Ann Surg Treat Res.
2022 May;102(5):241-247. 10.4174/astr.2022.102.5.241.
Avoiding unnecessary intraoperative sentinel lymph node frozen section biopsy of patients with early breast cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 2Division of Breast Surgery, Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Hospital Pathology, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Radiology, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2529498
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2022.102.5.241
Abstract
- Purpose
After the publication of the ACOSOG (American College of Surgeons Oncology Group) Z0011 trial, the rate of axillary lymph node dissection has reduced. Thus, the need for intraoperative frozen section biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes (SLNs) has become controversial. We identified patients for whom intraoperative SLN frozen section biopsy could be omitted and found that frozen section biopsy rate can be reduced.
Methods
We reviewed the records of patients with tumors ≤5 cm in diameter who underwent breast-conserving surgery between January 2013 and December 2019 at Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital. Clinicopathological and imaging characteristics were compared according to number of positive SLNs (0–2 SLNs positive vs. ≥3 SLNs positive).
Results
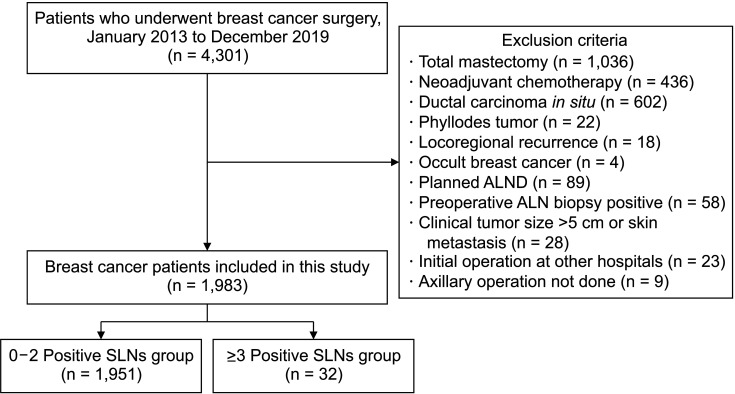
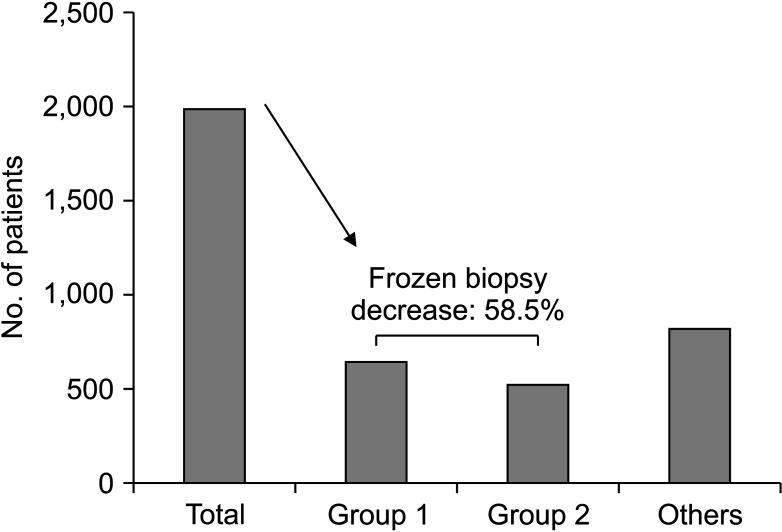
A total of 1,983 patients were included in this study. Thirty-two patients (1.6%) had at least 3 positive SLNs. Patients with ≥3 positive SLNs had significantly larger tumors and were more frequently high-grade tumors (P < 0.001 and P = 0.002, respectively). Identification of suspicious lymph nodes on imaging studies was also associated with the presence of ≥3 positive SLNs (hazard ratio, 11.54; 95% confidence interval, 4.42–30.10). All patients with none or only 1 suspicious lymph node on any imaging modality (n = 647, 32.6%) had 0–2 positive SLNs. Also, among patients with clinical T1-stage tumors and at least 2 suspicious lymph nodes on only 1 imaging modality (n = 514, 25.9%), only 2 cases had ≥3 positive SLNs.
Conclusion
We found that intraoperative SLN frozen biopsy could be omitted in patients using tumor size and axillary lymph node status on imaging modality.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Donker M, van Tienhoven G, Straver ME, Meijnen P, van de Velde CJ, Mansel RE, et al. Radiotherapy or surgery of the axilla after a positive sentinel node in breast cancer (EORTC 10981-22023 AMAROS): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014; 15:1303–1310. PMID: 25439688.2. Galimberti V, Cole BF, Zurrida S, Viale G, Luini A, Veronesi P, et al. Axillary dissection versus no axillary dissection in patients with sentinel-node micrometastases (IBCSG 23-01): a phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013; 14:297–305. PMID: 23491275.3. Giuliano AE, Ballman KV, McCall L, Beitsch PD, Brennan MB, Kelemen PR, et al. Effect of axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection on 10-year overall survival among women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: the ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017; 318:918–926. PMID: 28898379.4. Tseng J, Alban RF, Siegel E, Chung A, Giuliano AE, Amersi FF. Changes in utilization of axillary dissection in women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis after the ACOSOG Z0011 trial. Breast J. 2021; 27:216–221. PMID: 33586201.5. Poodt I, Spronk P, Vugts G, van Dalen T, Peeters M, Rots ML, et al. Trends on axillary surgery in nondistant metastatic breast cancer patients treated between 2011 and 2015: a Dutch population-based study in the ACOSOG-Z0011 and AMAROS era. Ann Surg. 2018; 268:1084–1090. PMID: 28742702.6. Kim EJ, Kim SH, Kang BJ, Choi BG, Song BJ, Choi JJ. Diagnostic value of breast MRI for predicting metastatic axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer patients: diffusion-weighted MRI and conventional MRI. Magn Reson Imaging. 2014; 32:1230–1236. PMID: 25072504.7. Choi WH, Yoo IR, O JH, Kim SH, Chung SK. The value of dual-time-point 18F-FDG PET/CT for identifying axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients. Br J Radiol. 2011; 84:593–599. PMID: 21081574.8. Bishop JA, Sun J, Ajkay N, Sanders MA. Decline in frozen section diagnosis for axillary sentinel lymph nodes as a result of the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Z0011 trial. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016; 140:830–835. PMID: 26716950.9. Cipolla C, Graceffa G, Cabibi D, Gangi G, Latteri M, Valerio MR, et al. Current role of intraoperative frozen section examination of sentinel lymph node in early breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2020; 40:1711–1717. PMID: 32132079.10. Jorns JM, Kidwell KM. Sentinel lymph node frozen-section utilization declines after publication of American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Z0011 trial results with no change in subsequent surgery for axillary lymph node dissection. Am J Clin Pathol. 2016; 146:57–66. PMID: 27373347.11. Lombardi A, Nigri G, Maggi S, Stanzani G, Vitale V, Vecchione A, et al. Role of frozen section in sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer in the era of the ACOSOG Z0011 and IBCSG 23-10 trials. Surgeon. 2018; 16:232–236. PMID: 29329752.12. Yoon KH, Park S, Kim JY, Park HS, Kim SI, Cho YU, et al. Is the frozen section examination for sentinel lymph node necessary in early breast cancer patients? Ann Surg Treat Res. 2019; 97:49–57. PMID: 31388507.13. Jung SM, Woo J, Ryu JM, Lee SK, Chae BJ, Yu J, et al. Is the intraoperative frozen section analysis of sentinel lymph nodes necessary in clinically negative node breast cancer? Ann Surg Treat Res. 2020; 99:251–258. PMID: 33163454.14. Lai SK, Masir N, Md Pauzi SH. Intraoperative frozen section sentinel lymph node assessment in breast cancer: a tertiary institution experience. Malays J Pathol. 2018; 40:121–128. PMID: 30173228.15. Godazande G, Moradi S, Naghshvar F, Shojaee L. Is necessary intraoprative frozen section in sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer patients? Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020; 21:647–651. PMID: 32212789.16. Ahn SK, Kim MK, Kim J, Lee E, Yoo TK, Lee HB, et al. Can we skip intraoperative evaluation of sentinel lymph nodes? Nomogram predicting involvement of three or more axillary lymph nodes before breast cancer surgery. Cancer Res Treat. 2017; 49:1088–1096. PMID: 28161935.17. Zeng D, Lin HY, Zhang YL, Wu JD, Lin K, Xu Y, et al. A negative binomial regression model for risk estimation of 0-2 axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer patients. Sci Rep. 2020; 10:21856. PMID: 33318591.18. Chang JM, Leung JW, Moy L, Ha SM, Moon WK. Axillary nodal evaluation in breast cancer: state of the art. Radiology. 2020; 295:500–515. PMID: 32315268.19. Zhang X, Liu Y, Luo H, Zhang J. PET/CT and MRI for identifying axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020; 52:1840–1851. PMID: 32567090.20. Liang X, Yu J, Wen B, Xie J, Cai Q, Yang Q. MRI and FDG-PET/CT based assessment of axillary lymph node metastasis in early breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Clin Radiol. 2017; 72:295–301. PMID: 28139203.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Use of Mammary Lymphoscintigraphy and Intraoperative Radioguided Gamma Probe in Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy of Breast Cancer
- The Number of Removed Lymph Nodes for an Acceptable False Negative Rate in Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Breast Cancer
- Reliability of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients
- Short Term Follow-up Data in Breast Cancer Patients with Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Alone
- Is the intraoperative frozen section analysis of sentinel lymph nodes necessary in clinically negative node breast cancer?