Korean J healthc assoc Infect Control Prev.
2022 Jun;27(1):35-42. 10.14192/kjicp.2022.27.1.35.
Effects of Stepwise Application of Active Surveillance Culture, Preemptive Isolation, and Chlorhexidine Bed Bath on the Acquisition of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Children Undergoing Cardiac Surgery in the Paediatric Intensive Care Unit
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Nursing, Graduate School of Industry, University of Ulsan, Ulsan, Korea
- 2Department of Nursing, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 3Office for Infection Control, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2530824
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14192/kjicp.2022.27.1.35
Abstract
- Background
This study aimed to investigate the effects of stepwise strengthening of methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection control on the acquisition and identification of risk factors for acquiring MRSA in children undergoing cardiac surgery in the paediatric intensive care unit (PICU).
Methods
Patients who underwent surgery for congenital heart disease between June 2017 and February 2019 were included. As a step-by-step MRSA infection control, step 1 was an active surveillance culture, step 2 was to add preemptive contact isolation, and step 3 was to add a chlorhexidine bed bath. In addition, the medical records of 346 participants were reviewed retrospectively. The difference between the occurrence of MRSA acquisition and timing was analysed using the Kruskal–Wallis, chi-square, and Fisher’s exact tests and the risk factors for children with MRSA were confirmed using logistic regression analysis.
Results
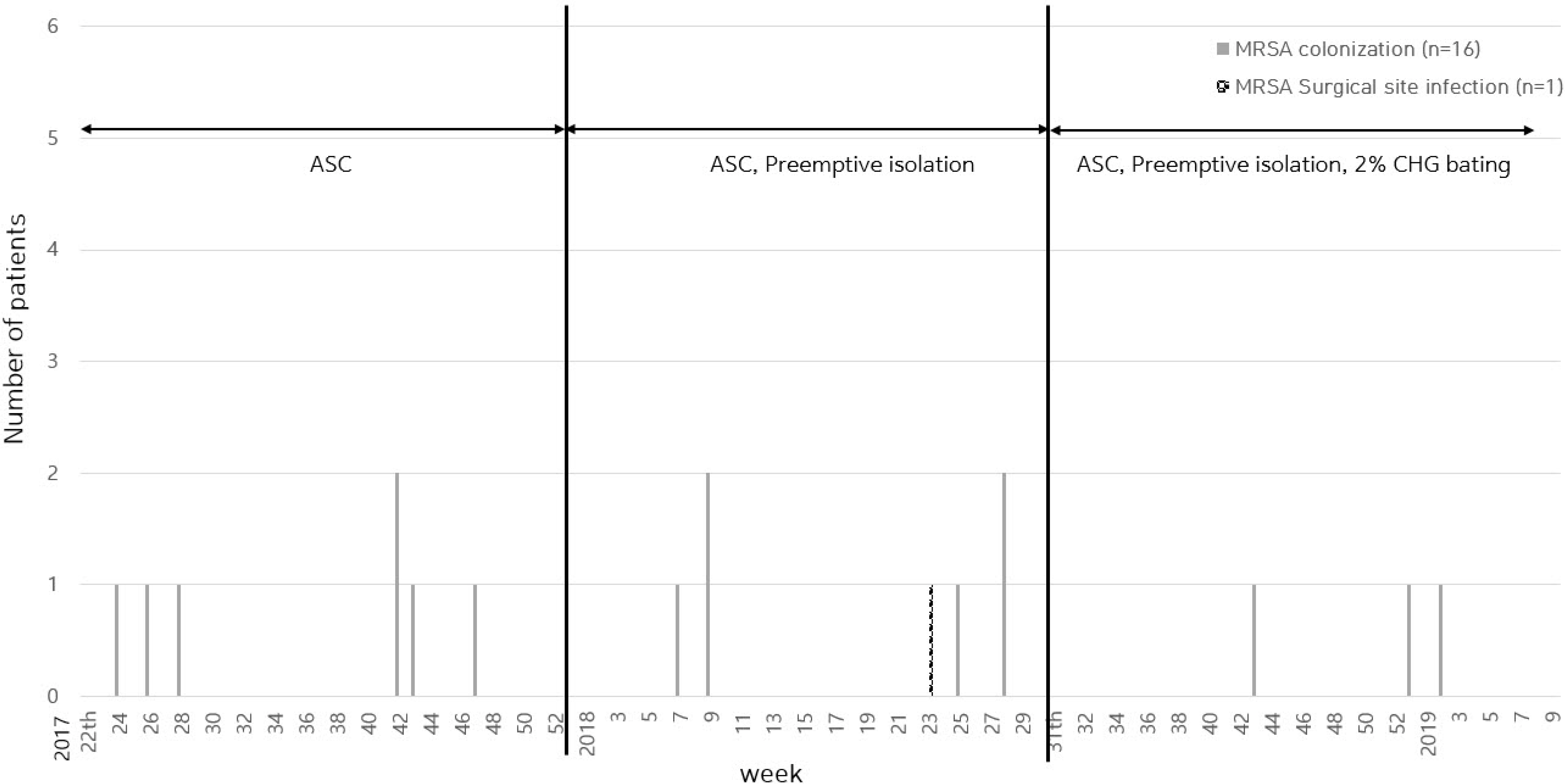
MRSA colonisation occurred in eight patients (6.4%) in stage 1, five (4.0%) in stage 2, and three (3.2%) in stage 3. MRSA infection occurred in one patient (0.8%) admitted in stage 2. The median day of occurrence of MRSA colonisation was 8.5 days in stage 1, 8 in stage 2, and 17 in stage 3. Steroid exposure was an independent factor influencing MRSA acquisition.
Conclusion
