Clin Endosc.
2022 May;55(3):408-416. 10.5946/ce.2021.200.
Comparison of conventional and new endoscopic band ligation devices for colonic diverticular bleeding
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, St. Luke’s International Hospital, Tokyo, Japan
- KMID: 2529963
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2021.200
Abstract
- Background/Aims
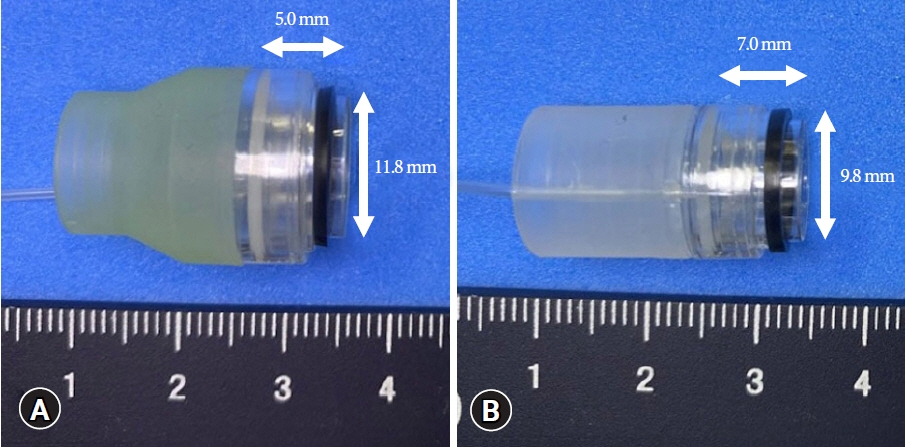
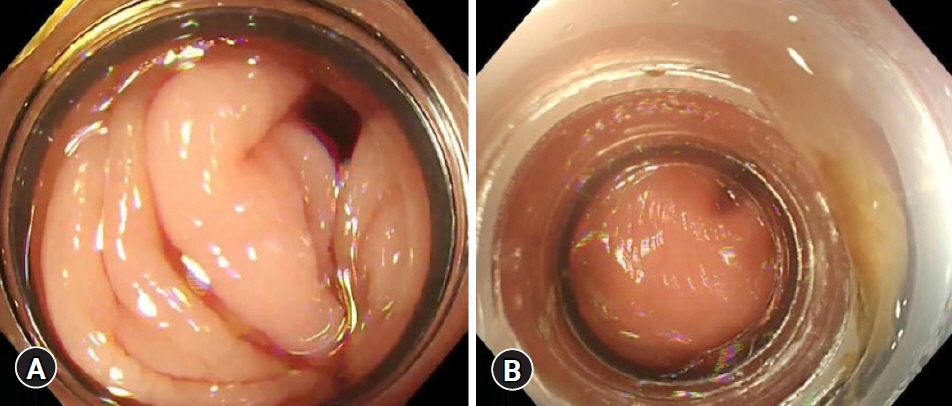
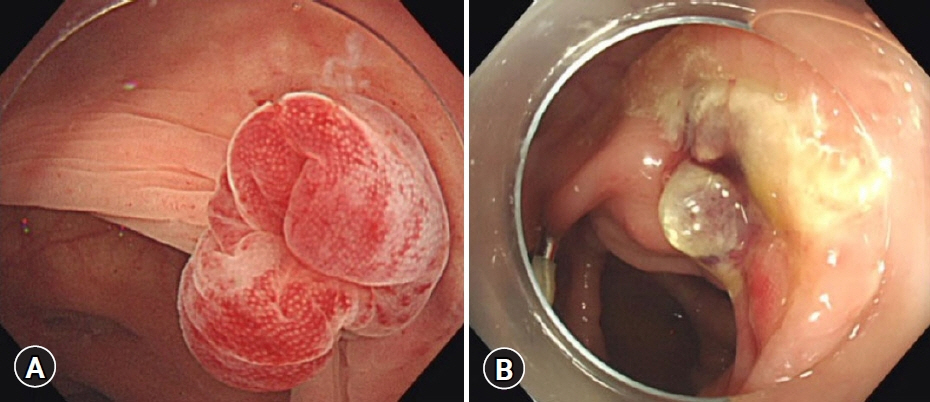
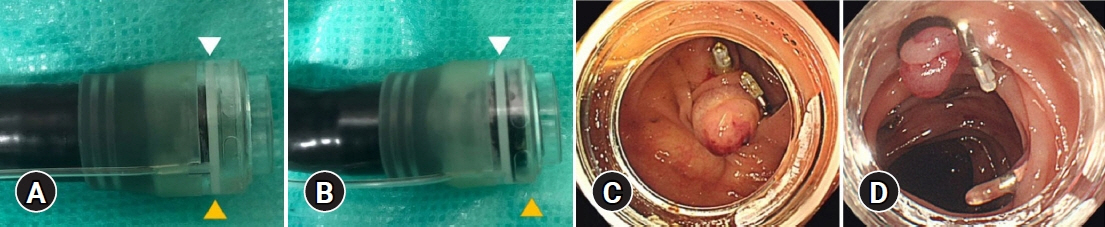
Endoscopic band ligation (EBL) is used to treat colonic diverticular bleeding (CDB). An endoscopic variceal ligation device for esophageal varices is used as a conventional EBL device (C-EBL). A new EBL device (N-EBL) was developed by Sumitomo Bakelite Co. in August 2018. We aimed to evaluate the clinical outcomes of N-EBL compared with those of C-EBL.
