Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2022 May;26(2):133-137. 10.14701/ahbps.21-161.
Pure laparoscopic versus open left lateral sectionectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma: A propensity score matching analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hepatobiliary Surgery and Liver transplantation, Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2530091
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.21-161
Abstract
- Backgrounds/Aims
Anatomical resection has superior oncologic outcomes over non-anatomical resection in hepatocellular carcinoma, and left lateral sectionectomy is the simplest and easiest perform anatomical resection procedure among liver resections. The purpose of this study was to find out the safety and feasibility of pure laparoscopic left lateral sectionectomy (PLLLS) for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Methods
Patients who underwent left lateral sectionectomy at a tertiary referral hospital, from August 2007 to April 2019 were enrolled in this retrospective study. After matching the 1 : 3 propensity score, 17 open and 51 pure laparoscopic cases were selected out of 102 cases of total left lateral resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. The group was analyzed in terms of patient demographics, preoperative data, and postoperative outcomes.
Results
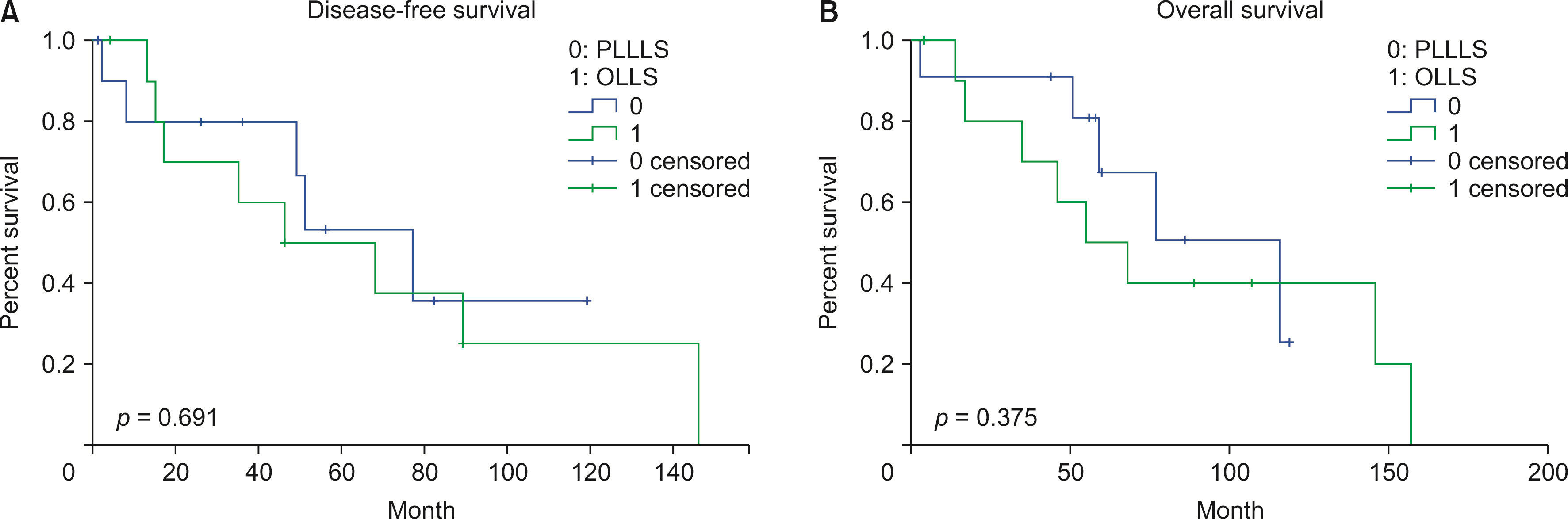
During the study period, there was no open conversion case. The mean operative time and complication were not statistically significant different between the two groups. There was no statistically significant difference in disease-free survival and overall survival had no statistical between the two groups. There were no mortality cases, and postoperative hospital stay was significantly shorter in the PLLLS group than in the open left lateral sectionectomy (OLLS) group.
Conclusions
The oncologic outcomes and complication rate were the same in the PLLLS and OLLS groups. However, the hospital stay was shorter in the PLLLS group than in the OLLS group. The present study findings demonstrate that the PLLLS is a safe and feasible procedure for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gagner M. 1992; Laparoscopic partial hepatectomy for liver tumor. Surg Endosc. 6:97–98.2. Nguyen KT, Gamblin TC, Geller DA. 2009; World review of laparoscopic liver resection-2,804 patients. Ann Surg. 250:831–841. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181b0c4df. PMID: 19801936.
