J Rhinol.
2022 Jul;29(2):88-95. 10.18787/jr.2021.00399.
Analysis of Lateral Decubitus Position During Sleep in Patients With Obstructive Sleep Apnea Using WatchPAT Device
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2532010
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2021.00399
Abstract
- Background and Objectives
Measurement of sleep parameters in both supine and non-supine positions is important for the diagnosis of positional obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). However, the influence of right and left lateral decubitus positions (RLDP and LLDP, respectively) on sleep parameters is relatively unknown and has not been well investigated. This study was performed to verify the associations between sleep parameters and lateral decubitus sleep position.
Methods
A retrospective study was performed on 38 patients who were diagnosed with OSA and underwent surgical interventions from January 2014 to December 2016. Preoperative sleep parameters were evaluated with WatchPAT, and patients who slept sufficiently in both RLDP and LLDP to accurately analyze sleep parameters were enrolled in the study. Basic clinical data including body mass index (BMI) and nasal endoscopic findings of patients were assessed.
Results
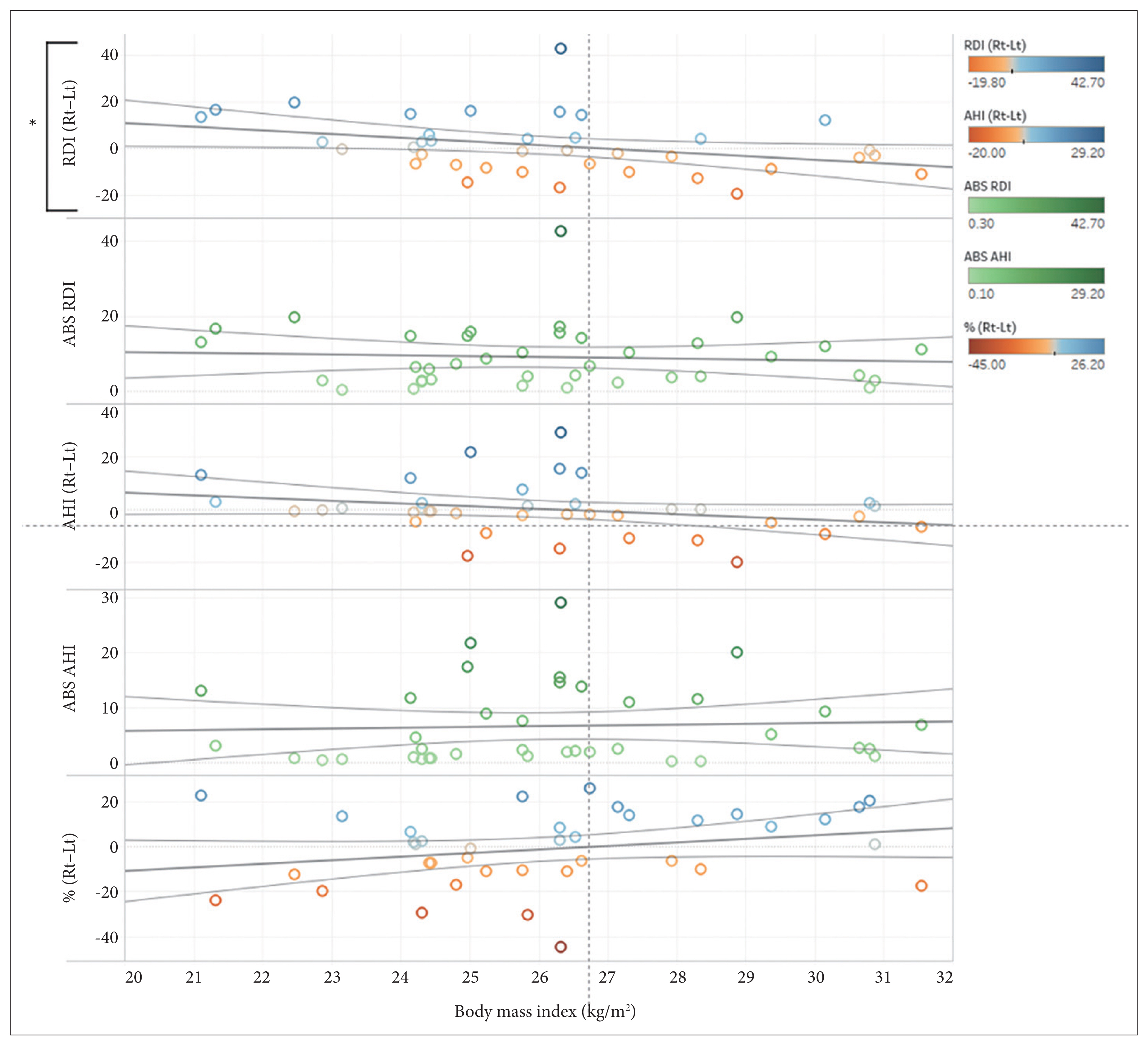
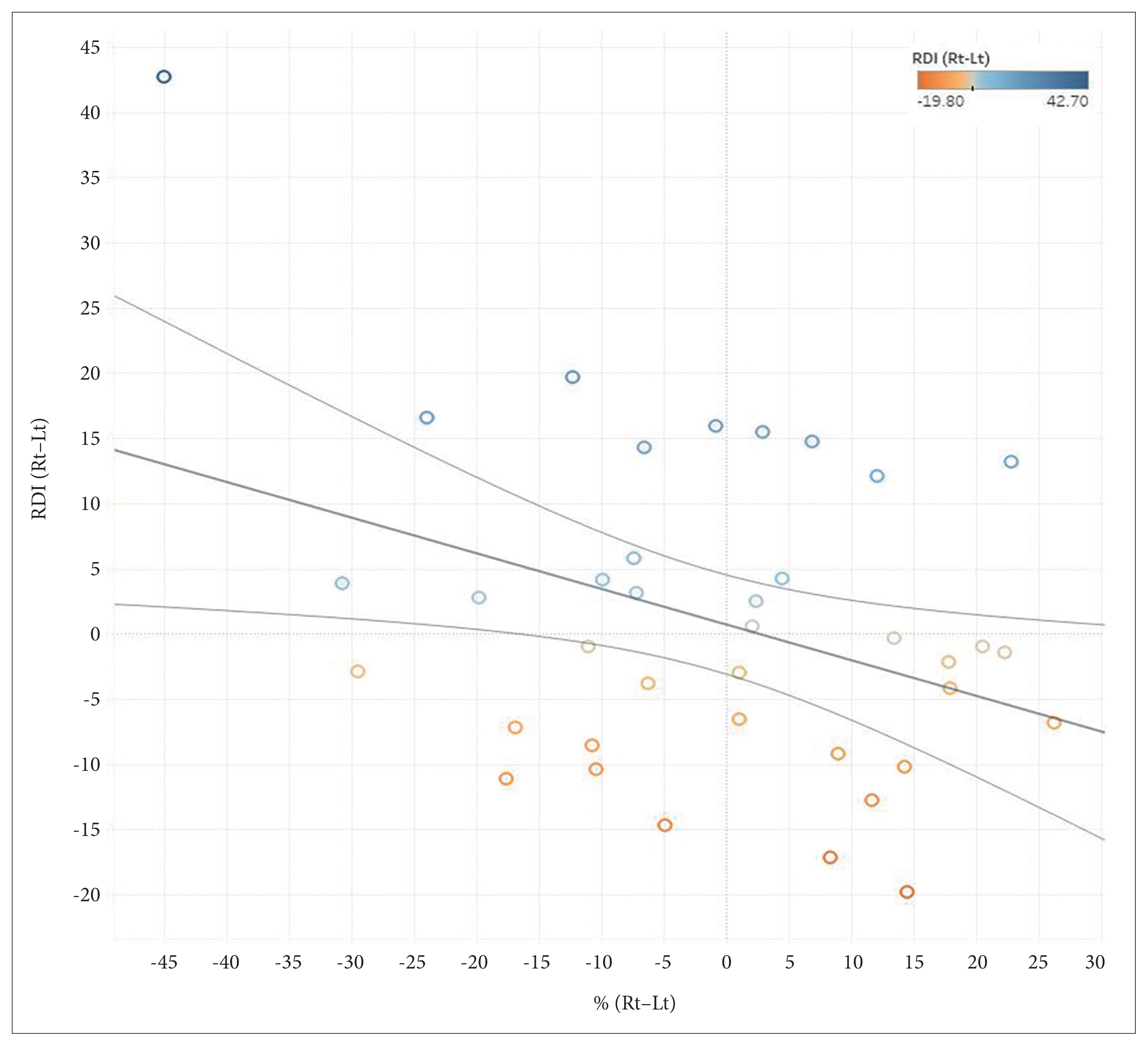
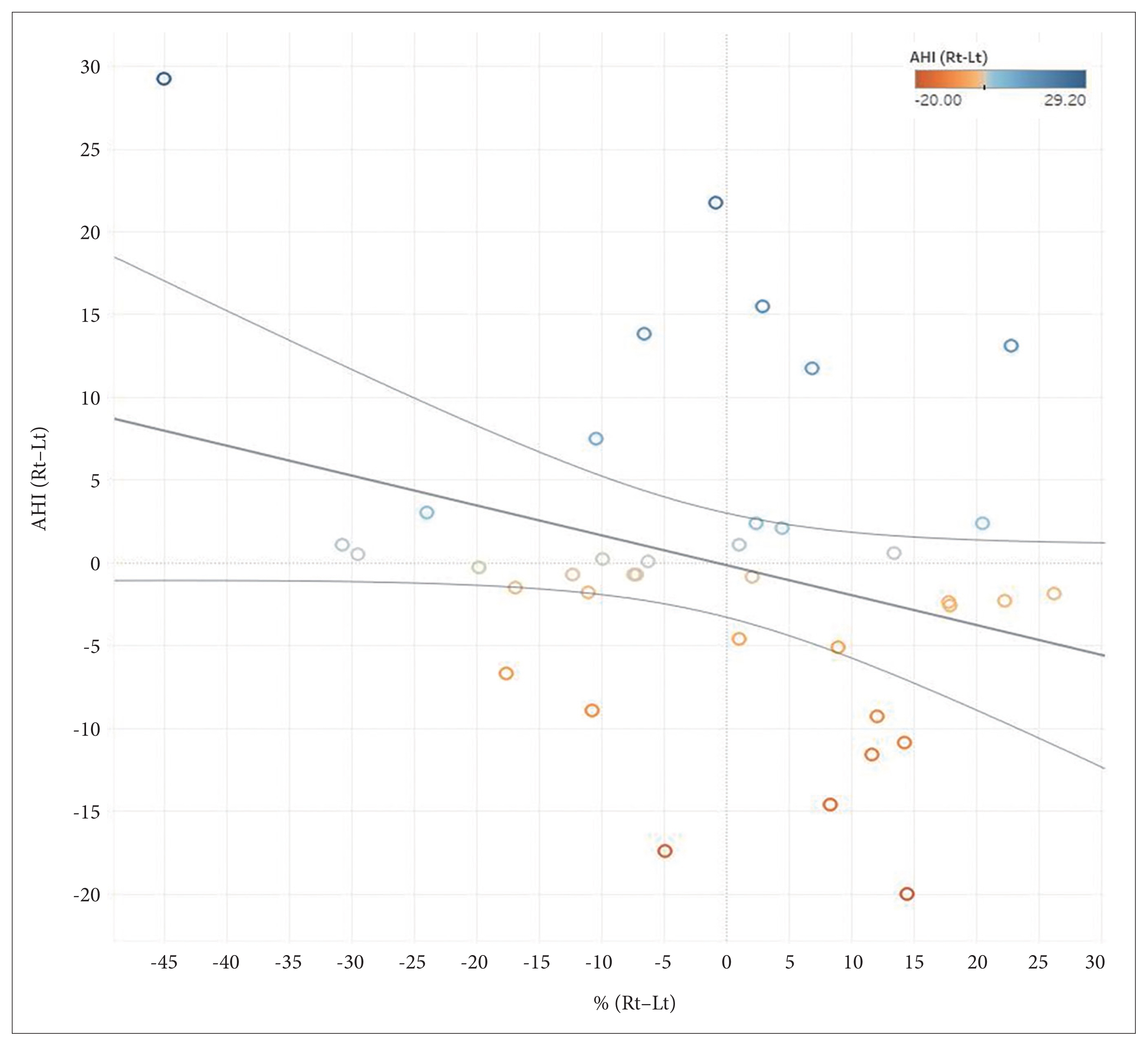