Methods
Seventy-nine patients who underwent EBL for CDB at St. Luke’s International Hospital, Japan, between 2017 and 2020 were included in this retrospective study. Patients were divided into the C-EBL and N-EBL groups. Their clinical outcomes, including achieving initial hemostasis, early rebleeding, procedure time, and EBL-associated adverse events, were evaluated.
Results
Of the 79 patients, 36 (45.6%) were in the C-EBL group and 43 (54.4%) were in the N-EBL group. The rate of achieving initial hemostasis was 100% in the C-EBL group and 93.0% in the N-EBL group. No significant difference was noted in the early rebleeding rate between the groups (p=0.24). The N-EBL group achieved a shorter median EBL procedure time than the C-EBL group (18.2 minutes vs. 14.2 minutes, p=0.02). No adverse events were observed in either group.
Conclusions
The N-EBL device is safe and useful and may reduce EBL procedure time.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nagata N, Niikura R, Aoki T, et al. Increase in colonic diverticulosis and diverticular hemorrhage in an aging society: lessons from a 9-year colonoscopic study of 28,192 patients in Japan. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2014; 29:379–385.2. Nakano K, Ishii N, Ikeya T, et al. Comparison of long-term outcomes between endoscopic band ligation and endoscopic clipping for colonic diverticular hemorrhage. Endosc Int Open. 2015; 3:E529–E533.3. Ishii N, Omata F, Nagata N, et al. Effectiveness of endoscopic treatments for colonic diverticular bleeding. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018; 87:58–66.4. Nagata N, Ishii N, Kaise M, et al. Long-term recurrent bleeding risk after endoscopic therapy for definitive colonic diverticular bleeding: band ligation versus clipping. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018; 88:841–853.e4.5. Nagata N, Ishii N, Manabe N, et al. Guidelines for colonic diverticular bleeding and colonic diverticulitis: Japan Gastroenterological Association. Digestion. 2019; 99(Suppl 1):1–26.6. Witte JT. Band ligation for colonic bleeding: modification of multiband ligating devices for use with a colonoscope. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 52:762–765.7. Farrell JJ, Graeme-Cook F, Kelsey PB. Treatment of bleeding colonic diverticula by endoscopic band ligation: an in-vivo and ex-vivo pilot study. Endoscopy. 2003; 35:823–829.8. Ishii N, Itoh T, Uemura M, et al. Endoscopic band ligation with a water-jet scope for the treatment of colonic diverticular hemorrhage. Dig Endosc. 2010; 22:232–235.9. Ishii N, Uemura M, Itoh T, et al. Endoscopic band ligation for the treatment of bleeding colonic and ileal diverticula. Endoscopy. 2010; 42(Suppl 2):E82–E83.10. Jensen DM, Machicado GA, Jutabha R, et al. Urgent colonoscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of severe diverticular hemorrhage. N Engl J Med. 2000; 342:78–82.11. Shimamura Y, Ishii N, Omata F, et al. Endoscopic band ligation for colonic diverticular bleeding: possibility of standardization. Endosc Int Open. 2016; 4:E233–E237.12. Setoyama T, Ishii N, Fujita Y. Enodoscopic band ligation (EBL) is superior to endoscopic clipping for the treatment of colonic diverticular hemorrhage. Surg Endosc. 2011; 25:3574–3578.13. Sato Y, Yasuda H, Fukuoka A, et al. Delayed perforation after endoscopic band ligation for colonic diverticular hemorrhage. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2020; 13:6–10.14. Takahashi S, Inaba T, Tanaka N. Delayed perforation after endoscopic band ligation for treatment of colonic diverticular bleeding. Dig Endosc. 2016; 28:484.15. Gilshtein H, Kluger Y, Khoury A, et al. Massive and recurrent diverticular hemorrhage, risk factors and treatment. Int J Surg. 2016; 33 Pt A:136–139.16. Nagata N, Niikura R, Aoki T, et al. Colonic diverticular hemorrhage associated with the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, low-dose aspirin, antiplatelet drugs, and dual therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014; 29:1786–1793.17. Barker KB, Arnold HL, Fillman EP, et al. Safety of band ligator use in the small bowel and the colon. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 62:224–227.18. Akimaru K, Suzuki H, Tsuruta H, et al. Eversion and ligation of a diverticulum: report of an inspirational case and subsequent animal study. J Nippon Med Sch. 2008; 75:157–161.19. Shiratori Y, Ikeya T, Suzuki K, et al. Comparison of endoscopic band ligation devices used for colonic diverticular bleeding: in vivo animal study. JGH Open. 2021; 5:50–55.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Therapy for Acute Diverticular Bleeding
- A new band ligation device to treat colonic diverticular bleeding
- Endoscopic Variceal Ligation by Use of Transparent Endoscopic Elastic Band Ligating Device
- The 3 cases of colonic diverticular bleeding treated by colonoscopic hemostatic procedures
- Endoscopic Ligation Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding