Acute Crit Care.
2022 Feb;37(1):127-130. 10.4266/acc.2021.01263.
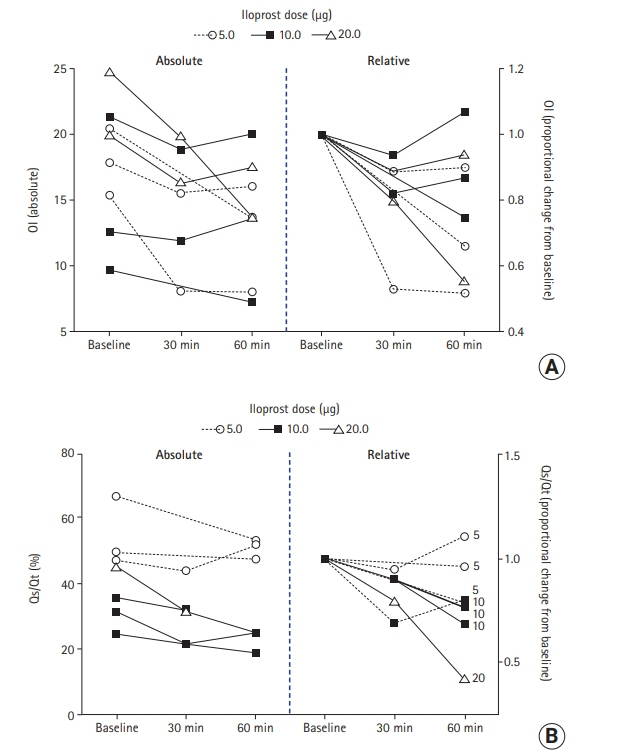
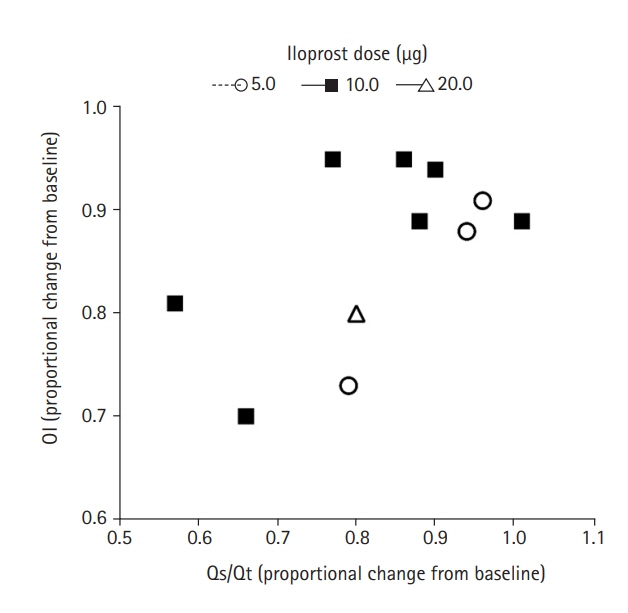
Inhaled iloprost can improve oxygenation and shunt fraction in severe COVID-19
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Intensive Care, VieCuri Medical Center, Venlo, Netherlands
- 2Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Maastricht University Medical Centre, Maastricht, Netherlands
- KMID: 2527917
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2021.01263
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gattinoni L, Coppola S, Cressoni M, Busana M, Rossi S, Chiumello D. COVID-19 Does not lead to a "typical" acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020; 201:1299–300.
Article2. Riva CM, Morganroth ML, Ljungman AG, Schoeneich SO, Marks RM, Todd RF 3rd, et al. Iloprost inhib-its neutrophil-induced lung injury and neutrophil adherence to endothelial monolayers. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990; 3:301–9.
Article3. Gu SX, Tyagi T, Jain K, Gu VW, Lee SH, Hwa JM, et al. Thrombocytopathy and endotheliopathy: crucial contributors to COVID-19 thromboinflammation. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021; 18:194–209.
Article4. Sonti R, Pike CW, Cobb N. Responsiveness of inhaled epoprostenol in respiratory failure due to COVID-19. J Intensive Care Med. 2021; 36:327–33.
Article5. Tsareva NA, Avdeev SN, Kosanovic D, Schermuly RT, Trushenko NV, Nekludova GV. Inhaled iloprost improves gas exchange in patients with COVID-19 and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care. 2021; 25:258.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: Treatment with inhaled iloprost
- The Therapeutic Effect of Inhaled Iloprost in Newborn Infants with Severe Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension Refractory to Inhaled Nitric Oxide
- Inhaled Iloprost as a First-Line Therapy for Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Newborn
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension is Normalized Following Six Years of Inhaled Iloprost Treatment in a Patient with Systemic Sclerosis
- Use of Inhaled Iloprost in an Infant With Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Pulmonary Artery Hypertension