J Rheum Dis.
2022 Jul;29(3):132-139. 10.4078/jrd.2022.29.3.132.
Osteoarthritis – Insights From Recent Research
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Anyang, Korea
- 2Institute for Skeletal Aging, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea
- KMID: 2530677
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2022.29.3.132
Abstract
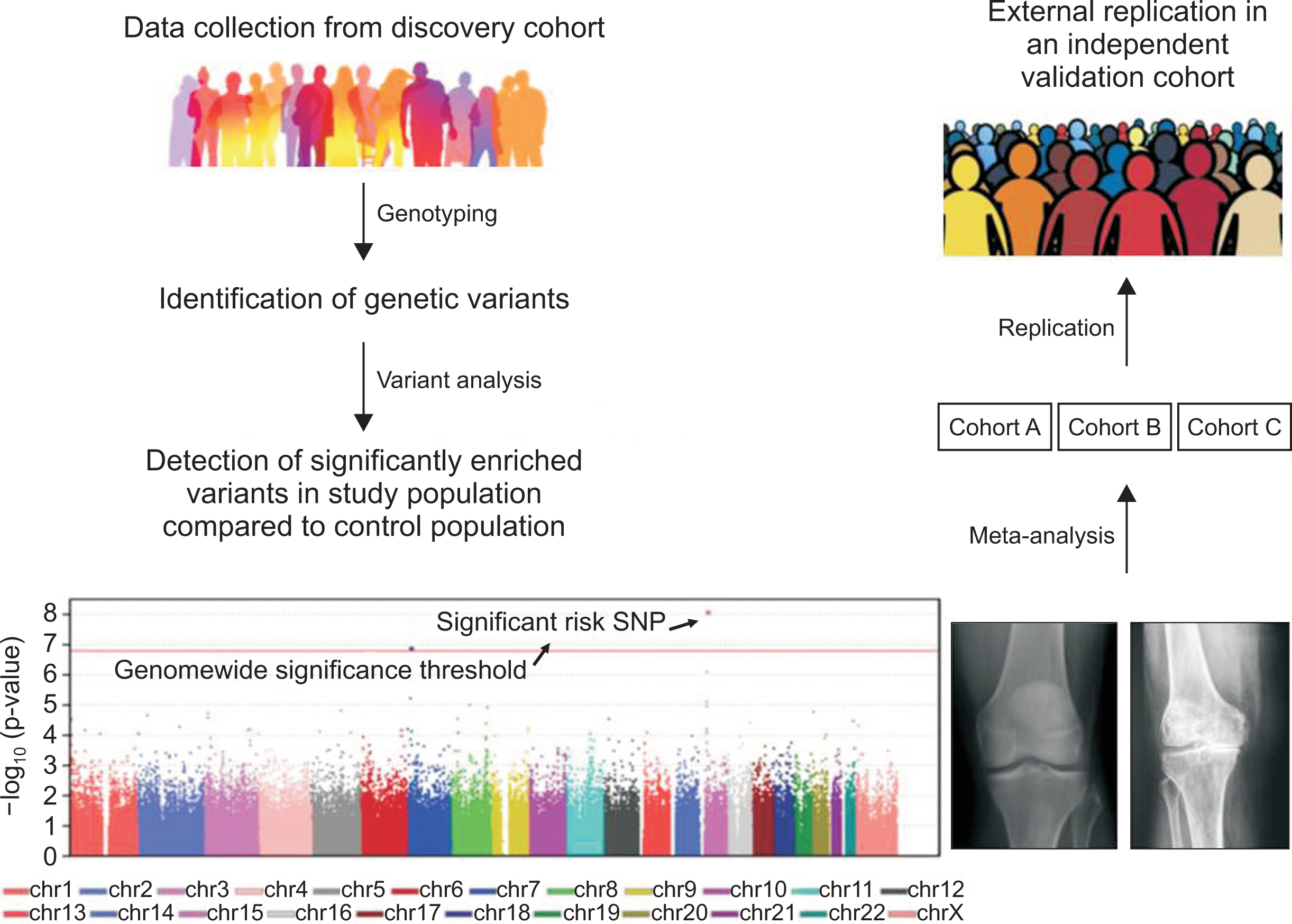
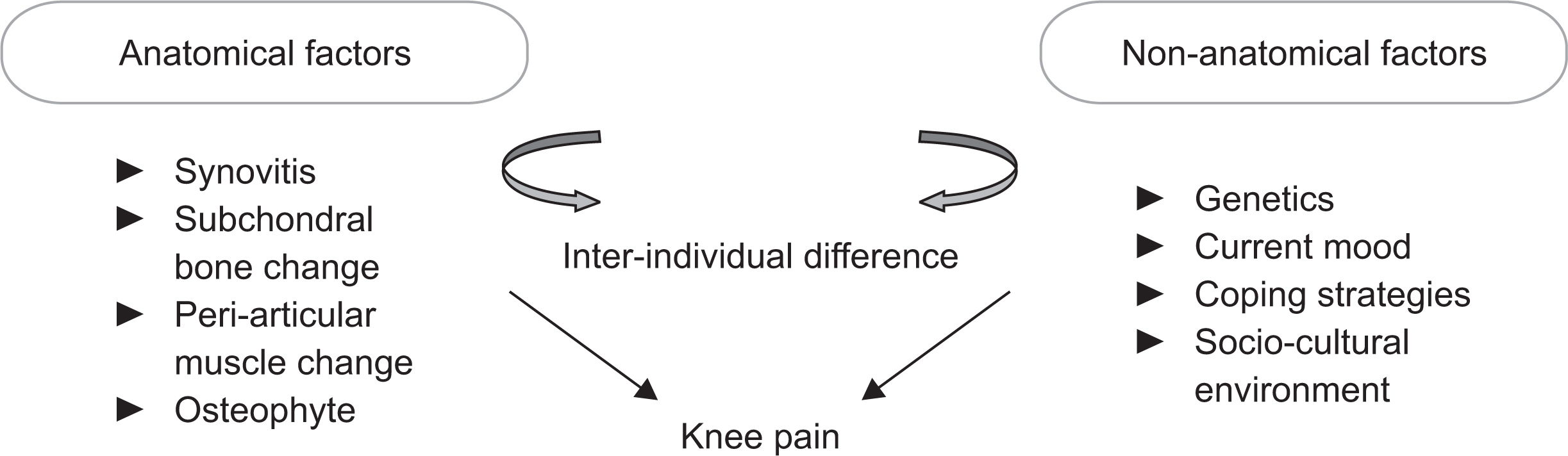
- Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis and is a growing public health concern in the aging society. In rapidly aging societies such as in Korea, the increasing prevalence of OA may present serious new health issues. There is no treatment for OA that can either prevent or slow the progression of joint damage. For the development of effective therapeutics, precise understating of its pathogenesis is important. In this review, the current evidence of etiopathogenesis of OA is discussed. First, while epidemiologic study of OA are still dominated by reports from Western countries, findings from Korean epidemiologic studies are highlighted. Then, recent progresses in genetics, especially in the field of genome wide association study and mendelian randomization studies, are reviewed with focus on Asian population. Lastly, sex difference in pain etopathogenesis is reviewed. Studies of OA pathogenesis including epidemiology, genetics, animal model and pain signaling will aid in progress towards treatment of OA.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dieleman JL, Cao J, Chapin A, Chen C, Li Z, Liu A, et al. 2020; US health care spending by payer and health condition, 1996-2016. JAMA. 323:863–84. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2020.0734. PMID: 32125402. PMCID: PMC7054840.
Article2. Bastick AN, Runhaar J, Belo JN, Bierma-Zeinstra SM. 2015; Prognostic factors for progression of clinical osteoarthritis of the knee: a systematic review of observational studies. Arthritis Res Ther. 17:152. DOI: 10.1186/s13075-015-0670-x. PMID: 26050740. PMCID: PMC4483213.
Article3. Muraki S, Akune T, Oka H, Ishimoto Y, Nagata K, Yoshida M, et al. 2012; Incidence and risk factors for radiographic knee osteoarthritis and knee pain in Japanese men and women: a longitudinal population-based cohort study. Arthritis Rheum. 64:1447–56. DOI: 10.1002/art.33508. PMID: 22135156.
Article4. Kim I, Kim HA, Seo YI, Song YW, Jeong JY, Kim DH. 2010; The prevalence of knee osteoarthritis in elderly community residents in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 25:293–8. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.293. PMID: 20119586. PMCID: PMC2811300.
Article5. Yoo JJ, Kim DH, Kim HA. 2018; Risk factors for progression of radiographic knee osteoarthritis in elderly community residents in Korea. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 19:80. DOI: 10.1186/s12891-018-1999-5. PMID: 29530005. PMCID: PMC5848445.
Article6. Kim HA, Koh SH, Lee B, Kim IJ, Seo YI, Song YW, et al. 2008; Low rate of total hip replacement as reflected by a low prevalence of hip osteoarthritis in South Korea. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 16:1572–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2008.04.024. PMID: 18558502. PMCID: PMC4373077.
Article7. Lau EM, Lin F, Lam D, Silman A, Croft P. 1995; Hip osteoarthritis and dysplasia in Chinese men. Ann Rheum Dis. 54:965–9. DOI: 10.1136/ard.54.12.965. PMID: 8546528. PMCID: PMC1010061.
Article8. Peat G, Thomas MJ. 2021; Osteoarthritis year in review 2020: epidemiology & therapy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 29:180–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2020.10.007. PMID: 33242603.
Article9. Wallace IJ, Felson DT, Worthington S, Duryea J, Clancy M, Aliabadi P, et al. 2019; Knee osteoarthritis risk in non-industrial societies undergoing an energy balance transition: evidence from the indigenous Tarahumara of Mexico. Ann Rheum Dis. 78:1693–8. Erratum. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215886. PMID: 31519654.
Article10. Losina E, Silva GS, Smith KC, Collins JE, Hunter DJ, Shrestha S, et al. 2020; Quality-adjusted life-years lost due to physical inactivity in a US population with osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 72:1349–57. DOI: 10.1002/acr.24035. PMID: 31350803. PMCID: PMC6982563.
Article11. Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J. 2015. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 19th ed. McGraw Hill Education;New York: p. 2226.12. Reynard LN, Barter MJ. 2020; Osteoarthritis year in review 2019: genetics, genomics and epigenetics. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 28:275–84. DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2019.11.010. PMID: 31874234.
Article13. Styrkarsdottir U, Lund SH, Thorleifsson G, Zink F, Stefansson OA, Sigurdsson JK, et al. 2018; Meta-analysis of Icelandic and UK data sets identifies missense variants in SMO, IL11, COL11A1 and 13 more new loci associated with osteoarthritis. Nat Genet. 50:1681–7. DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0247-0. PMID: 30374069.
Article14. Tachmazidou I, Hatzikotoulas K, Southam L, Esparza-Gordillo J, Haberland V, Zheng J, et al. 2019; Identification of new therapeutic targets for osteoarthritis through genome-wide analyses of UK Biobank data. Nat Genet. 51:230–6. DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0327-1. PMID: 30664745. PMCID: PMC6400267.
Article15. Ratneswaran A, Kapoor M. 2021; Osteoarthritis year in review: genetics, genomics, epigenetics. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 29:151–60. DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2020.11.003. PMID: 33227439.
Article16. Baird DA, Evans DS, Kamanu FK, Gregory JS, Saunders FR, Giuraniuc CV, et al. 2019; Identification of novel loci associated with hip shape: a meta-analysis of genomewide association studies. J Bone Miner Res. 34:241–51. DOI: 10.1002/jbmr.3605. PMID: 30320955. PMCID: PMC6375741.
