J Rhinol.
2022 Jul;29(2):69-75. 10.18787/jr.2021.00401.
Reconstruction Strategy After Endoscopic Skull-Base Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2532007
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2021.00401
Abstract
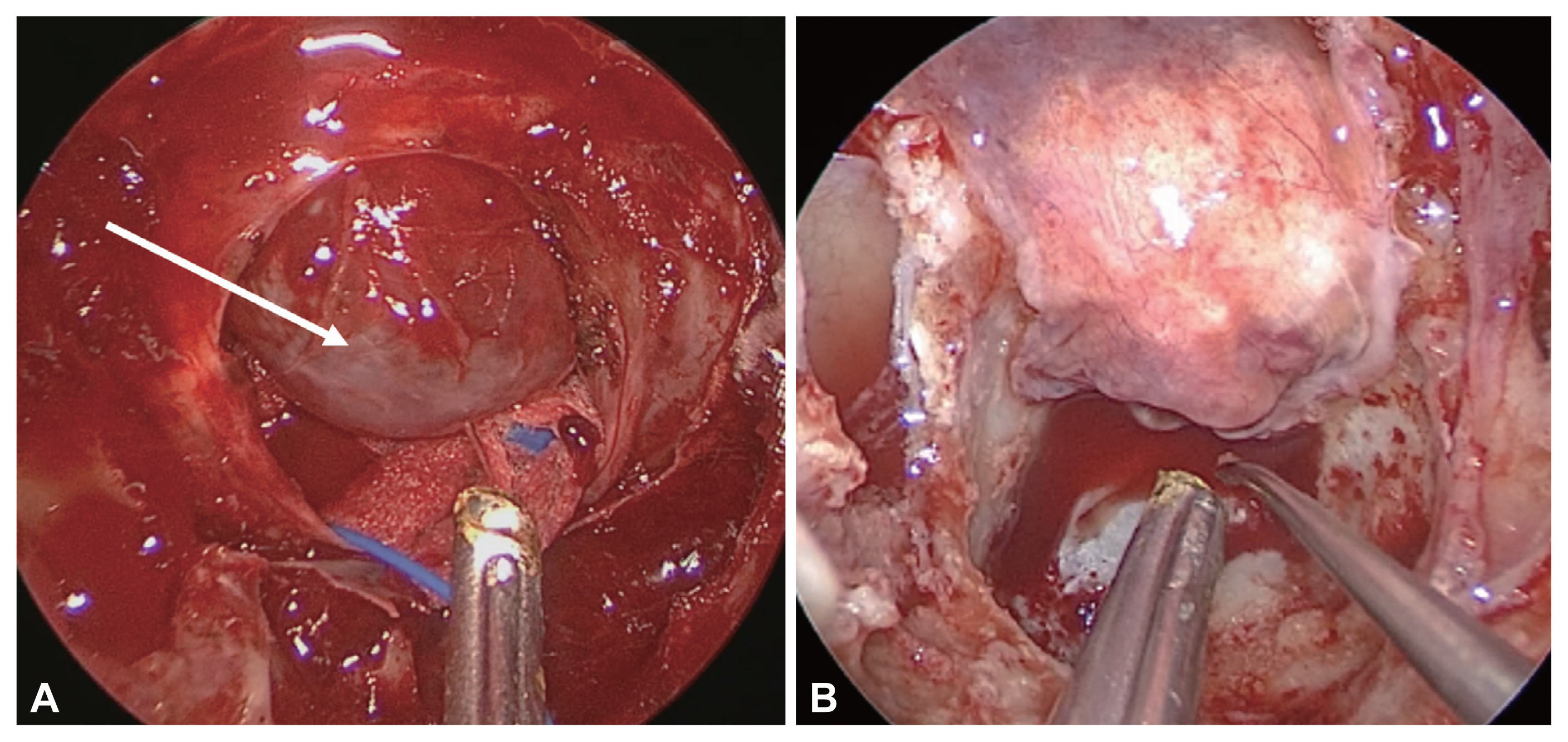
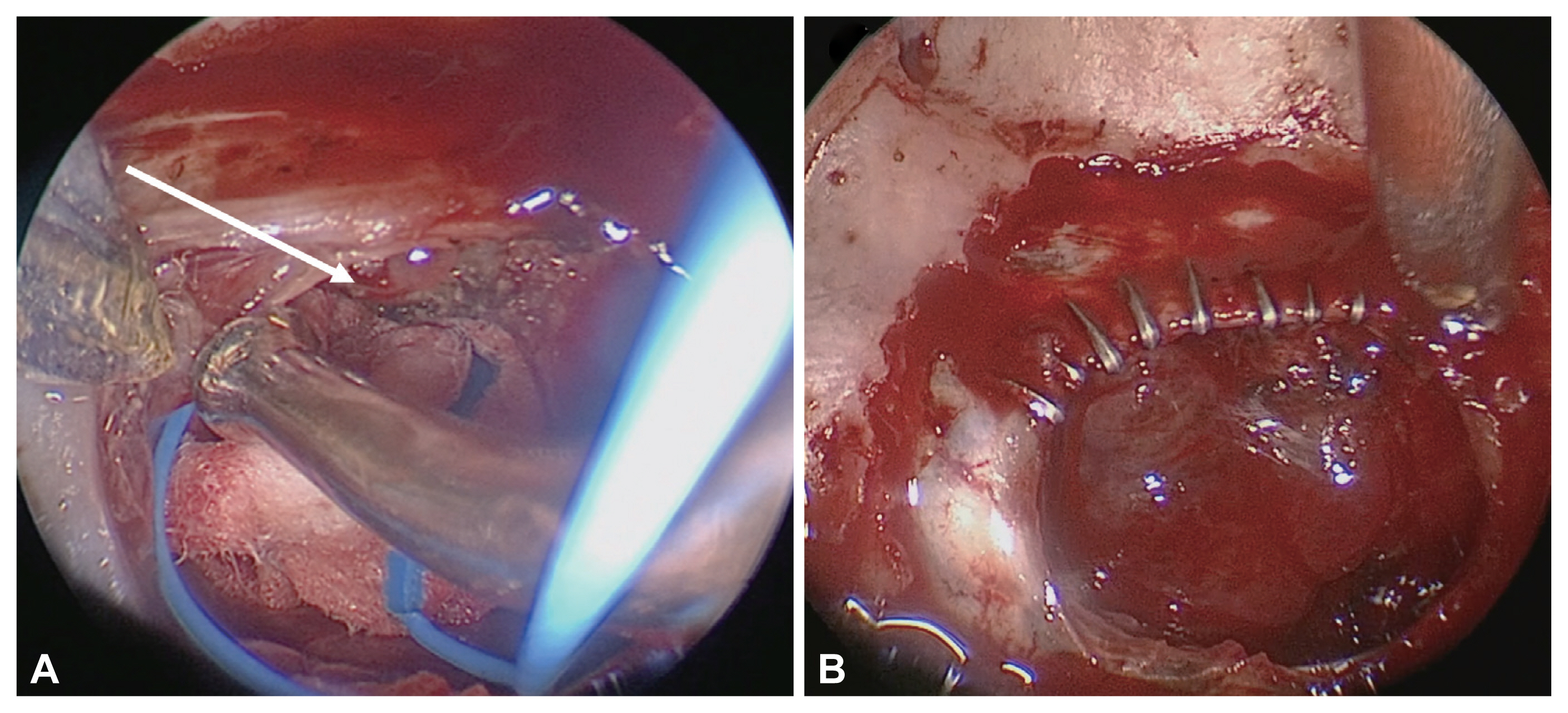
- Endoscopic skull-base surgery (ESBS) is a rapidly growing surgical area that involves collaboration of otolaryngology-head and neck surgeons and neurosurgeons. Various tumor pathologies and extents have been successfully treated with ESBS, and diverse reconstruction methods have been adopted since its introduction. The optimal reconstructive strategy should be based on heterogeneous surgical situations and tumor extent. Nevertheless, there are few current guidelines for selecting reconstructive methods. Therefore, we review diverse options for endoscopic skull-base reconstruction.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim JS, Hong SD. Risk factors for postoperative CSF leakage after endonasal endoscopic skull base surgery: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Rhinology. 2021; 59(1):10–20.2. Ahmed OH, Marcus S, Tauber JR, Wang B, Fang Y, Lebowitz RA. Efficacy of perioperative lumbar drainage following endonasal endoscopic cerebrospinal fluid leak repair: a meta-analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017; 156(1):52–60.3. Esposito F, Dusick JR, Fatemi N, Kelly DF. Graded repair of cranial base defects and cerebrospinal fluid leaks in transsphenoidal surgery. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown). 2007; 60(4 Suppl 2):295–303. discussion 303–4.4. Fraser S, Gardner PA, Koutourousiou M, Kubik M, Fernandez-Miranda JC, Snyderman CH, et al. Risk factors associated with postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leak after endoscopic endonasal skull base surgery. J Neurosurg. 2018; 128(4):1066–71.5. Wang EW, Gardner PA, Zanation AM. International consensus statement on endoscopic skull-base surgery: executive summary. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019; 9(S3):S127–44.6. Seo MY, Nam DH, Kong DS, Lee SH, Noh Y, Jung YG, et al. Extended approach or usage of nasoseptal flap is a risk factor for olfactory dysfunction after endoscopic anterior skullbase surgery: results from 928 patients in a single tertiary center. Rhinology. 