Ewha Med J.
2022 Jul;45(3):e3. 10.12771/emj.2022.e3.
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Youth
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children’s Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- KMID: 2532209
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12771/emj.2022.e3
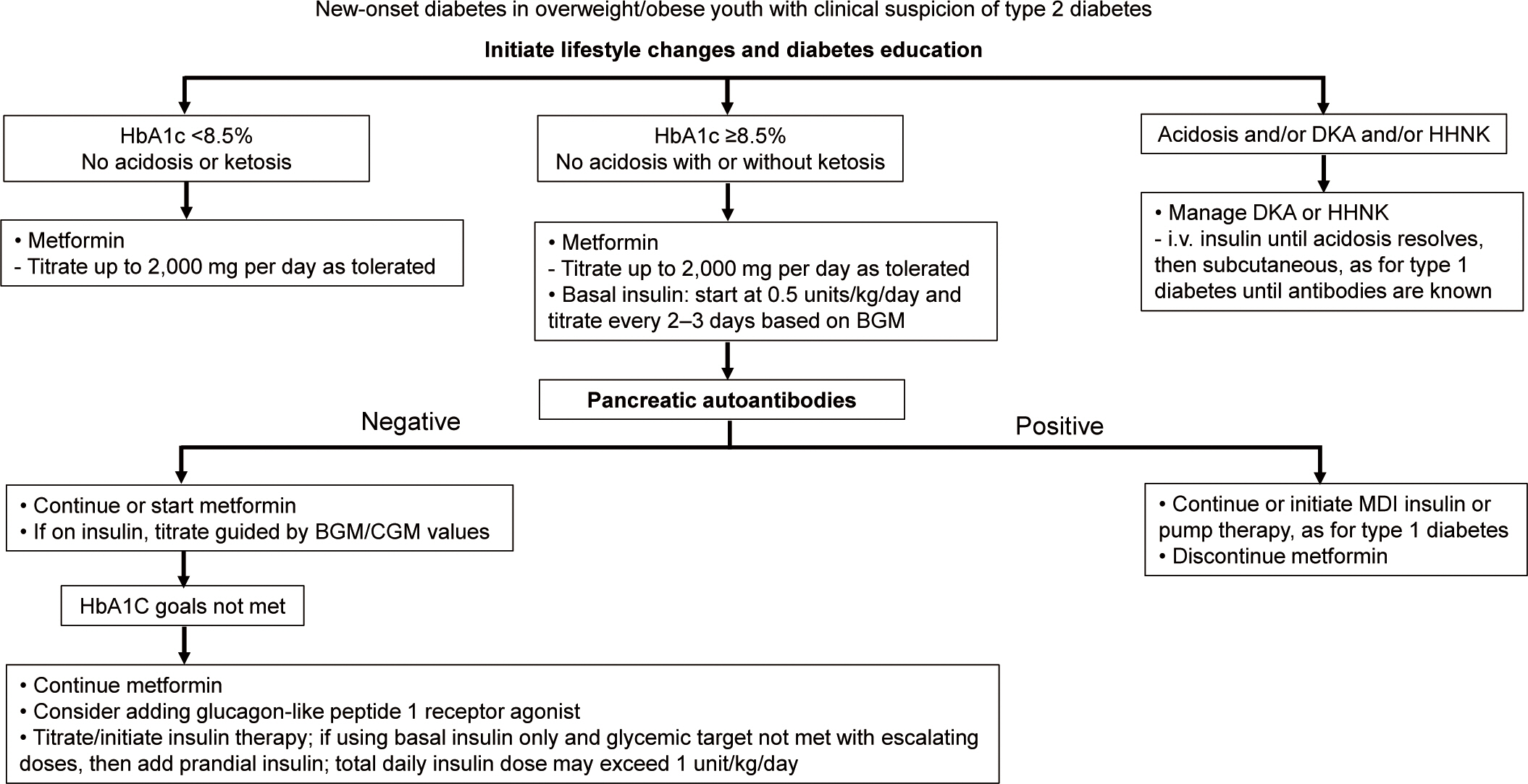
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Khan MAB, Hashim MJ, King JK, Govender RD, Mustafa H, Al Kaabi J.. Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes: global burden of disease and forecasted trends. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2020; 10:107–111. DOI: 10.2991/jegh.k.191028.001. PMID: 32175717. PMCID: PMC7310804.
Article2. Castorani V, Polidori N, Giannini C, Blasetti A, Chiarelli F. Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes in children. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020; 25:217–226. DOI: 10.6065/apem.2040090.045. PMID: 33401880. PMCID: PMC7788344.
