J Korean Foot Ankle Soc.
2022 Jun;26(2):103-106. 10.14193/jkfas.2022.26.2.103.
Peroneal Tendon Reconstruction Using Tibialis Posterior Allograft for Simultaneous Irreparable Peroneus Longus and Brevis Tendon Complete Rupture: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea
- KMID: 2530491
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14193/jkfas.2022.26.2.103
Abstract
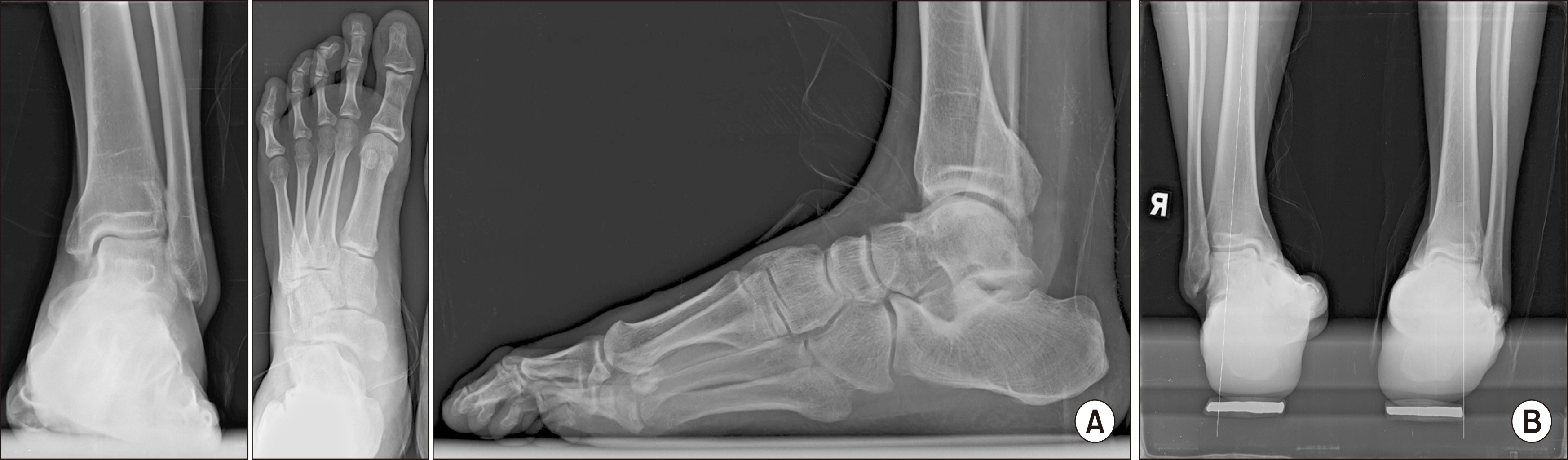
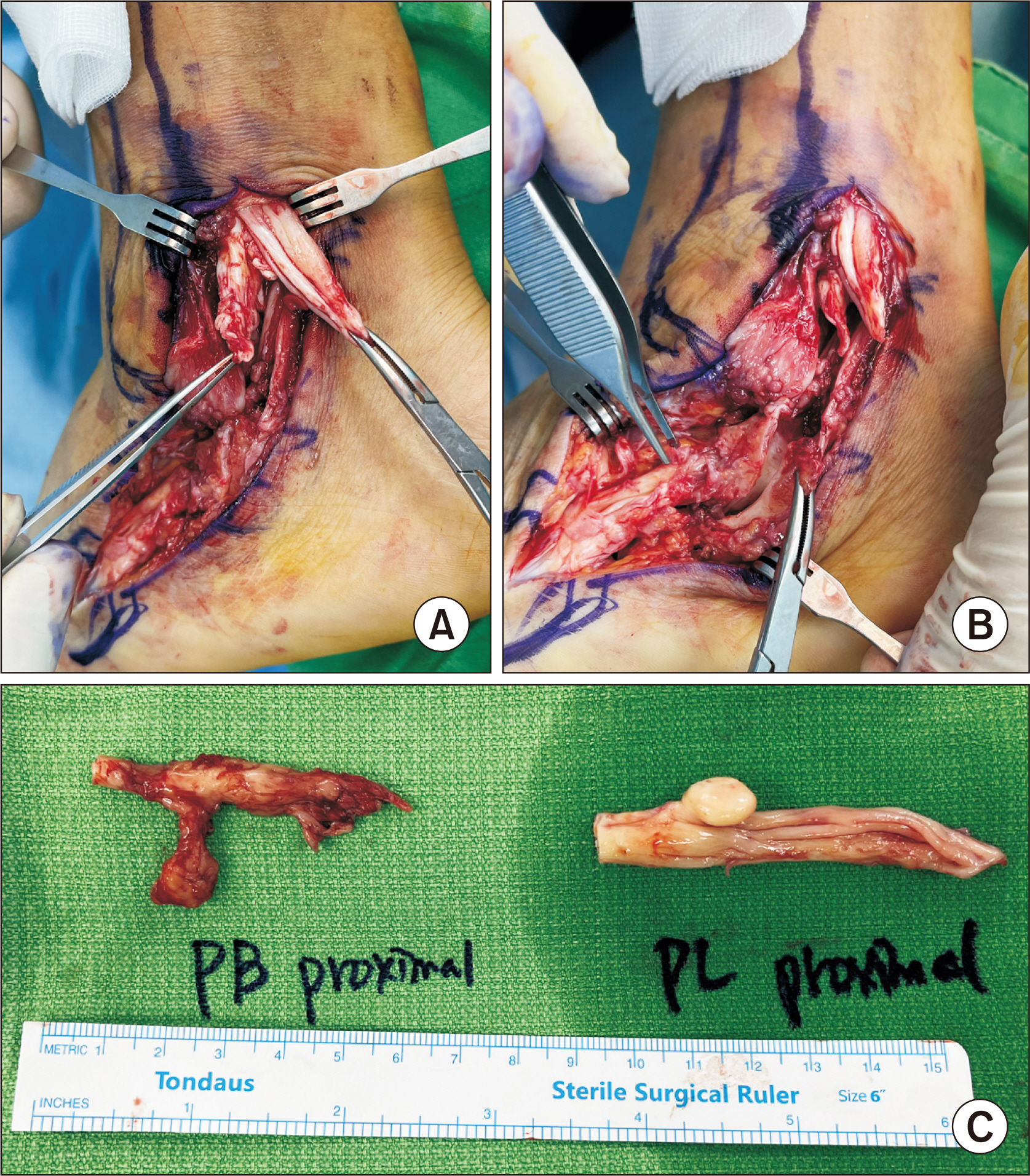
- Peroneal tendon disorders are one of many causes of chronic lateral ankle pain. They are related to chronic conditions and anatomical factors and can cause persistent pain and functional impairment if neglected. Peroneal tendon tears are frequently misdiagnosed due to the absence of clear symptoms. For subacute or chronic peroneal tendon ruptures, tendons often became irreparable, and hence various surgical options have been introduced to address this issue. Current surgical treatment options include debridement and tubularization, tenodesis, tendon transfer, and reconstruction with a graft. There have been a few reports on the use of reconstruction techniques with an allograft. In this report, we present a rare case of a peroneal tendon reconstruction technique using an allograft in a young male with simultaneous irreparable peroneus longus and a complete rupture of the brevis tendon. The management plan, prognostic outlook, and a subsequent review of the relevant literature are also presented.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Choudhary S, McNally E. 2011; Review of common and unusual causes of lateral ankle pain. Skeletal Radiol. 40:1399–413. doi: 10.1007/s00256-010-1040-z. DOI: 10.1007/s00256-010-1040-z. PMID: 20972871.
Article2. Molloy R, Tisdel C. 2003; Failed treatment of peroneal tendon injuries. Foot Ankle Clin. 8:115–29. ixdoi: 10.1016/s1083-7515(03)00006-8. DOI: 10.1016/S1083-7515(03)00006-8. PMID: 12760579.
Article3. Bahad SR, Kane JM. 2020; Peroneal tendon pathology: treatment and reconstruction of peroneal tears and instability. Orthop Clin North Am. 51:121–30. doi: 10.1016/j.ocl.2019.09.001. DOI: 10.1016/j.ocl.2019.09.001. PMID: 31739875.4. Davda K, Malhotra K, O'Donnell P, Singh D, Cullen N. 2017; Peroneal tendon disorders. EFORT Open Rev. 2:281–92. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.2. DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.2.160047. PMID: 28736620. PMCID: PMC5508858.
