Acute Crit Care.
2022 May;37(2):193-201. 10.4266/acc.2021.00857.
Incidence and risk factors associated with early death in patients with emergency department septic shock
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine, Department of Medicine, Emory University, Atlanta, GA, USA
- 2Center for Outcomes Research and Evaluation, Atrium Health, Charlotte, NC, USA
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Carolinas Medical Center, Charlotte, NC, USA
- 4Department of Emergency Medicine, Carolinas Medical Center, Charlotte, NC, USA
- KMID: 2531676
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2021.00857
Abstract
- Background
Limited research has explored early mortality among patients presenting with septic shock. The objective of this study was to determine the incidence and factors associated with early death following emergency department (ED) presentation of septic shock.
Methods
A prospective registry of patients enrolled in an ED septic shock clinical pathway was used to identify patients. Patients were compared across demographic, comorbid, clinical, and treatment variables by death within 72 hours of ED presentation.
Results
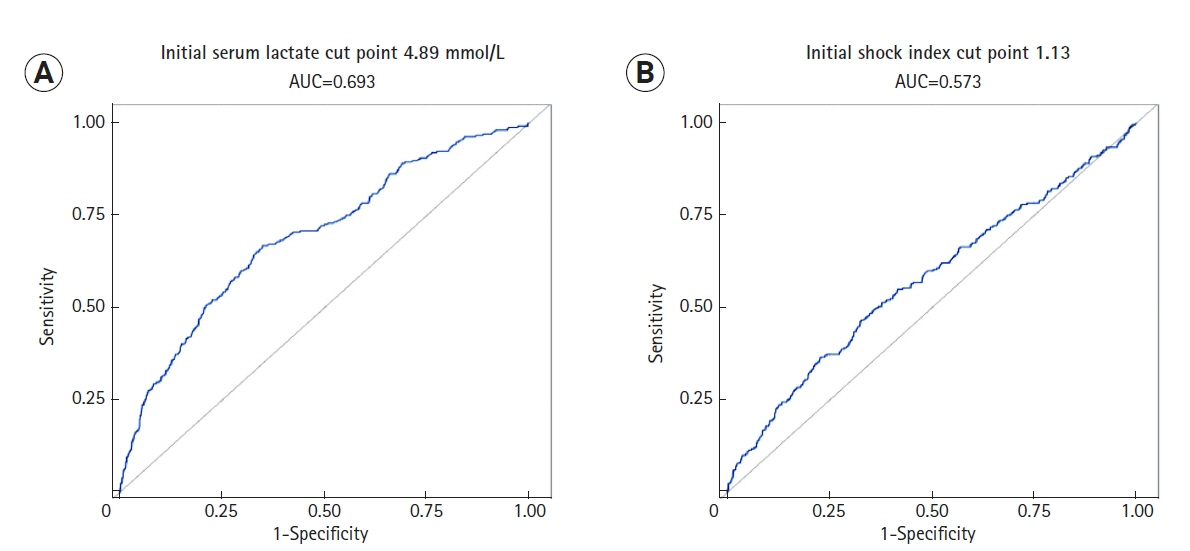
Among the sample of 2,414 patients, overall hospital mortality was 20.6%. Among patients who died in the hospital, mean and median time from ED presentation to death were 4.96 days and 2.28 days, respectively. Death at 24, 48, and 72 hours occurred in 5.5%, 9.5%, and 11.5% of patients, respectively. Multivariate regression analysis demonstrated that the following factors were independently associated with early mortality: age (odds ratio [OR], 1.04; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.03–1.05), malignancy (OR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.11–2.11), pneumonia (OR, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.02–1.88), urinary tract infection (OR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.44–0.89), first shock index (OR, 1.85; 95% CI, 1.27–2.70), early vasopressor use (OR, 2.16; 95% CI, 1.60–2.92), initial international normalized ratio (OR, 1.14; 95% CI, 1.07–1.27), initial albumin (OR, 0.55; 95% CI, 0.44–0.69), and first serum lactate (OR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.16–1.26).
Conclusions
Adult septic shock patients experience a high rate of early mortality within 72 hours of ED arrival. Recognizable clinical factors may aid the identification of patients at risk of early death.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gupta RG, Hartigan SM, Kashiouris MG, Sessler CN, Bearman GM. Early goal-directed resuscitation of patients with septic shock: current evidence and future directions. Crit Care. 2015; 19:286.
Article2. Angus DC, van der Poll T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369:840–51.