2020; 58(6):574–80.7. Seo MY, Nam DH, Kong DS, Lee JJ, Ryu G, Kim HY, et al. Quality of life after extended versus transsellar endoscopic skull base surgery from 767 patients. Laryngoscope. 2019; 129(6):1318–24.8. Seda L, Camara RB, Cukiert A, Burattini JA, Mariani PP. Sellar floor reconstruction after transsphenoidal surgery using fibrin glue without grafting or implants: technical note. Surg Neurol. 2006; 66(1):46–9. discussion 49.9. Clavenna MJ, Turner JH, Chandra RK. Pedicled flaps in endoscopic skull base reconstruction: review of current techniques. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015; 23(1):71–7.10. Zuniga MG, Turner JH, Chandra RK. Updates in anterior skull base reconstruction. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016; 24(1):75–82.11. Germani RM, Vivero R, Herzallah IR, Casiano RR. Endoscopic reconstruction of large anterior skull base defects using acellular dermal allograft. Am J Rhinol. 2007; 21(5):615–8.12. Taufique ZM, Bhatt N, Zagzag D, Lebowitz RA, Lieberman SM. Revascularization of AlloDerm used during endoscopic skull base surgery. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2019; 80(1):46–50.13. Kim S, Jeon C, Kong DS, Park K, Kim JH. Clinical efficacy of radiation-sterilized allografts for sellar reconstruction after transsphenoidal surgery. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2011; 50(6):503–6.14. Hadad G, Bassagasteguy L, Carrau RL, Mataza JC, Kassam A, Snyderman CH, et al. A novel reconstructive technique after endoscopic expanded endonasal approaches: vascular pedicle nasoseptal flap. Laryngoscope. 2006; 116(10):1882–6.15. Sigler AC, D'Anza B, Lobo BC, Woodard TD, Recinos PF, Sindwani R. Endoscopic skull base reconstruction: an evolution of materials and methods. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2017; 50(3):643–53.16. Cho JM, Ahn JY, Chang JH, Kim SH. Prevention of cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea after transsphenoidal surgery by collagen fleece coated with fibrin sealant without autologous tissue graft or postoperative lumbar drainage. Neurosurgery. 2011; 68(1 Suppl Operative):130–6. discussion 136–7.17. So J, Park H, Sung KS, Lee KS, Hong CK. Sandwich technique using fibrin-coated collagen fleece for sellar reconstruction in large dural defects during transsphenoidal surgery. J Clin Neurosci. 