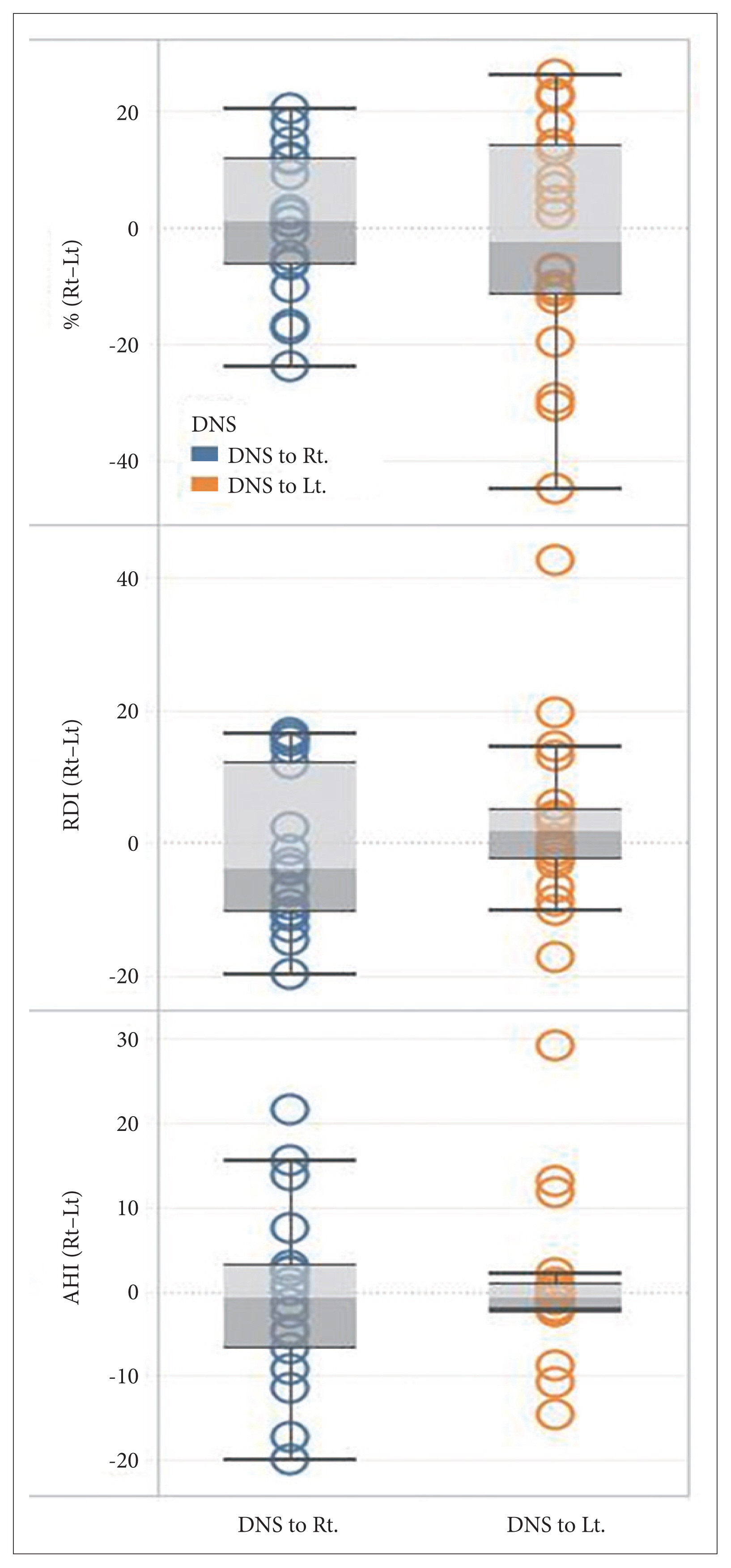
The difference in peripheral arterial tonometry apnea-hypopnea index (pAHI) and PAT respiratory disturbance index (pRDI) between RLDP and LLDP showed no association with the side of deviated nasal septum. Patients with higher BMI showed higher pRDI in LLDP than RLDP (p=0.038). The difference in sleep position percentage between RLDP and LLDP was negatively correlated with the difference in pRDI (p=0.023).
Conclusion
Higher BMI patients with OSA might benefit more from sleeping in RLDP than LLDP. Patients slept longer in the lateral decubitus position that produced lower pRDI. Not only supine and non-supine positions, but also RLDP and LLDP need to be evaluated in patients with OSA.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bidarian-Moniri A, Nilsson M, Rasmusson L, Attia J, Ejnell H. The effect of the prone sleeping position on obstructive sleep apnoea. Acta Otolaryngol. 2014; 135(1):79–84.2. Chou YT, Yang TM, Lin CK, Huang SY, Tsai YH, Chang JF, et al. Pay attention to treating a subgroup of positional obstructive sleep apnea patients. J Formos Med Assoc. 2017; 116(5):359–65.3. Frank MH, Ravesloot MJ, van Maanen JP, Verhagen E, de Lange J, de Vries N. Positional OSA part 1: towards a clinical classification system for position-dependent obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Breath. 2014; 19(2):473–80.4. Joosten SA, Sands SA, Edwards BA, Hamza K, Turton A, Lau KK, et al. Evaluation of the role of lung volume and airway size and shape in supine-predominant obstructive sleep apnoea patients. Respirology. 2015; 20(5):819–27.5. Oksenberg A, Khamaysi I, Silverberg DS, Tarasiuk A. Association of body position with severity of apneic events in patients with severe nonpositional obstructive sleep apnea. Chest. 2000; 118(4):1018–24.6. Ozeke O, Erturk O, Gungor M, Hızel SB, Aydın D, Celenk MK, et al. Influence of the right- versus left-sided sleeping position on the apnea-hypopnea index in patients with sleep apnea. Sleep Breath. 2011; 16(3):617–20.7. Ravesloot MJ, van Maanen JP, Dun L, de Vries N. The undervalued potential of positional therapy in position-dependent snoring and obstructive sleep apnea-a review of the literature. Sleep Breath. 2012; 17(1):39–49.8. Safiruddin F, Koutsourelakis I, de Vries N. Upper airway collapse during drug induced sleep endoscopy: head rotation in supine position compared with lateral head and trunk position. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014; 272(2):485–8.9. Tanaka F, Nakano H, Sudo N, Kubo C. Relationship between the body position-specific apnea-hypopnea index and subjective sleepiness. Respiration. 2009; 78(2):185–90.10. Victores AJ, Hamblin J, Gilbert J, Switzer C, Takashima M. Usefulness of sleep endoscopy in predicting positional obstructive sleep apnea. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014; 150(3):487–93.11. Cartwright RD. Effect of sleep position on sleep apnea severity. Sleep. 1984; 7(2):110–4.12. American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force. Sleep–related breathing disorders in adults: recommendations for syndrome definition and measurement techniques in clinical research. Sleep. 1999; 22(5):667–89.13. Onder NS, Akpinar ME, Yigit O, Gor AP. Watch peripheral arterial tonometry in the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea: influence of aging. Laryngoscope. 2012; 122(6):1409–14.14. Yalamanchali S, Farajian V, Hamilton C, Pott TR, Samuelson CG, Friedman M. Diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea by peripheral arterial tonometry: meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013; 139(12):1343–50.15. Guyuron B, Uzzo CD, Scull H. A practical classification of septonasal deviation and an effective guide to septal surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1999; 104(7):2202–9. discussion 2210–2.16. Jeong JI, Gu S, Cho J, Hong SD, Kim SJ, Dhong HJ, et al. Impact of gender and sleep position on relationships between anthropometric parameters and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Breath. 2016; 21(2):535–41.17. Sahlin C, Franklin KA, Stenlund H, Lindberg E. Sleep in women: normal values for sleep stages and position and the effect of age, obesity, sleep apnea, smoking, alcohol and hypertension. Sleep Med. 2009; 10(9):1025–30.18. Ciavarella D, Tepedino M, Chimenti C, Troiano G, Mazzotta M, Foschino Barbaro MP, et al. Correlation between body mass index and obstructive sleep apnea severity indexes—a retrospective study. Am J Otolaryngol. 