, USA: Elsevier Health Sciences;2019.2. Mathew AJ, Ravindran V. Infections and arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2014; 28(6):935–959. PMID: 26096095.3. Kay J, Upchurch KS. ACR/EULAR 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012; 51(Suppl 6):vi5–vi9. PMID: 23221588.4. Franco-Paredes C, Marcos LA, Henao-Martínez AF, Rodríguez-Morales AJ, Villamil-Gómez WE, Gotuzzo E, et al. Cutaneous mycobacterial infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2018; 32(1):e00069-18. PMID: 30429139.5. Wi YM. Treatment of extrapulmonary nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Infect Chemother. 2019; 51(3):245–255. PMID: 31583858.6. Wang SH, Pancholi P. Mycobacterial skin and soft tissue infection. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2014; 16(11):438. PMID: 25339245.7. Chung J, Ince D, Ford BA, Wanat KA. Cutaneous infections due to nontuberculosis mycobacterium: recognition and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018; 19(6):867–878. PMID: 30168084.8. Gauthier DT, Doss JH, LaGatta M, Gupta T, Karls RK, Quinn FD. Genomic degeneration and reduction in the fish pathogen Mycobacterium shottsii. Microbiol Spectr. 2022; 10(3):e0115821. PMID: 35579461.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Cavenous Hemangioma on the Left Forearm
- Two Cases of Occupational Radiodermatitis
- A case of mycobacterium fortuitum infection at the site for antibiotics susceptibility test
- Two Cases of Sparganosis
- A Case of Cavernous Hemangiomatosis involving all Tendon Sheath of Flexors and Median Nerve of the Right Forearm