Due to the small number of participants and short intervention period, the stepup intervention did not significantly reduce MRSA acquisition. However, as MRSA infection control was strengthened step-by-step, MRSA acquisition tended to decrease.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Daily Chlorhexidine Bathing as a Simple Solution for Prevention of Healthcare-associated Infections in the ICU
Seung Soon Lee
Korean J Healthc Assoc Infect Control Prev. 2022;27(1):1-3. doi: 10.14192/kjicp.2022.27.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Zervou FN, Zacharioudakis IM, Ziakas PD, Mylonakis E. 2014; MRSA colonization and risk of infection in the neonatal and pediatric ICU: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 133:e1015–23. DOI: 10.1542/peds.2013-3413. PMID: 24616358.
Article2. Katayanagi T. 2015; Nasal methicillin-resistant S. aureus is a major risk for mediastinitis in pediatric cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 21:37–44. DOI: 10.5761/atcs.oa.14-00157. PMID: 25641035. PMCID: PMC4989985.
Article3. Edwards FH, Engelman RM, Houck P, Shahian DM, Bridges CR. 2006; The Society of Thoracic Surgeons practice guideline series: antibiotic prophylaxis in cardiac surgery, part I: duration. Ann Thorac Surg. 81:397–404. DOI: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2005.06.034. PMID: 16368422.
Article4. Mehta PA, Cunningham CK, Colella CB, Alferis G, Weiner LB. 2000; Risk factors for sternal wound and other infections in pediatric cardiac surgery patients. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 19:1000–4. DOI: 10.1097/00006454-200010000-00012. PMID: 11055604.
Article5. Sochet AA, Cartron AM, Nyhan A, Spaeder MC, Song X, Brown AT, et al. 2017; Surgical site infection after pediatric cardiothoracic surgery: impact on hospital cost and length of stay. World J Pediatr Congenit Heart Surg. 8:7–12. DOI: 10.1177/2150135116674467. PMID: 28033082.
Article6. McNeil JC, Ligon JA, Hulten KG, Dreyer WJ, Heinle JS, Mason EO, et al. 2013; Staphylococcus aureus infections in children with congenital heart disease. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2:337–44. DOI: 10.1093/jpids/pit037. PMID: 26619497.
Article7. Huskins WC, Huckabee CM, O'Grady NP, Murray P, Kopetskie H, Zimmer L, et al. 2011; Intervention to reduce transmission of resistant bacteria in intensive care. N Engl J Med. 364:1407–18. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1000373. PMID: 21488763. PMCID: PMC3410743.