Article3. Seo MY, Kim SH, Park MJ. Changes in anthropometric indices among Korean school students based on the 2010 and 2018 Korea School Health Examination Surveys. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2021; 26:38–45. DOI: 10.6065/apem.2040100.050. PMID: 33819957. PMCID: PMC8026332.
Article4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC]. Rates of new diagnosed cases of type 1 and type 2 diabetes continue to rise among children, teens [Internet]. Atlanta (GA): Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;c2020. [cited 2022 May 25]. Available from. https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/rates-new-diagnosed-cases-type-1-type-2-diabetes-rise-among-children-teens.5. Kim JH, Lim JS. Trends of diabetes and prediabetes prevalence among Korean adolescents from 2007 to 2018. J Korean Med Sci. 2021; 36:e112. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e112. PMID: 33942577. PMCID: PMC8093603.
Article6. Hong YH, Chung IH, Han K, Chung S. Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus among Korean children, adolescents, and adults younger than 30 years: changes from 2002 to 2016. Diabetes Metab J. 2022; 46:297–306. DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0038. PMID: 34695908. PMCID: PMC8987690.
Article7. Yoo SE, Lee JH, Lee JW, Park HS, Lee HA, Kim HS. Increasing prevalence of fasting hyperglycemia in adolescents aged 10–18 years and its relationship with metabolic indicators: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Study (KNHANES), 2007–2018. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2022; 27:60–68. DOI: 10.6065/apem.2142068.034. PMID: 33971707. PMCID: PMC8984745.
Article8. Zeitler P, Hirst K, Pyle L, Linder B, Copeland K, Arslanian S, et al. A clinical trial to maintain glycemic control in youth with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:2247–2256. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1109333. PMID: 22540912. PMCID: PMC3478667.
Article9. Bacha F, Gungor N, Lee S, Arslanian SA. Progressive deterioration of β-cell function in obese youth with type 2 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2013; 14:106–111. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2012.00915.x. PMID: 22913617. PMCID: PMC3648791.
Article10. Nadeau KJ, Anderson BJ, Berg EG, Chiang JL, Chou H, Copeland KC, et al. Youth-onset type 2 diabetes consensus report: current status, challenges, and priorities. Diabetes Care. 2016; 39:1635–1642. DOI: 10.2337/dc16-1066. PMID: 27486237. PMCID: PMC5314694.
Article11. Constantino MI, Molyneaux L, Limacher-Gisler F, Al-Saeed A, Luo C, Wu T, et al. Long-term complications and mortality in young-onset diabetes: type 2 diabetes is more hazardous and lethal than type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:3863–3869. DOI: 10.2337/dc12-2455. PMID: 23846814. PMCID: PMC3836093.12. Dabelea D, Stafford JM, Mayer-Davis EJ, D’Agostino R Jr, Dolan L, Imperatore G, et al. Association of type 1 diabetes vs type 2 diabetes diagnosed during childhood and adolescence with complications during teenage years and young adulthood. J Am Med Assoc. 2017; 317:825–835. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2017.0686. PMID: 28245334. PMCID: PMC5483855.
Article13. Zeitler P, Arslanian S, Fu J, Pinhas-Hamiel O, Reinehr T, Tandon N, et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2018: Type 2 diabetes mellitus in youth. Pediatr Diabetes. 2018; 19:Suppl 27. 28–46. DOI: 10.1111/pedi.12719. PMID: 29999228.
Article14. Libman IM, Arslanian SA. Prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes in youth. Horm Res. 2007; 67:22–34. DOI: 10.1159/000095981. PMID: 17008794.
Article15. Kralisch S, Sommer G, Deckert CM, Linke A, Bluher M, Stumvoll M, et al. Adipokines in diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Minerva Endocrinol. 2007; 32:161–171.16. Kim J, Lee J. Role of obesity-induced inflammation in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: history of the research and remaining questions. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2021; 26:1–13. DOI: 10.6065/apem.2040188.094. PMID: 33819954. PMCID: PMC8026341.
Article17. Todd JN, Srinivasan S, Pollin TI. Advances in the genetics of youth-onset type 2 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2018; 18:57. DOI: 10.1007/s11892-018-1025-1. PMID: 29931398. PMCID: PMC6051541.
Article18. Valaiyapathi B, Gower B, Ashraf AP. Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2020; 16:220–229. DOI: 10.2174/1573399814666180608074510. PMID: 29879890. PMCID: PMC7516333.
