Current Status of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Target Achievement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea Compared with Recent Guidelines
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kyung Hee Medical Center, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Outcomes Research/Real World Data Team, Viatris Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Biostatistics, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of Endocrinology, Keimyung University Dongsan Hospital, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 7Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- 8Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea
- 9Department of Endocrinology, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea
- 10Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Hwasun, Korea
- 11Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 12Department of Endocrinology, St. Vincent’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Korea
- 13Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju National University College of Medicine, Jeju, Korea
- 14Department of Endocrinology, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 15Department of Endocrinology, Myongji Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea
- 16Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 17Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea
- 18Department of Endocrinology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 19Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Bucheon St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea
- KMID: 2530185
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0088
Abstract
- Background
We evaluated the achievement of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) targets in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) according to up-to-date Korean Diabetes Association (KDA), European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS), and American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines.
Methods
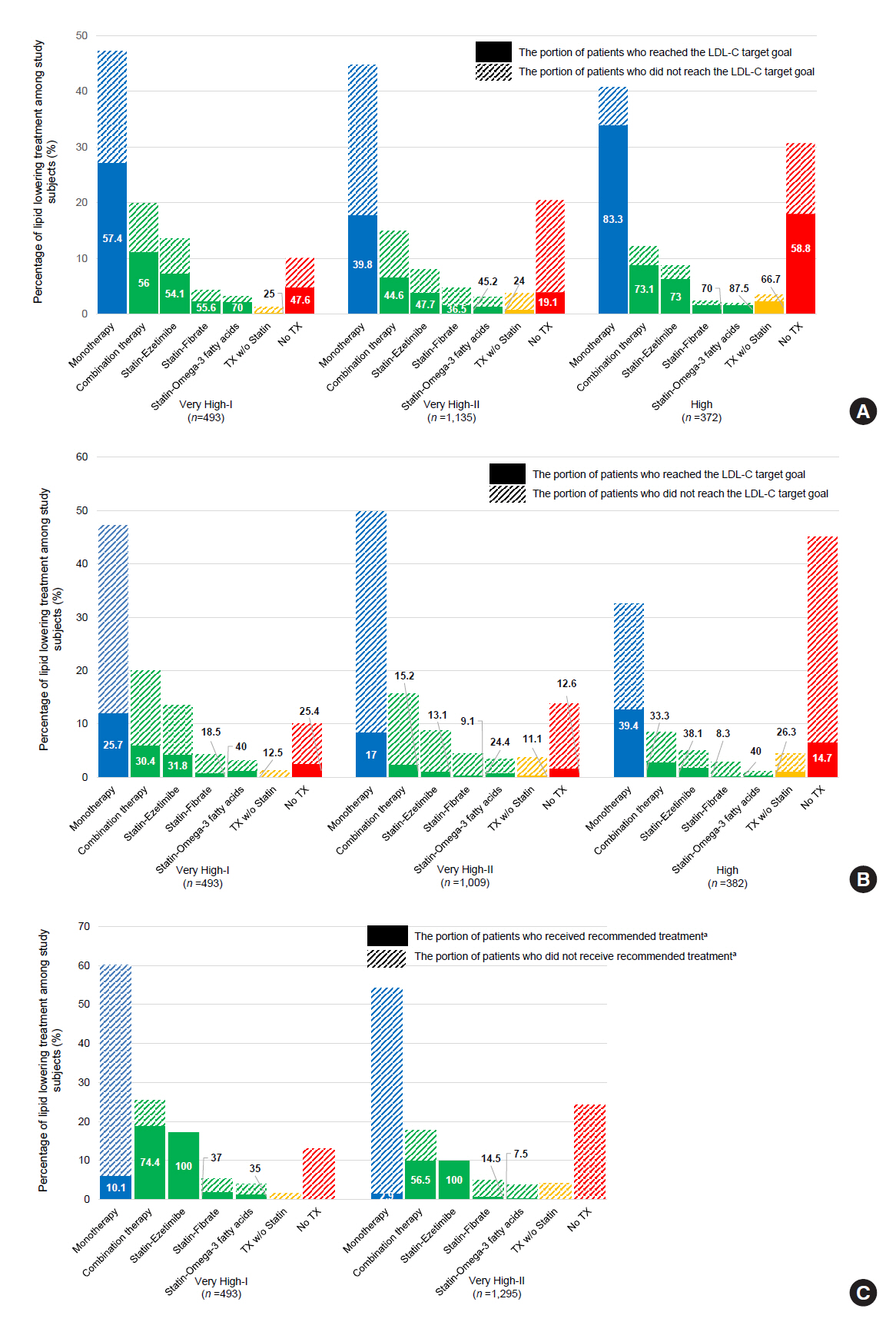
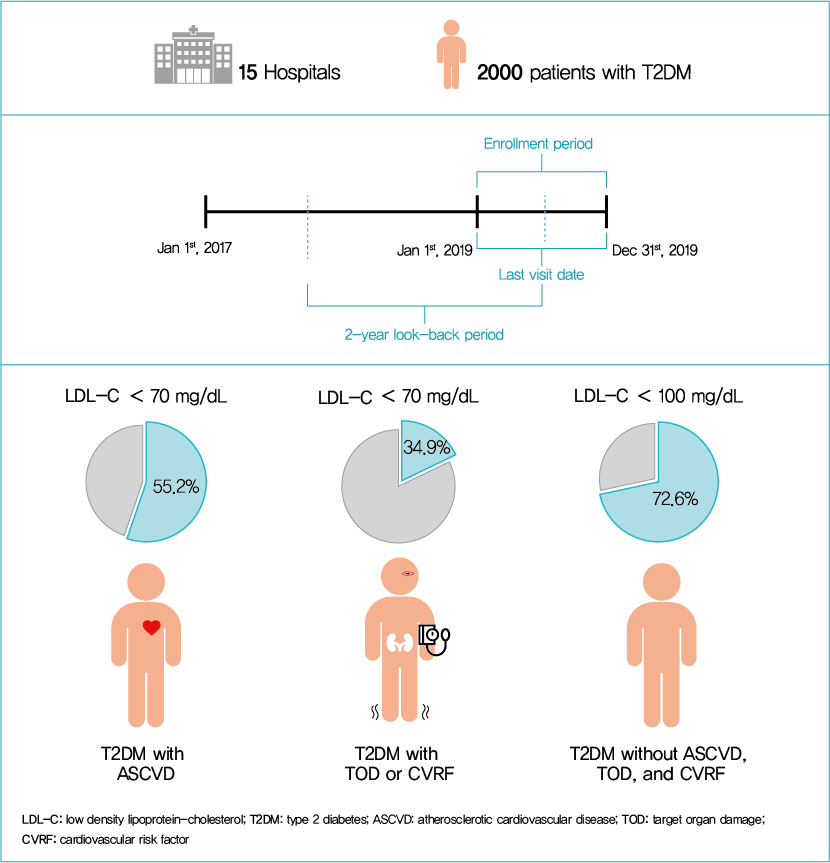
This retrospective cohort study collected electronic medical record data from patients with T2DM (≥20 years) managed by endocrinologists from 15 hospitals in Korea (January to December 2019). Patients were categorized according to guidelines to assess LDL-C target achievement. KDA (2019): Very High-I (atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [ASCVD]) <70 mg/dL; Very High-II (target organ damage [TOD], or cardiovascular risk factors [CVRFs]) <70 mg/dL; high (others) <100 mg/dL. ESC/EAS (2019): Very High-I (ASCVD): <55 mg/dL; Very High-II (TOD or ≥3-CVRF) <55 mg/dL; high (diabetes ≥10 years without TOD plus any CVRF) <70 mg/dL; moderate (diabetes <10 years without CVRF) <100 mg/dL. ADA (2019): Very High-I (ASCVD); Very High-II (age ≥40+ TOD, or any CVRF), for high intensity statin or statin combined with ezetimibe.
Results
Among 2,000 T2DM patients (mean age 62.6 years; male 55.9%; mean glycosylated hemoglobin 7.2%) ASCVD prevalence was 24.7%. Of 1,455 (72.8%) patients treated with statins, 73.9% received monotherapy. According to KDA guidelines, LDL-C target achievement rates were 55.2% in Very High-I and 34.9% in Very High-II patients. With ESC/EAS guidelines, target attainment rates were 26.6% in Very High-I, 15.7% in Very High-II, and 25.9% in high risk patients. Based on ADA guidelines, most patients (78.9%) were very-high risk; however, only 15.5% received high-intensity statin or combination therapy.