Article8. Glick SB, Samson DJ, Huang ES, Vats V, Aronson N, Weber SG. 2014; Screening for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a comparative effectiveness review. Am J Infect Control. 42:148–55. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajic.2013.07.020. PMID: 24360519.
Article9. Holzmann-Pazgal G, Monney C, Davis K, Wanger A, Strobel N, Zhong F. 2011; Active surveillance culturing impacts methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus acquisition in a pediatric intensive care unit. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 12:e171–5. DOI: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e3181f39222. PMID: 20838355.
Article10. Wells S, Anderson T, Tiemieier A, Wrobel J, Maraqa N, Smotherman C, et al. 2013; Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in patients with congenital heart disease in the pediatric intensive care unit. World J Pediatr Congenit Heart Surg. 4:344–8. DOI: 10.1177/2150135113493016. PMID: 24327625. PMCID: PMC5669037.
Article11. Milstone AM, Elward A, Song X, Zerr DM, Orscheln R, Speck K, et al. 2013; Daily chlorhexidine bathing to reduce bacteraemia in critically ill children: a multicentre, cluster-randomised, crossover trial. Lancet. 381:1099–106. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61687-0. PMID: 23363666. PMCID: PMC4128170.
Article12. Climo MW, Yokoe DS, Warren DK, Perl TM, Bolon M, Herwaldt LA, et al. 2013; Effect of daily chlorhexidine bathing on hospital-acquired infection. N Engl J Med. 368:533–42. Erratum in: N Engl J Med 2013;368: 2341. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1113849. PMID: 23388005. PMCID: PMC5703051.
Article13. Frost SA, Alogso MC, Metcalfe L, Lynch JM, Hunt L, Sanghavi R, et al. 2016; Chlorhexidine bathing and health care-associated infections among adult intensive care patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 20:379. DOI: 10.1186/s13054-016-1553-5. PMID: 27876075. PMCID: PMC5120440.
Article14. Lewis SR, Schofield-Robinson OJ, Rhodes S, Smith AF. 2019; Chlorhexidine bathing of the critically ill for the prevention of hospital-acquired infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 8:CD012248. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012248.pub2. PMID: 31476022. PMCID: PMC6718196.
Article15. Lee JY, Jeong JS, Kim MY, Park SH, Hwang YH. 2018; Effects of daily chlorhexidine bathing on the acquisition of multidrug-resistant organisms and healthcare-associated infection in an intensive care unit. J Korean Biol Nurs Sci. 20:38–46. DOI: 10.7586/jkbns.2018.20.1.38.
Article16. Korean National Healthcare-associated Infections Surveillance System. KONIS manual 2020. http://konis.cafe24.com/xe/index.php?mid=manual&category=251&document_srl=20922. (Updated on 5 November 2020).17. Saraswat MK, Magruder JT, Crawford TC, Gardner JM, Duquaine D, Sussman MS, et al. 2017; Preoperative Staphylococcus Aureus screening and targeted decolonization in cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 104:1349–56. DOI: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2017.03.018. PMID: 28577844.
Article18. Choi SM, Jeong JS, Whang DH, Woo JH. 2010; The effect of contact precautions and active surveillance culture on the methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus reduction in an intensive care unit. Korean J Nosocomial Infect Control. 15:112–9.19. Ando M, Park IS, Wada N, Takahashi Y. 2005; Steroid supplementation: a legitimate pharmacotherapy after neonatal open heart surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 80:1672–8. discusison 1678. DOI: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2005.04.035. PMID: 16242437.
Article20. Millar KJ, Thiagarajan RR, Laussen PC. 2007; Glucocorticoid therapy for hypotension in the cardiac intensive care unit. Pediatr Cardiol. 28:176–82. DOI: 10.1007/s00246-006-0053-9. PMID: 17375351.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Eradication of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Neonatal Intensive Care unit by Aggressive Infection Control Measures : Isolation Program and the Use of Chlorhexidine
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infection in Neonates
- Decolonization of Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Role in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- Risk Factors for Acquisition of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a Neurosurgical Intensive Care Unit(NSICU): Case-Control Study
- Detection of Multidrug Resistant Patterns and Associated - genes of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus ( MRSA ) Isolated from Clinical Specimens