2018; 39(4):388–91.19. Lovin S, Bercea R, Cojocaru C, Rusu G, Mihăescu T. Body composition in obstructive sleep apneahypopnea syndrome bio-impedance reflects the severity of sleep apnea. Multidiscip Respir Med. 2010; 5:44–9.20. Chandra S, Sica AL, Wang J, Lakticova V, Greenberg HE. Respiratory effort-related arousals contribute to sympathetic modulation of heart rate variability. Sleep Breath. 2013; 17(4):1193–200.21. Leung RS, Bowman ME, Parker JD, Newton GE, Bradley TD. Avoidance of the left lateral decubitus position during sleep in patients with heart failure: relationship to cardiac size and function. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003; 41(2):227–30.22. Palermo P, Cattadori G, Bussotti M, Apostolo A, Contini M, Agostoni P. Lateral decubitus position generates discomfort and worsens lung function in chronic heart failure. Chest. 2005; 128(3):1511–6.23. Chen GY, Kuo CD. The effect of the lateral decubitus position on vagal tone. Anaesthesia. 1997; 52(7):653–7.24. Zhai AB, Haddad H. The impact of obesity on heart failure. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2017; 32(2):196–202.25. Lorrain D, De Koninck J, Dionne H, Goupil G. Sleep positions and postural shifts in elderly persons. Percept Mot Skills. 1986; 63(2 Pt 1):352–4.26. De Koninck J, Lorrain D, Gagnon P. Sleep positions and position shifts in five age groups: an ontogenetic picture. Sleep. 1992; 15(2):143–9.27. Pillar G, Berall M, Berry R, Etzioni T, Shrater N, Hwang D, et al. Detecting central sleep apnea in adult patients using WatchPAT—A multicenter validation study. Sleep Breath. 2019; 24(1):387–98.28. Bahammam AS, Tate R, Manfreda J, Kryger MH. Upper airway resistance syndrome: effect of nasal dilation, sleep stage, and sleep position. Sleep. 1999; 22:592–8.29. Heimer D, Scharf SM, Lieberman A, Lavie P. Sleep apnea syndrome treated by repair of deviated nasal septum. Chest. 1983; 84(2):184–5.30. Ishii L, Godoy A, Ishman SL, Gourin CG, Ishii M. The nasal obstruction symptom evaluation survey as a screening tool for obstructive sleep apnea. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011; 137(2):119–23.31. Kim ST, Choi JH, Jeon HG, Cha HE, Kim DY, Chung YS. Polysomnographic effects of nasal surgery for snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. Acta Otolaryngol. 2004; 124(3):297–300.32. Koutsourelakis I, Georgoulopoulos G, Perraki E, Vagiakis E, Roussos C, Zakynthinos SG. Randomised trial of nasal surgery for fixed nasal obstruction in obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur Respir J. 2008; 31(1):110–7.33. Li HY, Lee LA, Wang PC, Chen NH, Lin Y, Fang TJ. Nasal surgery for snoring in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Laryngoscope. 2008; 118(2):354–9.34. Li HY, Lin Y, Chen NH, Lee LA, Fang TJ, Wang PC. Improvement in quality of life after nasal surgery alone for patients with obstructive sleep apnea and nasal obstruction. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008; 134(4):429–33.35. Liu SA, Su MC, Jiang RS. Nasal patency measured by acoustic rhinometry in East Asian patients with sleep-disordered breathing. Am J Rhinol. 2006; 20(3):274–7.36. Cho YS, Go MJ, Kim YJ, Heo JY, Oh JH, Ban HJ, et al. A large-scale genome-wide association study of Asian populations uncovers genetic factors influencing eight quantitative traits. Nat Genet. 2009; 41(5):527–34.37. Wang J, Thornton JC, Russell M, Burastero S, Heymsfield S, Pierson RN Jr. Asians have lower body mass index (BMI) but higher percent body fat than do whites: comparisons of anthropometric measurements. Am J Clin Nutr. 1994; 60(1):23–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of the Body Position Changes on Upper Airway Caliber in Obstructive Sleep Apnea during Sleep
- Effects of Menopause on Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Pathogenesis of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- The Clinical Characteristics Between the Positional Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients with the Non-positional Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients
- Long-Term Side Effects of Mandibular Advancement Devices in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea