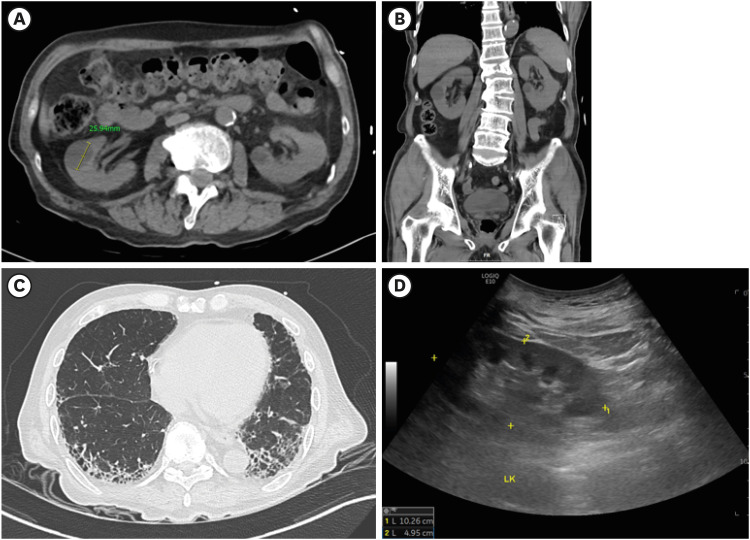
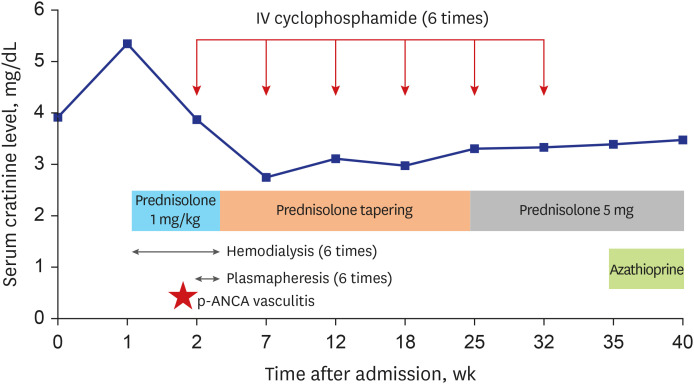
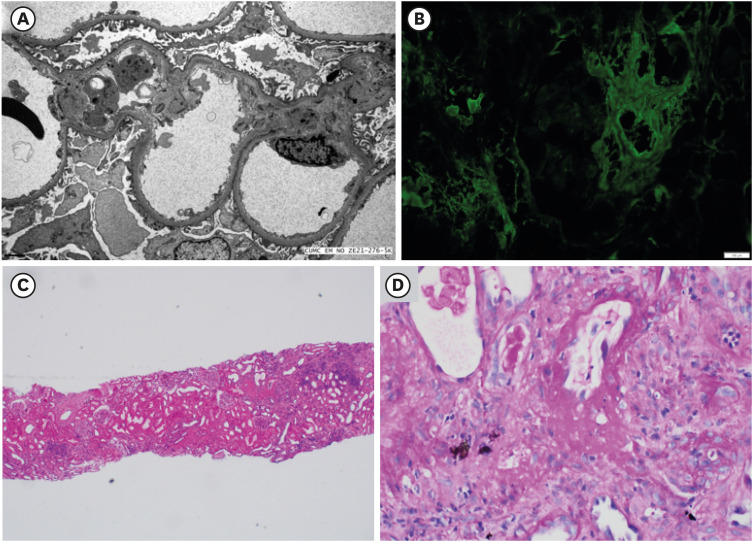
J Korean Med Sci.
2022 Oct;37(38):e298. 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e298.
Case 3: A 81-Year-Old Man Presented With Abnormal Serum Creatinine Levels
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Eunpyeong St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 2Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yeouido St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2533566
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e298
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zappitelli M. Epidemiology and diagnosis of acute kidney injury. Semin Nephrol. 2008; 28(5):436–446. PMID: 18790363.
Article2. Geetha D, Jefferson JA. ANCA-associated vasculitis: core curriculum 2020. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020; 75(1):124–137. PMID: 31358311.
Article3. Salvador F. ANCA associated vasculitis. Eur J Intern Med. 2020; 74:18–28. PMID: 32005600.
Article4. Rovin BH, Adler SG, Barratt J, Bridoux F, Burdge KA, Chan TM, et al. KDIGO 2021 clinical practice guideline for the management of glomerular diseases. Kidney Int. 2021; 100(4S):S1–S276. PMID: 34556256.5. Jones RB, Tervaert JW, Hauser T, Luqmani R, Morgan MD, Peh CA, et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363(3):211–220. PMID: 20647198.
Article6. Stone JH, Merkel PA, Spiera R, Seo P, Langford CA, Hoffman GS, et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for ANCA-associated vasculitis. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363(3):221–232. PMID: 20647199.
Article7. Jones RB, Hiemstra TF, Ballarin J, Blockmans DE, Brogan P, Bruchfeld A, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide for remission induction in ANCA-associated vasculitis: a randomised, non-inferiority trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019; 78(3):399–405. PMID: 30612116.
Article8. Jayne DR, Gaskin G, Rasmussen N, Abramowicz D, Ferrario F, Guillevin L, et al. Randomized trial of plasma exchange or high-dosage methylprednisolone as adjunctive therapy for severe renal vasculitis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007; 18(7):2180–2188. PMID: 17582159.
Article9. Walsh M, Merkel PA, Peh CA, Szpirt W, Guillevin L, Pusey CD, et al. Plasma exchange and glucocorticoid dosing in the treatment of anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody associated vasculitis (PEXIVAS): protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2013; 14(1):73. PMID: 23497590.
Article10. Guillevin L, Pagnoux C, Karras A, Khouatra C, Aumaître O, Cohen P, et al. Rituximab versus azathioprine for maintenance in ANCA-associated vasculitis. N Engl J Med. 2014; 371(19):1771–1780. PMID: 25372085.11. Karras A, Pagnoux C, Haubitz M, Groot K, Puechal X, Tervaert JW, et al. Randomised controlled trial of prolonged treatment in the remission phase of ANCA-associated vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017; 76(10):1662–1668. PMID: 28546260.12. Charles P, Terrier B, Perrodeau É, Cohen P, Faguer S, Huart A, et al. Comparison of individually tailored versus fixed-schedule rituximab regimen to maintain ANCA-associated vasculitis remission: results of a multicentre, randomised controlled, phase III trial (MAINRITSAN2). Ann Rheum Dis. 2018; 77(8):1143–1149. PMID: 29695500.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study on Serum Creatinine and BUN Levels in Newborn Infants
- Prognostic significance of serum creatinine and sarcopenia for 5-year overall survival in patients with colorectal cancer in Korea: a comparative study
- Postnatal Changes of Serum Creatinine Levels in Neonates
- Change in Plasma Homocysteine Concentration during the Recovery Phase of Renal Transplantation
- Two Cases of Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonphritis treated with ?ulse Methylprednisolone Therapy