Article17. Hatzikotoulas K, Roposch A, Shah KM, Clark MJ, Bratherton S, Limbani V, et al. 2018; Genome-wide association study of developmental dysplasia of the hip identifies an association with GDF5. Commun Biol. 1:56. DOI: 10.1038/s42003-018-0052-4. PMID: 30273415. PMCID: PMC6123669.18. Sun Y, Wang C, Hao Z, Dai J, Chen D, Xu Z, et al. 2015; A common variant of ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex is associated with DDH. PLoS One. 10:e0120212. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120212. PMID: 25848760. PMCID: PMC4388640.
Article19. Hindy G, Åkesson KE, Melander O, Aragam KG, Haas ME, Nilsson PM, et al. 2019; Cardiometabolic polygenic risk scores and osteoarthritis outcomes: a Mendelian randomization study using data from the Malmö Diet and Cancer Study and the UK Biobank. Arthritis Rheumatol. 71:925–34. DOI: 10.1002/art.40812. PMID: 30615301. PMCID: PMC6563114.
Article20. Funck-Brentano T, Nethander M, Movérare-Skrtic S, Richette P, Ohlsson C. 2019; Causal factors for knee, hip, and hand osteoarthritis: a Mendelian randomization study in the UK Biobank. Arthritis Rheumatol. 71:1634–41. DOI: 10.1002/art.40928. PMID: 31099188. PMCID: PMC6790695.21. Zhou A, Morris HA, Hyppönen E. 2019; Health effects associated with serum calcium concentrations: evidence from MR-PheWAS analysis in UK Biobank. Osteoporos Int. 30:2343–8. DOI: 10.1007/s00198-019-05118-z. PMID: 31392400.
Article22. Magnusson K, Turkiewicz A, Englund M. 2019; Nature vs nurture in knee osteoarthritis - the importance of age, sex and body mass index. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 27:586–92. DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2018.12.018. PMID: 30634033.
Article23. Weldingh E, Johnsen MB, Hagen KB, Østerås N, Risberg MA, Natvig B, et al. 2019; The maternal and paternal effects on clinically and surgically defined osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 71:1844–8. DOI: 10.1002/art.41023. PMID: 31237417.
Article24. Richard D, Liu Z, Cao J, Kiapour AM, Willen J, Yarlagadda S, et al. 2020; Evolutionary selection and constraint on human knee chondrocyte regulation impacts osteoarthritis risk. Cell. 181:362–81.e28. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.057. PMID: 32220312. PMCID: PMC7179902.
Article25. Zhao T, Zhao J, Ma C, Wei J, Wei B, Liu J. 2020; Common variants in LTBP3 gene contributed to the risk of hip osteoarthritis in Han Chinese population. Biosci Rep. 40:BSR20192999. DOI: 10.1042/BSR20192999. PMID: 32452514. PMCID: PMC7284319.
Article26. Wang B, Sun Y, Liu H, Cao Y, Lei T. 2020; Evaluation of relationship between DNA methyltransferase 3 β gene and the risk of hip osteoarthritis: a case-control study based on a Han Chinese population. Int J Rheum Dis. 23:1404–11. DOI: 10.1111/1756-185X.13943. PMID: 32776659.
Article27. Chu M, Zhu X, Wang C, Rong J, Wang Y, Wang S, et al. 2017; The rs4238326 polymorphism in ALDH1A2 gene potentially associated with non-post traumatic knee osteoarthritis susceptibility: a two-stage population-based study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 25:1062–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2017.01.003. PMID: 28089900.
Article28. Hsueh MF, Önnerfjord P, Bolognesi MP, Easley ME, Kraus VB. 2019; Analysis of "old" proteins unmasks dynamic gradient of cartilage turnover in human limbs. Sci Adv. 5:eaax3203. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aax3203. PMID: 31633025. PMCID: PMC6785252.
Article29. Bedson J, Croft PR. 2008; The discordance between clinical and radiographic knee osteoarthritis: a systematic search and summary of the literature. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 9:116. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-9-116. PMID: 18764949. PMCID: PMC2542996.
Article30. Hong JI, Park IY, Kim HA. 2020; Understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of arthritis pain using animal models. Int J Mol Sci. 21:533. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21020533. PMID: 31947680. PMCID: PMC7013391.