Article3. Cho HD, Kim KH, Hwang S, Ahn CS, Moon DB, Ha TY, et al. 2018; Comparison of pure laparoscopic versus open left hemihepatectomy by multivariate analysis: a retrospective cohort study. Surg Endosc. 32:643–650. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-017-5714-7. PMID: 28733730.
Article4. Yoon YI, Kim KH, Kang SH, Kim WJ, Shin MH, Lee SK, et al. 2017; Pure laparoscopic versus open right hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: a propensity score matched analysis. Ann Surg. 265:856–863. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002072. PMID: 27849661.
Article5. Cheung TT, Poon RT, Dai WC, Chok KS, Chan SC, Lo CM. 2016; Pure laparoscopic versus open left lateral sectionectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a single-center experience. World J Surg. 40:198–205. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-015-3237-8. PMID: 26316115.
Article6. Yamamoto M, Takasaki K, Ohtsubo T, Katsuragawa H, Fukuda C, Katagiri S. 2001; Effectiveness of systematized hepatectomy with Glisson's pedicle transection at the hepatic hilus for small nodular hepatocellular carcinoma: retrospective analysis. Surgery. 130:443–448. DOI: 10.1067/msy.2001.116406. PMID: 11562668.
Article7. Eguchi S, Kanematsu T, Arii S, Okazaki M, Okita K, Omata M, et al. 2008; Comparison of the outcomes between an anatomical subsegmentectomy and a non-anatomical minor hepatectomy for single hepatocellular carcinomas based on a Japanese nationwide survey. Surgery. 143:469–475. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2007.12.003. PMID: 18374043.
Article8. Jung DH, Hwang S, Lee YJ, Kim KH, Song GW, Ahn CS, et al. 2019; Small hepatocellular carcinoma with low tumor marker expression benefits more from anatomical resection than tumors with aggressive biology. Ann Surg. 269:511–519. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002486. PMID: 28837444.
Article9. Yang TH, Chen JL, Lin YJ, Chao YJ, Shan YS, Hsu HP, et al. 2018; Laparoscopic surgery for large left lateral liver tumors: safety and oncologic outcomes. Surg Endosc. 32:4314–4320. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-018-6287-9. PMID: 29959523.
Article10. Macacari RL, Coelho FF, Bernardo WM, Kruger JAP, Jeismann VB, Fonseca GM, et al. 2019; Laparoscopic vs. open left lateral sectionectomy: an update meta-analysis of randomized and non-randomized controlled trials. Int J Surg. 61:1–10. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.11.021. PMID: 30496866.
Article11. Vigano L, Laurent A, Tayar C, Tomatis M, Ponti A, Cherqui D. 2009; The learning curve in laparoscopic liver resection: improved feasibility and reproducibility. Ann Surg. 250:772–782. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181bd93b2. PMID: 19801926.12. Chua D, Syn N, Koh YX, Goh BKP. 2021; Learning curves in minimally invasive hepatectomy: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Br J Surg. 108:351–358. DOI: 10.1093/bjs/znaa118. PMID: 33779690.
Article13. Dokmak S, Raut V, Aussilhou B, Ftériche FS, Farges O, Sauvanet A, et al. 2014; Laparoscopic left lateral resection is the gold standard for benign liver lesions: a case-control study. HPB (Oxford). 16:183–187. DOI: 10.1111/hpb.12108. PMID: 23600942. PMCID: PMC3921015.
Article14. Wakabayashi G, Cherqui D, Geller DA, Buell JF, Kaneko H, Han HS, et al. 2015; Recommendations for laparoscopic liver resection: a report from the second international consensus conference held in Morioka. Ann Surg. 261:619–629. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001184. PMID: 25742461.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Laparoscopic hepatectomy versus open hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma: A propensity case-matched analysis of the long-term survival
- Is left lateral sectionectomy of the liver without operative site drainage safe and effective?
- Current status of laparoscopic liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma
- Laparoscopic right posterior sectionectomy for a large hepatocellular carcinoma close to inferior vena cava
- Outcomes of Laparoscopic Left Lateral Sectionectomy vs. Open Left Lateral Sectionectomy: Single Center Experience