Article3. Winters BD, Eberlein M, Leung J, Needham DM, Pronovost PJ, Sevransky JE. Long-term mortality and quality of life in sepsis: a systematic review. Crit Care Med. 2010; 38:1276–83.
Article4. Javed A, Guirgis FW, Sterling SA, Puskarich MA, Bowman J, Robinson T, et al. Clinical predictors of early death from sepsis. J Crit Care. 2017; 42:30–4.
Article5. Daviaud F, Grimaldi D, Dechartres A, Charpentier J, Geri G, Marin N, et al. Timing and causes of death in septic shock. Ann Intensive Care. 2015; 5:16.
Article6. Doost Hosseiny A, Moloi S, Chandrasekhar J, Farshid A. Mortality pattern and cause of death in a long-term follow-up of patients with STEMI treated with primary PCI. Open Heart. 2016; 3:e000405.
Article7. Paoli CJ, Reynolds MA, Sinha M, Gitlin M, Crouser E. Epidemiology and costs of sepsis in the united states-an analysis based on timing of diagnosis and severity level. Crit Care Med. 2018; 46:1889–97.
Article8. Haas B, Wunsch H. How does prior health status (age, comorbidities and frailty) determine critical illness and outcome? Curr Opin Crit Care. 2016; 22:500–5.
Article9. Danai PA, Moss M, Mannino DM, Martin GS. The epidemiology of sepsis in patients with malignancy. Chest. 2006; 129:1432–40.
Article10. He XL, Liao XL, Xie ZC, Han L, Yang XL, Kang Y. Pulmonary infection is an independent risk factor for long-term mortality and quality of life for sepsis patients. Biomed Res Int. 2016; 2016:4213712.
Article11. Honselmann KC, Buthut F, Heuwer B, Karadag S, Sayk F, Kurowski V, et al. Long-term mortality and quality of life in intensive care patients treated for pneumonia and/or sepsis: Predictors of mortality and quality of life in patients with sepsis/pneumonia. J Crit Care. 2015; 30:721–6.12. Tseng J, Nugent K. Utility of the shock index in patients with sepsis. Am J Med Sci. 2015; 349:531–5.
Article13. Heffner AC, Swords DS, Neale MN, Jones AE. Incidence and factors associated with cardiac arrest complicating emergency airway management. Resuscitation. 2013; 84:1500–4.
Article14. Shapiro NI, Howell MD, Talmor D, Nathanson LA, Lisbon A, Wolfe RE, et al. Serum lactate as a predictor of mortality in emergency department patients with infection. Ann Emerg Med. 2005; 45:524–8.
Article15. Mikkelsen ME, Miltiades AN, Gaieski DF, Goyal M, Fuchs BD, Shah CV, et al. Serum lactate is associated with mortality in severe sepsis independent of organ failure and shock. Crit Care Med. 2009; 37:1670–7.
Article16. Ryoo SM, Lee J, Lee YS, Lee JH, Lim KS, Huh JW, et al. Lactate level versus lactate clearance for predicting mortality in patients with septic shock defined by sepsis-3. Crit Care Med. 2018; 46:e489–95.
Article17. Horvatits T, Drolz A, Trauner M, Fuhrmann V. Liver injury and failure in critical illness. Hepatology. 2019; 70:2204–15.
Article18. Barbash IJ, Davis B, Kahn JM. National performance on the Medicare SEP-1 sepsis quality measure. Crit Care Med. 2019; 47:1026–32.
Article19. Nowak RM, Nanayakkara P, DiSomma S, Levy P, Schrijver E, Huyghe R, et al. Noninvasive hemodynamic monitoring in emergency patients with suspected heart failure, sepsis and stroke: the PREMIUM registry. West J Emerg Med. 2014; 15:786–94.
Article20. De Backer D, Donadello K. Assessment of microperfusion in sepsis. Minerva Anestesiol. 2015; 81:533–40.21. Liu Z, Meng Z, Li Y, Zhao J, Wu S, Gou S, et al. Prognostic accuracy of the serum lactate level, the SOFA score and the qSOFA score for mortality among adults with Sepsis. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2019; 27:51.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Prognostic Factors of Pneumonia with Septic Shock in Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department
- Cardiac Functions and Hemodynamic Values Related to Prognosis of The Septic Shock Patients in the Emergency Department
- A case of full-term delivery after septic shock during second trimester of pregnancy
- Polymyxin B Hemoperfusion in Pneumonic Septic Shock Caused by Gram-Negative Bacteria
- The Risk Factors of Septic Shock in Childhood Cancer Patients with Neutropenic Fever