Neurointervention.
2022 Jul;17(2):106-109. 10.5469/neuroint.2022.00059.
Retrieval of Displaced Woven EndoBridge Intrasaccular Flow Disruptor Using Solitaire Platinum Revascularization Device
- Affiliations
-
- 1Interventional Neuroradiology Service, Department of Medical Imaging, Royal Hobart Hospital, Hobart, TAS, Australia
- 2Interventional Neuroradiology Unit, Monash Imaging, Monash Health, Melbourne, VIC, Australia
- KMID: 2531566
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5469/neuroint.2022.00059
Abstract
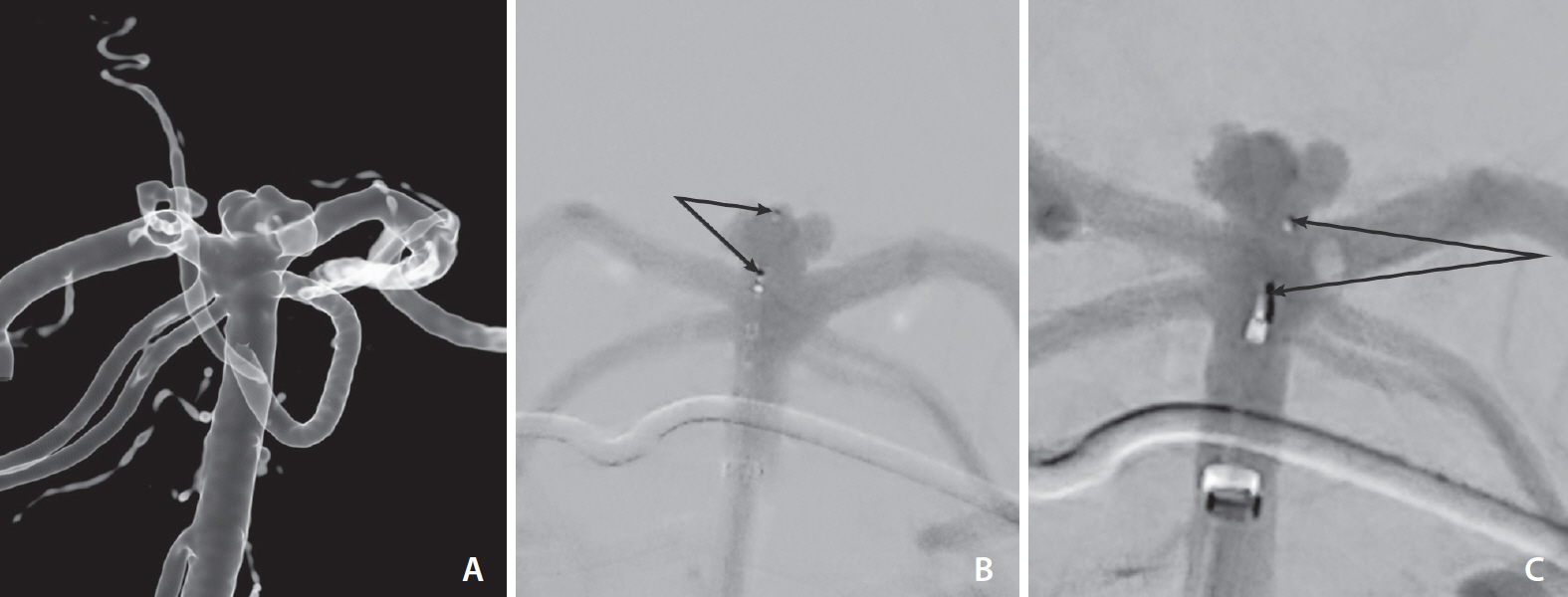
- The Woven EndoBridge (WEB; MicroVention, Aliso Viejo, CA, USA) intrasaccular flow disruptor is a therapeutic option for wide neck bifurcation intracranial aneurysms that does not require the use of adjunctive techniques such as stents or balloon remodeling. As with other endovascular devices, displacement of the WEB is a recognized complication. Few reports have been published regarding the management of this type of complication. We describe a case of retrieval of a displaced WEB using a Solitaire Platinum revascularization device (Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN, USA). Interventionists should be aware of this option in the management of such a complication.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Woven EndoBridge Device Migration and Microsnare Retrieval Strategy: Single Institutional Case Reports with Technical Video Demonstration
Brandon A. Santhumayor, Timothy G. White, Cassidy Werner, Kevin Shah, Henry H. Woo
Neurointervention. 2023;18(2):129-134. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2023.00136.
Reference
-
1. Pierot L, Moret J, Barreau X, Szikora I, Herbreteau D, Turjman F, et al. Safety and efficacy of aneurysm treatment with WEB in the cumulative population of three prospective, multicenter series. J Neurointerv Surg. 2018; 10:553–559.
Article2. Papagiannaki C, Spelle L, Januel AC, Benaissa A, Gauvrit JY, Costalat V, et al. WEB intrasaccular flow disruptor-prospective, multicenter experience in 83 patients with 85 aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014; 35:2106–2111.
Article3. Asnafi S, Rouchaud A, Pierot L, Brinjikji W, Murad MH, Kallmes DF. Efficacy and safety of the Woven EndoBridge (WEB) device for the treatment of intracranial aneurysms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016; 37:2287–2292.
Article4. van Rooij WJ, Peluso JP, Bechan RS, Sluzewski M. WEB treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016; 37:1679–1683.
Article5. König I, Weber A, Weber W, Fischer S. Dislocation of a WEB device into the middle cerebral artery: removal with the alligator retrieval device. Clin Neuroradiol. 2019; 29:361–364.
Article6. Nikoubashman O, Badenschier R, Müller M, Brockmann C, Schubert G, Brockmann MA, et al. Endovascular retrieval of a dislocated coil in the peroneal artery with a stent retriever. BJR Case Rep. 2016; 2:20150278.
Article7. Leslie-Mazwi TM, Heddier M, Nordmeyer H, Stauder M, Velasco A, Mosimann PJ, et al. Stent retriever use for retrieval of displaced microcoils: a consecutive case series. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013; 34:1996–1999.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Adjustment of Malpositioned Woven EndoBridge Device Using Gooseneck Snare: Complication Management Technique
- Woven Endobridge (WEB) augmented by Y-stent in a shallow basilar tip aneurysm
- Ten Years of Clinical Evaluation of the Woven EndoBridge: A Safe and Effective Treatment for Wide-Neck Bifurcation Aneurysms
- Intrasaccular Flow Disruptor (Woven EndoBridge) Assisted Embolization of Vertebral Arteriovenous Fistulas
- Vertebro-Vertebral Fistula Occlusion Using a Woven EndoBridgeTM-Device