Clin Endosc.
2022 Sep;55(5):683-687. 10.5946/ce.2021.144.
Less invasive transoral resection of esophageal fibrovascular polyps: case reports
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Thoracic and Surgical Oncology, Jagiellonian University Collegium Medicum, John Paul II Hospital, Cracow, Poland
- KMID: 2533308
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2021.144
Abstract
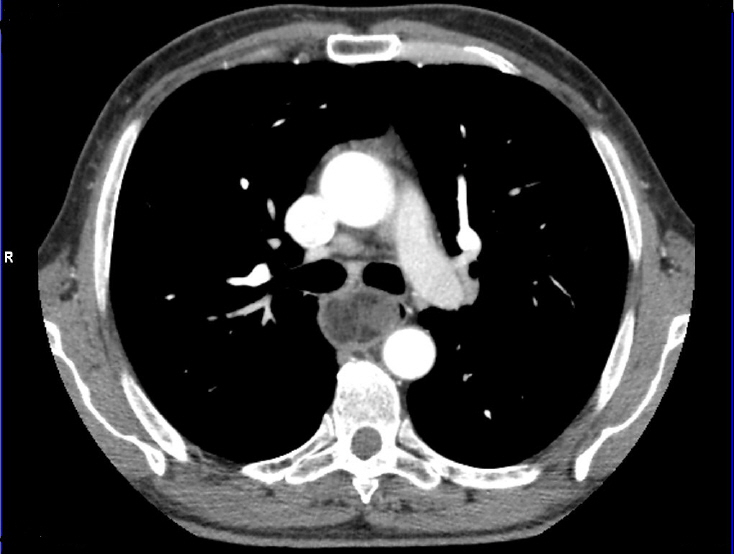
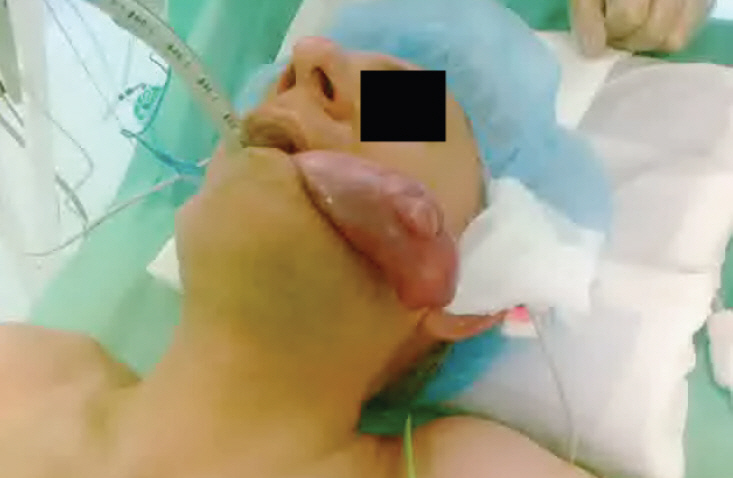
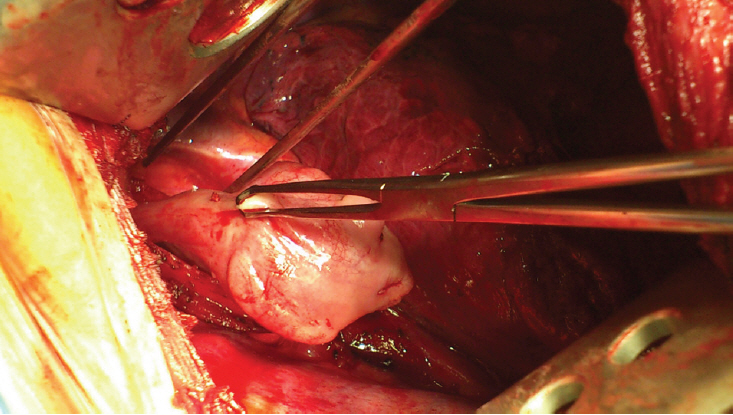
- We report five patients treated for esophageal fibrovascular polyps using a minimally invasive technique. Esophageal fibrovascular polyps are benign pedunculated submucosal tumors of considerable size. The treated polyps size ranged from 1.5 to 13 cm. The polyps were removed by relocation to the oral cavity under endoscopic control. No perioperative complications occurred after the treatment. The follow-up of patients after surgery was 9–89 months, with no evidence of polyp recurrence. Thus, the described treatment is safe but requires experience with endoscopy as well as esophageal surgery.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jose P, Scott N, Sarela AI. Two-stage removal of giant fibrovascular polyp of the oesophagus. BMJ Case Rep. 2010; 2010:bcr0520103011.2. Alobid I, Vilaseca I, Fernández J, et al. Giant fibrovascular polyp of the esophagus causing sudden dyspnea: endoscopic treatment. Laryngoscope. 2007; 117:944–945.3. Watanabe H, Jass JR, Sobin LH. Histological typing of oesophageal and gastric tumours: in collaboration with pathologists in 8 countries. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer;1990. p. 122.4. Graham RP, Yasir S, Fritchie KJ, et al. Polypoid fibroadipose tumors of the esophagus: “giant fibrovascular polyp” or liposarcoma? A clinicopathological and molecular cytogenetic study of 13 cases. Mod Pathol. 2018; 31:337–342.5. I H, Kim JS, Shim YM. Giant fibrovascular polyp of the hypopharynx: surgical treatment with the biappoach. J Korean Med Sci. 2006; 21:749–751.6. Pham AM, Rees CJ, Belafsky PC. Endoscopic removal of a giant fibrovascular polyp of the esophagus. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2008; 117:587–590.7. Ward MA, Beard KW, Teitelbaum EN, et al. Endoscopic resection of giant fibrovascular esophageal polyps. Surg Endosc. 2018; 32:1066–1067.8. Li J, Yu H, Pu R, et al. Gastroscopic removal of a giant fibrovascular polyp from the esophagus. Thorac Cancer. 2016; 7:363–366.9. Cockbain AJ, England R, Dexter SPL, et al. Surveillance is important after surgical excision of giant fibrovascular polyps of the esophagus. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017; 104:e341–e343.10. Quijano Y, Ferri V, Duran H, et al. Recurrent giant fibrovascualr oesophageal polyp: benefits and pitfalls of a multimodal approach. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021; 83:105935.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Giant Fibrovascular Polyp of the Esophagus, Treated Successfully by Endoscopic Resection
- A Case of Giant Fibrovascular Polyp of the Hypopharynx Removed by Transoral Approach
- Fibrovascular polyp of the esophagus in infant
- A Case of Large Fibrovascular Polyp of the Stomach
- A Case of Fibrovascular Polyp in the Esophagus