2017; 43:256–60.18. Ganesh PB, Basavarajaiah BM, Rudrappa BA, Kasaragod SK. Cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhoea: does fibrin glue change the surgical outcome? J Laryngol Otol. 2020; 134(7):582–5.19. Park JH, Choi JH, Kim YI, Kim SW, Hong YK. Modified graded repair of cerebrospinal fluid leaks in endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015; 58(1):36–42.20. Kuan EC, Yoo F, Patel PB, Su BM, Bergsneider M, Wang MB. An algorithm for sellar reconstruction following the endoscopic endonasal approach: a review of 300 consecutive cases. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2018; 79(2):177–83.21. Yoon TM, Lim SC, Jung S. Utility of sphenoid mucosal flaps in transnasal transsphenoidal surgery. Acta Otolaryngol. 2008; 128(7):785–9.22. Kim EH, Moon JH, Kim SH. Clipping technique for the repair of the intraoperative cerebrospinal fluid leakage during transsphenoidal pituitary tumor surgery. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown). 2019; 17(4):382–8.23. Bakhsheshian J, Hwang MS, Friedman M. What is the evidence for postoperative lumbar drains in endoscopic repair of CSF leaks? Laryngoscope. 2015; 125(10):2245–6.24. Zwagerman NT, Wang EW, Shin SS, Chang YF, Fernandez-Miranda JC, Snyderman CH, et al. Does lumbar drainage reduce postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leak after endoscopic endonasal skull base surgery? A prospective, randomized controlled trial. J Neurosurg. 2018; 131(4):1172–8.25. Liu JK, Schmidt RF, Choudhry OJ, Shukla PA, Eloy JA. Surgical nuances for nasoseptal flap reconstruction of cranial base defects with high-flow cerebrospinal fluid leaks after endoscopic skull base surgery. Neurosurg Focus. 2012; 32(6):E7.26. Lee KH, Yang CW. Endoscopic endonasal skull base repair with nasoseptal flap. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2015; 58(1):7–11.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Endonasal Skull Base Repair with Nasoseptal Flap
- Iatrogenic Skull Base Defect Accompanied by Brain Injury After Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: A Report of Two Cases
- Endoscopic Skull Base Surgery
- Extended temporalis flap for skull base reconstruction
- Endoscopic Skull Reconstruction: Nasoseptal Flap Based Reconstructive Options