Conclusion
According to current dyslipidemia management guidelines, LDL-C goal achievement remains suboptimal in Korean patients with T2DM.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):1-9. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0448.Study Design and Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial to Assess Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of a Triple Combination of Ezetimibe, Fenofibrate, and Moderate-Intensity Statin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Modifiable Cardiovascular Risk Factors (ENSEMBLE)
Nam Hoon Kim, Juneyoung Lee, Suk Chon, Jae Myung Yu, In-Kyung Jeong, Soo Lim, Won Jun Kim, Keeho Song, Ho Chan Cho, Hea Min Yu, Kyoung-Ah Kim, Sang Soo Kim, Soon Hee Lee, Chong Hwa Kim, Soo Heon Kwak, Yong‐ho Lee, Choon Hee Chung, Sihoon Lee, Heung Yong Jin, Jae Hyuk Lee, Gwanpyo Koh, Sang-Yong Kim, Jaetaek Kim, Ju Hee Lee, Tae Nyun Kim, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Ji Hyun Lee, Jae-Han Jeon, Hye Jin Yoo, Hee Kyung Kim, Hyeong-Kyu Park, Il Seong Nam-Goong, Seongbin Hong, Chul Woo Ahn, Ji Hee Yu, Jong Heon Park, Keun-Gyu Park, Chan Ho Park, Kyong Hye Joung, Ohk-Hyun Ryu, Keun Yong Park, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Bong-Soo Cha, Kyu Chang Won, Yoon-Sok Chung, Sin Gon Kim
Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(5):722-731. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2024.1995.
Reference
-
1. International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas. Brussels: IDF;2019.2. Kim BY, Won JC, Lee JH, Kim HS, Park JH, Ha KH, et al. Diabetes fact sheets in Korea, 2018: an appraisal of current status. Diabetes Metab J. 2019; 43:487–94.
Article3. Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010; 87:4–14.
Article4. Jung CH, Son JW, Kang S, Kim WJ, Kim HS, Kim HS, et al. Diabetes fact sheets in Korea, 2020: an appraisal of current status. Diabetes Metab J. 2021; 45:1–10.
Article5. Vital Statistics Division Statistics Korea, Shin HY, Kim J, Lee S, Park MS, Park S, et al. Cause-of-death statistics in 2018 in the Republic of Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2020; 63:286–97.
Article6. Kim MK, Ko SH, Kim BY, Kang ES, Noh J, Kim SK, et al. 2019 Clinical practice guidelines for type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2019; 43:398–406.
Article7. Park JH, Ha KH, Kim BY, Lee JH, Kim DJ. Trends in cardiovascular complications and mortality among patients with diabetes in South Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2021; 45:120–4.
Article8. Kang YM, Kim YJ, Park JY, Lee WJ, Jung CH. Mortality and causes of death in a national sample of type 2 diabetic patients in Korea from 2002 to 2013. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2016; 15:131.
Article9. Kim KJ, Kwon TY, Yu S, Seo JA, Kim NH, Choi KM, et al. Tenyear mortality trends for adults with and without diabetes mellitus in South Korea, 2003 to 2013. Diabetes Metab J. 2018; 42:394–401.
Article10. American Diabetes Association. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care. 2019; 42(Suppl 1):S103–23.11. Cosentino F, Grant PJ, Aboyans V, Bailey CJ, Ceriello A, Delgado V, et al. 2019 ESC guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur Heart J. 2020; 41:255–323.12. Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, Beam C, Birtcher KK, Blumenthal RS, et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA guideline on the management of blood cholesterol: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. 2019; 139:e1082–143.13. Gerstein HC, Colhoun HM, Dagenais GR, Diaz R, Lakshmanan M, Pais P, et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): a double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2019; 394:121–30.14. Rhee EJ, Kim HC, Kim JH, Lee EY, Kim BJ, Kim EM, et al. 2018 Guidelines for the management of dyslipidemia in Korea. J Lipid Atheroscler. 2019; 8:78–131.
Article15. Catapano AL, Graham I, De Backer G, Wiklund O, Chapman MJ, Drexel H, et al. 2016 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias. Eur Heart J. 2016; 37:2999–3058.
Article16. Ko SH, Kim SR, Kim DJ, Oh SJ, Lee HJ, Shim KH, et al. 2011 Clinical practice guidelines for type 2 diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:431–6.
Article17. Hwang JY, Jung CH, Lee WJ, Park CY, Kim SR, Yoon KH, et al. Low density lipoprotein cholesterol target goal attainment rate and physician perceptions about target goal achievement in Korean patients with diabetes. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:628–36.