Article19. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 14. Children and adolescents: standards of medical care in diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care. 2022; 45:S208–S231. DOI: 10.2337/dc22-S014. PMID: 34964865.20. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care. 2022; 45:Suppl 1. S17–S38. DOI: 10.2337/dc22-S002. PMID: 34964875.21. Mayer-Davis EJ, Kahkoska AR, Jefferies C, Dabelea D, Balde N, Gong CX, et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2018: Definition, epidemiology, and classification of diabetes in children and adolescents. Pediatr Diabetes. 2018; 19:Suppl 27. 7–19. DOI: 10.1111/pedi.12773. PMID: 30226024. PMCID: PMC7521365.
Article22. Kim KY, Kim MS, Lee YJ, Lee YA, Lee SY, Shin CH, et al. Glutamic acid decarboxylase and tyrosine phosphatase-related islet antigen-2 positivity among children and adolescents with diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2022; DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0332. PMID: 35263538.
Article23. Lee YJ, Yoo S, Yi S, Kim S, Lee C, Cho J, et al. Trajectories in glycated hemoglobin and body mass index in children and adolescents with diabetes using the common data model. Sci Rep. 2021; 11:14614. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-94194-5. PMID: 34272437. PMCID: PMC8285411.
Article24. Bjornstad P, Drews KL, Caprio S, Gubitosi-Klug R, Nathan DM, Tesfaldet B, et al. Long-term complications in youth-onset type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2021; 385:416–426. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2100165. PMID: 34320286. PMCID: PMC8697255.
Article25. Rodriguez BL, Fujimoto WY, Mayer-Davis EJ, Imperatore G, Williams DE, Bell RA, et al. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease risk factors in U.S. children and adolescents with diabetes: the SEARCH for diabetes in youth study. Diabetes Care. 2006; 29:1891–1896. DOI: 10.2337/dc06-0310. PMID: 16873798.
Article26. Eppens MC, Craig ME, Cusumano J, Hing S, Chan AKF, Howard NJ, et al. Prevalence of diabetes complications in adolescents with type 2 compared with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006; 29:1300–1306. DOI: 10.2337/dc05-2470. PMID: 16732012.
Article27. Copeland KC, Zeitler P, Geffner M, Guandalini C, Higgins J, Hirst K, et al. Characteristics of adolescents and youth with recent-onset type 2 diabetes: the TODAY cohort at baseline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 96:159–167. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2010-1642. PMID: 20962021. PMCID: PMC3038479.
Article28. Copeland KC, Silverstein J, Moore KR, Prazar GE, Raymer T, Shiffman RN, et al. Management of newly diagnosed type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2013; 131:364–382. DOI: 10.1542/peds.2012-3494. PMID: 23359574.
Article29. Wright JA, Adams WG, Laforge RG, Berry D, Friedman RH. Assessing parental self-efficacy for obesity prevention related behaviors. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2014; 11:53. DOI: 10.1186/1479-5868-11-53. PMID: 24750693. PMCID: PMC4004451.
Article30. Smart CE, Annan F, Higgins LA, Jelleryd E, Lopez M, Acerini CL. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2018: Nutritional management in children and adolescents with diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2018; 19:Suppl 27. 136–154. DOI: 10.1111/pedi.12738. PMID: 30062718.
Article31. Kim JY, Jeon JY. Role of exercise on insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function: is exercise sufficient for the prevention of youth-onset type 2 diabetes? Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020; 25:208–216. DOI: 10.6065/apem.2040140.070. PMID: 33401879. PMCID: PMC7788350.
Article32. Kelsey MM, Geffner ME, Guandalini C, Pyle L, Tamborlane WV, Zeitler PS, et al. Presentation and effectiveness of early treatment of type 2 diabetes in youth: lessons from the TODAY study. Pediatr Diabetes. 2016; 17:212–221. DOI: 10.1111/pedi.12264. PMID: 25690268. PMCID: PMC4539288.
Article33. Chadda KR, Cheng TS, Ong KK. GLP-1 agonists for obesity and type 2 diabetes in children: systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2021; 22:e13177. DOI: 10.1111/obr.13177. PMID: 33354917.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Update on the current modalities used to screen high risk youth for prediabetes and/or type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Intervention Strategies for Older Adults with Diabetes
- Treatment Strategies for Diabetic Neuropathy
- Effect of Diabetes on Dementia and Its Preventive Strategies
- Pancreas transplant in type 1 diabetes mellitus: the emerging role of islet cell transplant