Ewha Med J.
2022 Oct;45(4):e14. 10.12771/emj.2022.e14.
Comparative Analysis of Health Patterns and Gaps due to Environmental Influences in South Korea and North Korea, 2000–2017
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute for Development and Human Security, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Environmental Medicine, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- 3Graduate School of International Studies, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Public Administration, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of North Korean Studies, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- 7Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- 8Department of Nutrition Science and Food Management, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- 9Graduate Program in System Health Science and Engineering, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- 10Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- 11Department of Sociology, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- 12Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- 13Department of Women’s Studies, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- 14College of Nursing, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- 15Institute of Ewha-SCL for Environmental Health (IESEH), College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2534733
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12771/emj.2022.e14
Abstract
Objectives
To conduct a comparative study of children’s health in South Korea versus North Korea focusing on air pollution.
Methods
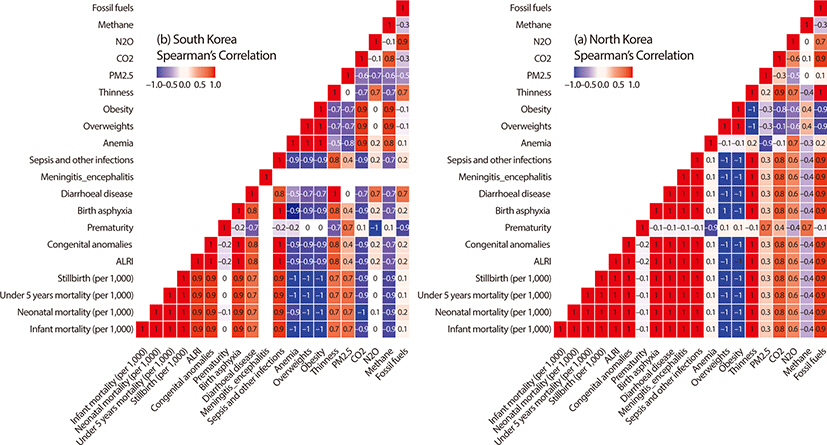
We used annual mortality rate, prevalence, and environmental indicators data from the World Bank and World Health Organizations (WHO). Trend analysis of the two Koreas was conducted to evaluate changes in health status over time. Spearman’s correlation analysis was used to find out the correlation between environmental indicators and children’s health status.
Results
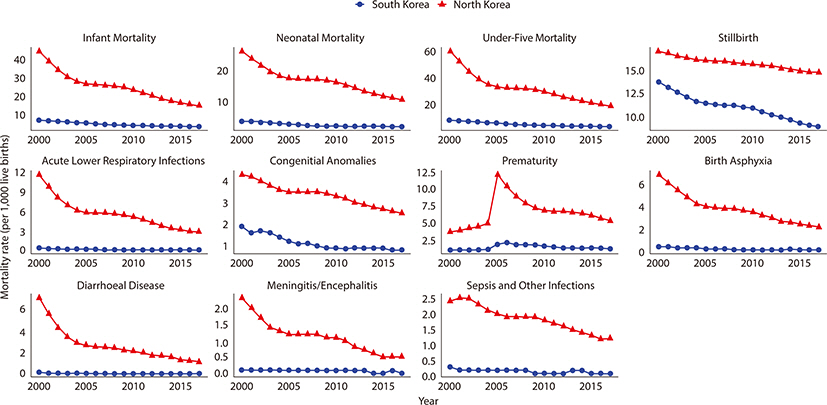
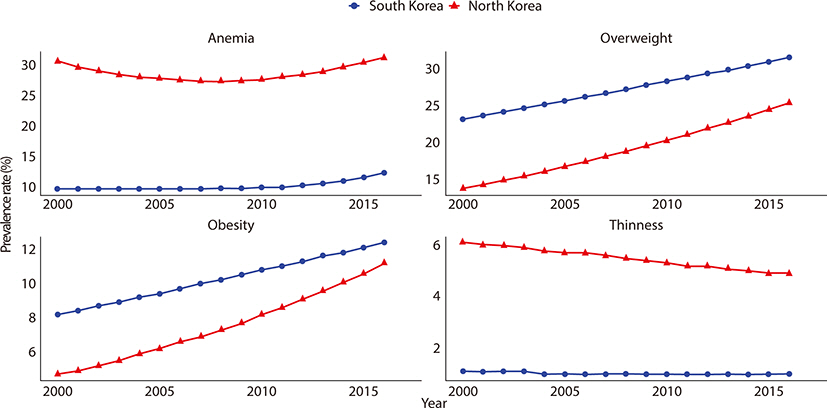
We found a distinct gap in children’s health status between the two Koreas. While North Korea reported a higher death rate of children than South Korea, both showed a decreasing trend with the gap narrowing from 2000 to 2017. The prevalence of overweight and obesity increased and that of thinness decreased in both Koreas. Except PM2.5 exposure, South Korea reported higher figures in most indicators of air pollutant emissions (South Korea, mean (SD)=28.3 (2.0); North Korea, mean (SD)=36.5 (2.8), P-value=0.002).
Conclusion
This study empirically discovered the gaps and patterns of children’s health between South Korea and North Korea. North Korean children experienced more severe health outcomes than children in South Korea. These findings imply that epigenetic modification caused by environmental stressors affect children’s health in the two Koreas despite similar genetic characteristics. Considering the gaps in children’s health between the two Koreas, more attention and resources need to be directed towards North Korea because the necessary commodities and services to improve children’s health are lacking in North Korea.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Sheffield PE, Landrigan PJ. Global climate change and children’s health: threats and strategies for prevention. Environ Health Perspect. 2011; 119(3):291–298. DOI: 10.1289/ehp.1002233. PMID: 20947468. PMCID: PMC3059989.
Article2. Suk WA, Ruchirawat KM, Balakrishnan K, Berger M, Carpenter D, Damstra T, et al. Environmental threats to children’s health in Southeast Asia and the Western Pacific. Environ Health Perspect. 2003; 111(10):1340–1347. DOI: 10.1289/ehp.6059. PMID: 12896856. PMCID: PMC1241616.
Article3. Suk WA, Ahanchian H, Asante KA, Carpenter DO, Diaz-Barriga F, Ha EH, et al. Environmental pollution: an under-recognized threat to children’s health, especially in low and middle-income countries. Environ Health Perspect. 2016; 124(3):A41–A45. DOI: 10.1289/ehp.1510517. PMCID: PMC4786991.4. Cordova JED, Aguirre VT, Apestegui VV, Ibarguen LO, Vu BN, Steenland K, et al. Association of PM2.5 concentration with health center outpatient visits for respiratory diseases of children under 5 years old in Lima, Peru. Environ Health. 2020; 19(1):7. DOI: 10.1186/s12940-020-0564-5. PMID: 31941512. PMCID: PMC6964058.5. Buka I, Koranteng S, Osornio-Vargas AR. The effects of air pollution on the health of children. Paediatr Child Health. 2006; 11(8):513–516.6. Cohen AJ, Brauer M, Burnett R, Anderson HR, Frostad J, Estep K, et al. Estimates and 25-year trends of the global burden of disease attributable to ambient air pollution: an analysis of data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. Lancet. 2017; 389(10082):1907–1918. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30505-6.
Article7. Karimi B, Shokrinezhad B. Air pollution and mortality among infant and children under five years: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Atmos Pollut Res. 2020; 11(6):61–70. DOI: 10.1016/j.apr.2020.02.006.
Article8. Mannucci PM, Harari S, Martinelli I, Franchini M. Effects on health of air pollution: a narrative review. Intern Emerg Med. 2015; 10(6):657–662. DOI: 10.1007/s11739-015-1276-7. PMID: 26134027.
Article9. Smith KR, Samet JM, Romieu I, Bruce N. Indoor air pollution in developing countries and acute lower respiratory infections in children. Thorax. 2000; 55(6):518–532. DOI: 10.1136/thorax.55.6.518. PMID: 10817802. PMCID: PMC1745777.
Article10. Nwude EC, Ugwoke RO, Uruakpa PC, Ugwuegbe US, Nwonye NG. Official development assistance, income per capita and health outcomes in developing countries: is Africa different? Cogent Econ Finance. 2020; 8(1):1774970. DOI: 10.1080/23322039.2020.1774970.11. Ali SH, Oliveira JAP. Pollution and economic development: an empirical research review. Environ Res Lett. 2018; 13(12):123003. DOI: 10.1088/1748-9326/aaeea7.12. Breton CV, Landon R, Kahn LG, Enlow MB, Peterson AK, Bastain T, et al. Exploring the evidence for epigenetic regulation of environmental influences on child health across generations. Commun Biol. 2021; 4(1):769. DOI: 10.1038/s42003-021-02316-6. PMID: 34158610. PMCID: PMC8219763.13. Toraño EG, García MG, Fernández-Morera JL, Niño-García P, Fernández AF. The impact of external factors on the epigenome: in utero and over lifetime. BioMed Res Int. 2016; 2016:2568635. DOI: 10.1155/2016/2568635. PMID: 27294112. PMCID: PMC4887632.14. Vojdani A, Pollard KM, Campbell AW. Environmental triggers and autoimmunity. Autoimmune Dis. 2014; 2014:798029. DOI: 10.1155/2014/798029. PMID: 25610638. PMCID: PMC4290643.
Article15. Campbell JR. The wrong war: the Soviets and the Korean war, 1945–1953. Int Soc Sci Rev. 2014; 88(3):1.16. World Bank. World Bank Open Data - Indicators [Internet]. c2022. cited 2022 Apr 28. Available from. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator.17. World Health Organization. The Global Health Observatory [Internet]. c2022. cited 2022 May 13. Available from. https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/indicators.18. van Donkelaar A, Martin RV, Brauer M, Hsu NC, Kahn RA, Levy RC, et al. Global estimates of fine particulate matter using a combined geophysical-statistical method with information from satellites, models, and monitors. Environ Sci Technol. 2016; 50(7):3762–3772. DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.5b05833. PMID: 26953851.
Article19. GBD 2017 Risk Factor Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018; 392(10159):1923–1994. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32225-6.20. Shaddick G, Thomas ML, Amini H, Broday D, Cohen A, Frostad J, et al. Data integration for the assessment of population exposure to ambient air pollution for Global Burden of Disease assessment. Environ Sci Technol. 2018; 52(16):9069–9078. DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.8b02864. PMID: 29957991.
Article21. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. OECD Data - Korea [Internet]. c2022. cited 2022 Aug 8. Available from. https://data.oecd.org/korea.htm.22. Statistics Korea. North Korea Statistics Portal [Internet]. c2022. cited 2022 Aug 2. Available from. https://kosis.kr/bukhan/index.jsp.23. Kim JA, Kim SM, Lee JS, Oh HJ, Han JH, Song Y, et al. Dietary patterns and the metabolic syndrome in Korean adolescents: 2001 Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30(7):1904–1905. DOI: 10.2337/dc06-2591. PMID: 17416789.24. Ashford G, Dews G, Carter RW, Smith TF. Democratic People’s Republic of Korea environment and climate change outlook [Internet]. Pyongyang: Ministry of Land and Environment Protection;c2012. cited 2022 Aug 10. Available from. https://europa.eu/capacity4dev/unep/documents/democratic-peoples-republic-korea-environment-and-climate-change-outlook.25. Lee SK. North Korean children: nutrition and growth. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2017; 22(4):231–239. DOI: 10.6065/apem.2017.22.4.231. PMID: 29301183. PMCID: PMC5769832.
Article26. Guo C, Hoek G, Chang L, Bo Y, Lin C, Huang B, et al. Long-term exposure to ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and lung function in children, adolescents, and young adults: a longitudinal cohort study. Environ Health Perspect. 2019; 127(12):127008. DOI: 10.1289/EHP5220. PMID: 31873044. PMCID: PMC6957275.27. Dapul H, Laraque D. Lead poisoning in children. Adv Pediatr. 2014; 61(1):313–333. DOI: 10.1016/j.yapd.2014.04.004. PMID: 25037135.
Article28. Knollmann-Ritschel BEC, Markowitz M. Educational case: lead poisoning. Acad Pathol. 2017; 4:2374289517700160. DOI: 10.1177/2374289517700160. PMID: 28815198. PMCID: PMC5528905.
Article29. Bach JF. The hygiene hypothesis in autoimmunity: the role of pathogens and commensals. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018; 18(2):105–120. DOI: 10.1038/nri.2017.111. PMID: 29034905.
Article30. Okada H, Kuhn C, Feillet H, Bach JF. The ‘hygiene hypothesis’ for autoimmune and allergic diseases: an update. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010; 160(1):1–9. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04139.x. PMID: 20415844. PMCID: PMC2841828.31. Bach JF. The effect of infections on susceptibility to autoimmune and allergic diseases. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347(12):911–920. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra020100. PMID: 12239261.
Article32. Bloomfield SF, Stanwell-Smith R, Crevel RWR, Pickup J. Too clean, or not too clean: the hygiene hypothesis and home hygiene. Clin Exp Allergy. 2006; 36(4):402–425. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2006.02463.x. PMID: 16630145. PMCID: PMC1448690.
Article33. Kim JS. Children of peace. Seoul: Bookludens;2018.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Changes in health status of North Korean children and emerging health challenges of North Korean refugee children
- Comparison of the nutritional status of infants and young children in South Korea and North Korea
- Issues and problems of adaptation of North Korean defectors to South Korean society: an in-depth interview study with 32 defectors
- A small window into the status of malaria in North Korea: estimation of imported malaria incidence among visitors from South Korea
- A Seven-Year Panel Study on North Korean Defectors Perception and Satisfaction on Life in South Korea