Article18. Yang YS, Yang BR, Kim MS, Hwang Y, Choi SH. Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol goal attainment rates in high-risk patients with cardiovascular diseases and diabetes mellitus in Korea: a retrospective cohort study. Lipids Health Dis. 2020; 19:5.
Article19. Cho S, Jang H, Park K. Trends in the management levels of metabolic risk factors in middle-aged and elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1998-2014. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0189361.
Article20. Yang YS, Lee SY, Kim JS, Choi KM, Lee KW, Lee SC, et al. Achievement of LDL-C targets defined by ESC/EAS (2011) guidelines in risk-stratified Korean patients with dyslipidemia receiving lipid-modifying treatments. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2020; 35:367–76.
Article21. Salami JA, Warraich H, Valero-Elizondo J, Spatz ES, Desai NR, Rana JS, et al. National trends in statin use and expenditures in the US adult population from 2002 to 2013: insights from the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey. JAMA Cardiol. 2017; 2:56–65.
Article22. Cannon CP, Braunwald E, McCabe CH, Rader DJ, Rouleau JL, Belder R, et al. Intensive versus moderate lipid lowering with statins after acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:1495–504.
Article23. Dinneen SF, Gerstein HC. The association of microalbuminuria and mortality in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. A systematic overview of the literature. Arch Intern Med. 1997; 157:1413–8.
Article24. Kannel WB, McGee DL. Diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors: the Framingham study. Circulation. 1979; 59:8–13.
Article25. Collins R, Reith C, Emberson J, Armitage J, Baigent C, Blackwell L, et al. Interpretation of the evidence for the efficacy and safety of statin therapy. Lancet. 2016; 388:2532–61.
Article26. Mooradian AD. Dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 5:150–9.
Article27. Jellinger PS, Handelsman Y, Rosenblit PD, Bloomgarden ZT, Fonseca VA, Garber AJ, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology guidelines for management of dyslipidemia and prevention of cardiovascular disease. Endocr Pract. 2017; 23(Suppl 2):1–87.
Article28. Cannon CP, Giugliano RP, Blazing MA, Harrington RA, Peterson JL, Sisk CM, et al. Rationale and design of IMPROVE-IT (IMProved Reduction of Outcomes: Vytorin Efficacy International Trial): comparison of ezetimbe/simvastatin versus simvastatin monotherapy on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Am Heart J. 2008; 156:826–32.
Article29. Breuker C, Clement F, Mura T, Macioce V, Castet-Nicolas A, Audurier Y, et al. Non-achievement of LDL-cholesterol targets in patients with diabetes at very-high cardiovascular risk receiving statin treatment: incidence and risk factors. Int J Cardiol. 2018; 268:195–9.
Article30. Ding R, Ye P, Zhao S, Zhao D, Yan X, Dong Y, et al. Effect of physician characteristics and knowledge on the quality of dyslipidemia management and LDL-C target goal achievement in China: subgroup analysis of the Dyslipidemia International Study. J Glob Health. 2017; 7:020702.
Article31. Khunti K, Ceriello A, Cos X, De Block C. Achievement of guideline targets for blood pressure, lipid, and glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018; 137:137–48.
Article32. Lee SH, Song WH, Jeong MH, Hur SH, Jeon DW, Jeung W, et al. Dyslipidemia and rate of under-target low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol in patients with coronary artery disease in Korea. J Lipid Atheroscler. 2019; 8:242–51.
Article33. Kim S, Han S, Rane PP, Qian Y, Zhao Z, Suh HS. Achievement of the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol goal among patients with dyslipidemia in South Korea. PLoS One. 2020; 15:e0228472.
Article34. Liao JK. Safety and efficacy of statins in Asians. Am J Cardiol. 2007; 99:410–4.
Article35. Naito R, Miyauchi K, Daida H. Racial differences in the cholesterol-lowering effect of statin. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2017; 24:19–25.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent Guideline for the Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes
- Recent dyslipidemia guidelines for patients with diabetes mellitus
- Dyslipidemia Treatment in Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- Non-achievement of the Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Goal in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and a Very High Cardiovascular Disease Risk: A Multicenter Study in Vietnam
- Therapeutic Target Achievement in Type 2 Diabetic Patients after Hyperglycemia, Hypertension, Dyslipidemia Management