Article31. Neogi T, Felson D, Niu J, Nevitt M, Lewis CE, Aliabadi P, et al. 2009; Association between radiographic features of knee osteoarthritis and pain: results from two cohort studies. BMJ. 339:b2844. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.b2844. PMID: 19700505. PMCID: PMC2730438.
Article32. Wang K, Kim HA, Felson DT, Xu L, Kim DH, Nevitt MC, et al. 2018; Radiographic knee osteoarthritis and knee pain: cross-sectional study from five different racial/ethnic populations. Sci Rep. 8:1364. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-19470-3. PMID: 29358690. PMCID: PMC5777996.
Article33. Son KM, Hong JI, Kim DH, Jang DG, Crema MD, Kim HA. 2020; Absence of pain in subjects with advanced radiographic knee osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 21:640. DOI: 10.1186/s12891-020-03647-x. PMID: 32993609. PMCID: PMC7526196.
Article34. Yusuf E, Kortekaas MC, Watt I, Huizinga TW, Kloppenburg M. 2011; Do knee abnormalities visualised on MRI explain knee pain in knee osteoarthritis? A systematic review. Ann Rheum Dis. 70:60–7. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2010.131904. PMID: 20829200.
Article35. Aso K, Shahtaheri SM, Hill R, Wilson D, McWilliams DF, Walsh DA. 2019; Associations of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis with histopathologic features in subchondral bone. Arthritis Rheumatol. 71:916–24. DOI: 10.1002/art.40820. PMID: 30663865.
Article36. Zhu S, Zhu J, Zhen G, Hu Y, An S, Li Y, et al. 2019; Subchondral bone osteoclasts induce sensory innervation and osteoarthritis pain. J Clin Invest. 129:1076–93. DOI: 10.1172/JCI121561. PMID: 30530994. PMCID: PMC6391093.
Article37. Neogi T, Frey-Law L, Scholz J, Niu J, Arendt-Nielsen L, Woolf C, et al. Multicenter Osteoarthritis (MOST) Study. 2015; Sensitivity and sensitisation in relation to pain severity in knee osteoarthritis: trait or state? Ann Rheum Dis. 74:682–8. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204191. PMID: 24351516. PMCID: PMC4062615.
Article38. Suri S, Gill SE, Massena de Camin S, Wilson D, McWilliams DF, Walsh DA. 2007; Neurovascular invasion at the osteochondral junction and in osteophytes in osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 66:1423–8. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.063354. PMID: 17446239. PMCID: PMC2111605.
Article39. Meng W, Adams MJ, Palmer CNA, et al. 23andMe Research Team, Shi J, Auton A. 2019; Genome-wide association study of knee pain identifies associations with GDF5 and COL27A1 in UK Biobank. Commun Biol. 2:321. Erratum. DOI: 10.1038/s42003-020-0880-x. PMID: 32218487. PMCID: PMC7098975.40. Boer CG, Hatzikotoulas K, Southam L, Stefánsdóttir L, Zhang Y, Coutinho de Almeida R, et al. 2021; Deciphering osteoarthritis genetics across 826,690 individuals from 9 populations. Cell. 184:4784–818.e17.41. Kim JR, Kim HA. 2020; Molecular mechanisms of sex-related differences in arthritis and associated pain. Int J Mol Sci. 21:7938. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21217938. PMID: 33114670. PMCID: PMC7663489.
Article42. Sorge RE, Mapplebeck JC, Rosen S, Beggs S, Taves S, Alexander JK, et al. 2015; Different immune cells mediate mechanical pain hypersensitivity in male and female mice. Nat Neurosci. 18:1081–3. DOI: 10.1038/nn.4053. PMID: 26120961. PMCID: PMC4772157.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent development in the treatment of osteoarthritis
- Cooled radiofrequency ablation of genicular nerves for knee osteoarthritis
- Current Trends of Research to Overcome Osteoarthritis
- Streptococcus pyogenes : Recent Research Provides New Insights into an Important Pathogen
- Association between Allergic Rhinitis and Osteoarthritis in the Korean Adult Population-Based on the 3rd to 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey