Obstet Gynecol Sci.
2022 Sep;65(5):420-429. 10.5468/ogs.22106.
Ritodrine in external cephalic version: is it effective and safe?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 2Korean Mothersafe Counselling Center, Pregnancy & Breastfeeding Medicines Information Center, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Inje University, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- KMID: 2533815
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5468/ogs.22106
Abstract
Objective
The external cephalic version (ECV) has been shown to lower the likelihood of cesarean section requirements among pregnant women with breech presentations. In the current study, we investigated the effectiveness and safety of ritodrine as a tocolytic for ECV.
Methods
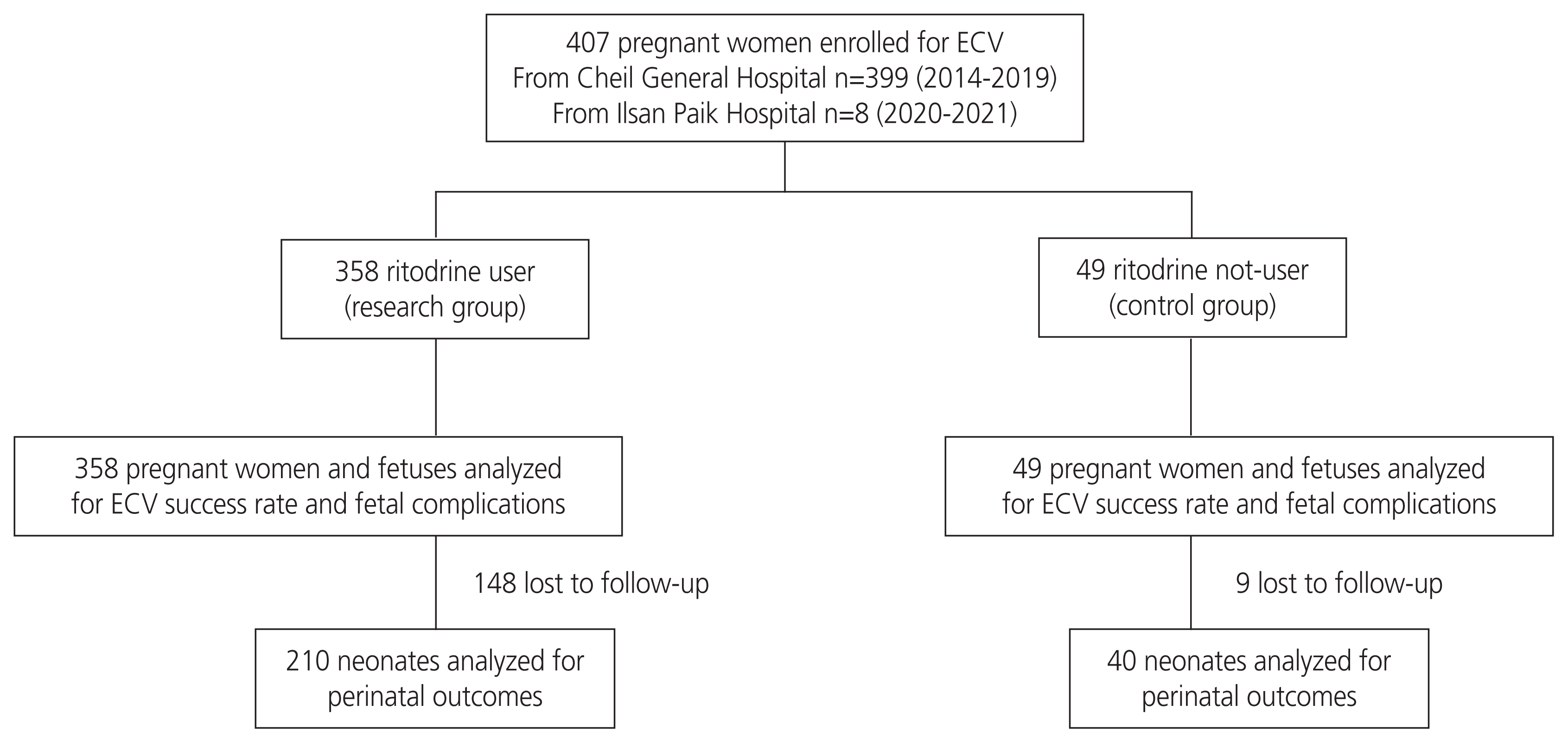
A total of 407 pregnant women with breech presentations, who had no contraindications for ECV, were enrolled in this study. Multivariable logistic regression analyses were used to assess the impact of ritodrine use on the safety and efficacy of ECV.
Results
The overall success rate was 67.6%, and ritodrine use was associated with significantly higher odds of successful ECV after adjusting for confounders. Moreover, using ritodrine did not increase the risk of adverse effects, including temporary changes in fetal heart rate, need for elective or emergency cesarean section due to fetal distress during ECV, low Apgar scores, and perinatal mortality.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that using ritodrine as a tocolytic during ECV may increase the likelihood of ECV success and may not increase adverse perinatal outcomes.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kim AM, Park JH, Kang S, Yoon TH, Kim Y. An ecological study of geographic variation and factors associated with cesarean section rates in South Korea. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019; 19162.
Article2. World Health Organization (WHO). WHO statement on caesarean section rates. Geneva: WHO;2015.3. Betrán AP, Ye J, Moller AB, Zhang J, Gülmezoglu AM, Torloni MR. The increasing trend in caesarean section rates: global, regional and national estimates: 1990–2014. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0148343.
Article4. Mylonas I, Friese K. Indications for and risks of elective cesarean section. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2015; 112:489–95.
Article5. Kim GJ. Reviving external cephalic version: a review of its efficacy, safety, and technical aspects. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2019; 62:371–81.
Article6. Collins S, Ellaway P, Harrington D, Pandit M, Impey LW. The complications of external cephalic version: results from 805 consecutive attempts. BJOG. 2007; 114:636–8.
Article7. Marquette GP, Boucher M, Thériault D, Rinfret D. Does the use of a tocolytic agent affect the success rate of external cephalic version? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1996; 175:859–61.
Article8. Nor Azlin MI, Haliza H, Mahdy ZA, Anson I, Fahya MN, Jamil MA. Tocolysis in term breech external cephalic version. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2005; 88:5–8.
Article9. Levin G, Cahan T, Weill Y, Axelrod M, Pollack RN, Meyer R. Ritodrine versus salbutamol for external cephalic version. Minerva Obstet Gynecol. 2022; 74:337–42.
Article10. Couceiro Naveira E, López Ramón y Cajal C. Atosiban versus ritodrine as tocolytics in external cephalic version. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022; 35:80–5.
Article11. Levin G, Ezra Y, Weill Y, Kabiri D, Pollack RN, Rottenstreich A. Nifedipine versus ritodrine during external cephalic version procedure: a case control study. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021; 34:3008–13.
Article12. Bujold E, Marquette GP, Ferreira E, Gauthier RJ, Boucher M. Sublingual nitroglycerin versus intravenous ritodrine as tocolytic for external cephalic version: a double-blinded randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003; 188:1454–7.
Article13. Lee JY, Kim Y, Sohn IS, Han YJ, Chung JH, Kim MY, et al. Height of elevated fetal buttock for prediction of successful external cephalic version. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2020; 63:1–13.
Article14. Kim MY, Park MY, Kim GJ. External cephalic version experiences in Korea. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2016; 59:85–90.
Article15. Cluver C, Gyte GM, Sinclair M, Dowswell T, Hofmeyr GJ. Interventions for helping to turn term breech babies to head first presentation when using external cephalic version. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015; (2):CD000184.
Article16. Haram K, Mortensen JH, Morrison JC. Tocolysis for acute preterm labor: does anything work. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015; 28:371–8.
Article17. Cunningham FG, Leveno KJ, Bloom SL, Spong CY, Dashe JS. Williams obstetrics. 24th ed. New York (NY): Mcgraw-hill;2014.18. Impey L, Pandit M. Tocolysis for repeat external cephalic version in breech presentation at term: a randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. BJOG. 2005; 112:627–31.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- External Cephalic Version Attempted under Epidural Anesthesia : Case reports
- Reviving external cephalic version: a review of its efficacy, safety, and technical aspects
- External cephalic version experiences in Korea
- Comparative trial of combination therapy of indomethacin and ritodrine versus single therapy of ritodrine for the premature labor
- The effect of intravenous ritodrine hydrochloride on premature labor