Article5. Pellegrini MJ, Glisson RR, Matsumoto T, Schiff A, Laver L, Easley ME, et al. 2016; Effectiveness of allograft reconstruction vs tenodesis for irreparable peroneus brevis tears: a cadaveric model. Foot Ankle Int. 37:803–8. doi: 10.1177/1071100716658469. DOI: 10.1177/1071100716658469. PMID: 27480963.6. Krause JO, Brodsky JW. 1998; Peroneus brevis tendon tears: pathophysiology, surgical reconstruction, and clinical results. Foot Ankle Int. 19:271–9. doi: 10.1177/107110079801900502. DOI: 10.1177/107110079801900502. PMID: 9622416.
Article7. Nishikawa DRC, Duarte FA, Saito GH, de Cesar Netto C, Monteiro AC, Prado MP, et al. 2019; Reconstruction of the peroneus brevis tendon tears with semitendinosus tendon autograft. Case Rep Orthop. 2019:5014687. doi: 10.1155/2019/5014687. DOI: 10.1155/2019/5014687. PMID: 31285931. PMCID: PMC6594286.
Article8. Mook WR, Nunley JA. 2013; Allograft reconstruction of irreparable peroneal tendon tears: a preliminary report. Duke Orthop J. 3:1–7. DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1022.
Article9. Mroz TE, Joyce MJ, Steinmetz MP, Lieberman IH, Wang JC. 2008; Musculoskeletal allograft risks and recalls in the United States. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 16:559–65. doi: 10.5435/00124635-200810000-00001. DOI: 10.5435/00124635-200810000-00001. PMID: 18832599.
Article10. Mook WR, Parekh SG, Nunley JA. 2013; Allograft reconstruction of peroneal tendons: operative technique and clinical outcomes. Foot Ankle Int. 34:1212–20. doi: 10.1177/1071100713487527. DOI: 10.1177/1071100713487527. PMID: 23613331.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fracture of the Os Peroneum with Rupture of the Peroneus Longus Tendon: A Case Report
- Operative Treatment of Stenosing Tenosynovitis of the Peroneus Longus Tendon Associated with Hypertrophy of the Peroneal Tubercle: A Case Report - 1 Case
- Tenodesis after Tendon Lengthening for Irreparable Tibialis Anterior Tendon Avulsion Injury: A Case Report
- Rupture of Peroneus Brevis Combined with Bimaileolar Fracture: A case Report
- Total Rupture of Peroneus Longus Tendon Through an Os Peroneum Fracture Treated by Tendon Transfer (A Case Report)