Korean J Transplant.
2022 Mar;36(1):54-60. 10.4285/kjt.21.0034.
The influence of socioeconomic factors on deceased organ donation in Iran
- Affiliations
-
- 1Organ Procurement Unit, Sina Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 2Department of Urology, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 3Department of Urology, AJA University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- KMID: 2527898
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/kjt.21.0034
Abstract
- Background
There is a large gap between the number of patients on organ waiting lists and the number of available organs for donation. This study investigated the socioeconomic factors in Iran that influenced decisions for organ donation among the families of brain-dead donors.
Methods
This retrospective cross-sectional study was performed among the families of 333 organ donors in Iran. Two trained researchers interviewed family members about the donor’s age, sex, cause of brain death, education level, marital status, number of children, history of addiction, the financial status of the donor’s family, and reasons for which they considered refusing organ donation.
Results
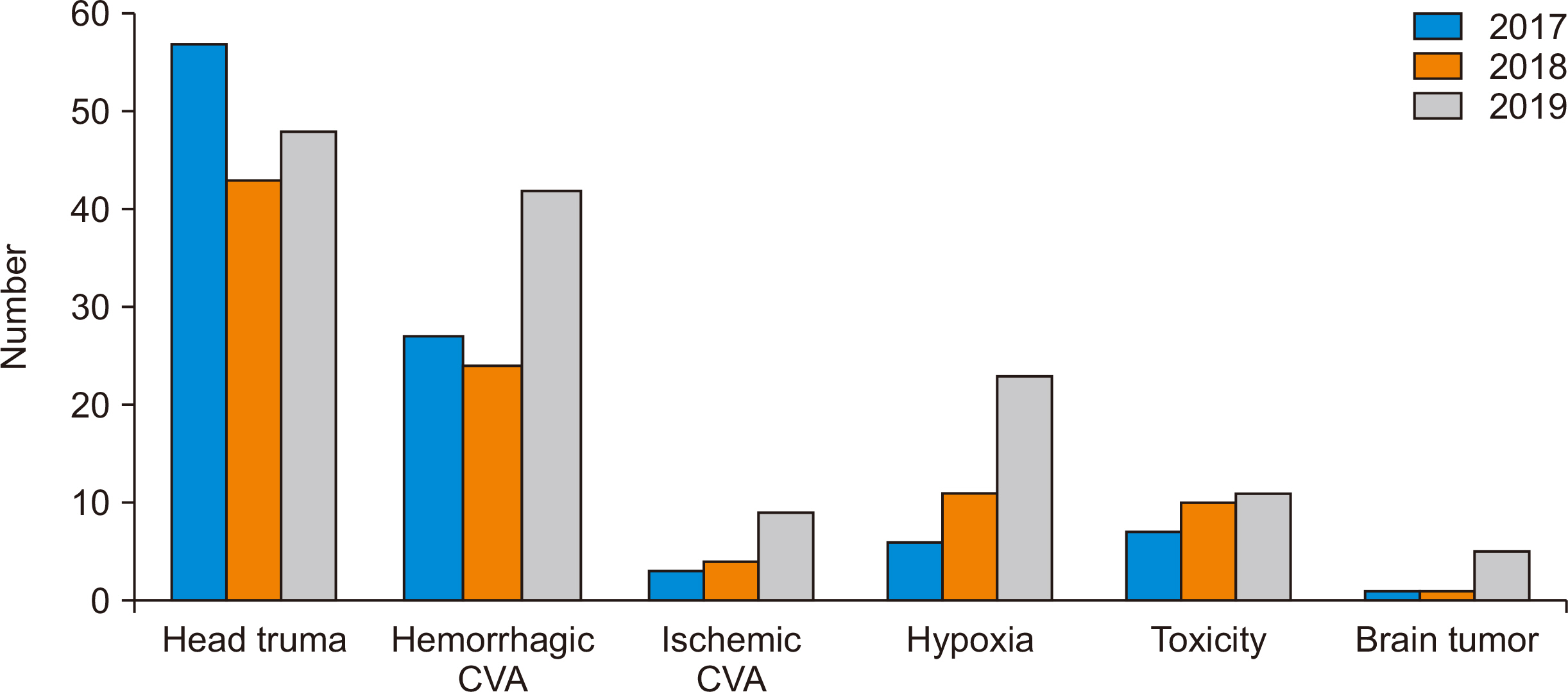
The mean age of the donors was 37.23±16.59 years. During 2017–2019, significant differences were found according to income (P<0.001), marital status (P<0.001), sex (P=0.04), and occupation (P=0.04). More than half of the organ donors were of low socioeconomic status, and nearly half were the sole income earners of large families. Trauma was the most common cause of death (44.6%). The most common reasons for which the families considered refusing organ donation were unfamiliarity with the concept of brain death, denial, and the expectation of a miracle.
Conclusions
The donor’s socioeconomic status and availability of social services, such as insurance coverage, psychological services, and mourning therapy courses, play an important role in organ donation. Adequate support for the deceased’s family after organ donation is imperative.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Da Silva IR, Frontera JA. 2015; Worldwide barriers to organ donation. JAMA Neurol. 72:112–8. DOI: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.3083. PMID: 25402335.
Article2. Iliyasu Z, Abubakar IS, Lawan UM, Abubakar M, Adamu B. 2014; Predictors of public attitude toward living organ donation in Kano, northern Nigeria. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 25:196–205. DOI: 10.4103/1319-2442.124577. PMID: 24434412.
Article3. Heng NW. 2019. Nudging family decision-making process on organ donation [thesis]. National University of Singapore;Singapore:4. Dhakate NN, Joshi R. 2020; Analysing process of organ donation and transplantation services in India at hospital level: SAP-LAP model. Glob J Flex Syst Manag. 21:323–39. DOI: 10.1007/s40171-020-00251-9.
Article5. Ministry of Health. 2021 Organ dontion statistics Tehran [Internet]. Tehran: Ministry of Health;cited 2022 Mar 15. Available from: medcare.health.gov.ir/hospman/dtsd/default.aspx.6. Lawlor M, Kerridge I, Ankeny R, Billson F. 2007; Public education and organ donation: untested assumptions and unexpected consequences. J Law Med. 14:360–6. PMID: 17355099.7. Najafizadeh K, Latifi M, Ghobadi O. 2019; What are the most important causes of family's refusal of organ donation from Iran's 10 provinces' organ donation coordinators? Transplantation. 103:S82–3. DOI: 10.1097/01.tp.0000612036.55662.30.8. Nathan HM, Conrad SL, Held PJ, McCullough KP, Pietroski RE, Siminoff LA, et al. 2003; Organ donation in the United States. Am J Transplant. 3 Suppl 4:29–40. DOI: 10.1034/j.1600-6143.3.s4.4.x. PMID: 12694048.
Article9. Hill EM. 2016; Posthumous organ donation attitudes, intentions to donate, and organ donor status: examining the role of the big five personality dimensions and altruism. Pers Individ Dif. 88:182–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.paid.2015.09.021.
Article10. Yilmaz TU. 2011; Importance of education in organ donation. Exp Clin Transplant. 9:370–5. PMID: 22142043.11. Riyanti S, Hatta M, Norhafizah S, Balkish MN, Siti ZM, Hamizatul Akmal AH, et al. 2014; Organ donation by sociodemographic characteristics in Malaysia. Asian Soc Sci. 10:264–72. DOI: 10.5539/ass.v10n4p264.12. Ranjbaran M, Soori H, Etemad K, Khodadost M. 2014; Relationship between Socioeconomic Status and review article health status and application of principal component analysis. J Jiroft Univ Med Sci. 1:9–19.13. Bahadorimonfared A, Soori H, Mehrabi Y, Delpisheh A, Esmaili A, Salehi M, et al. 2013; Trends of fatal road traffic injuries in Iran (2004-2011). PLoS One. 8:e65198. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065198. PMID: 23724132. PMCID: PMC3665536.
Article14. Afzal-Aghaee M, Khorsand Vakilzadeh A, Rahmanifar F, Movahed Nia N, Khaleghi E. 2016; Factors related to organ donation from brain dead patients in teaching hospitals of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences during 1392-1385. Med J Mashhad Univ Med Sci. 59:148–54.15. Adewole OA, Shoga MO, Williams OM, Famude OS, Kayode MO, Idowu SO. 2019; A 2-year review of the rotary-supported ponseti Clubfoot Clinic in Lagos, Nigeria. Niger J Orthop Trauma. 18:60–4. DOI: 10.4103/njot.njot_20_19.
Article16. Frutos MA, Blanca MJ, Mansilla JJ, Rando B, Ruiz P, Guerrero F, et al. 2005; Organ donation: a comparison of donating and nondonating families. Transplant Proc. 37:1557–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2005.02.048. PMID: 15866672.
Article17. Duyu M, Karakaya Z. 2020; Evaluation of patients diagnosed with brain death in paediatric critical care. J Pediatr Res. 7:250–6. DOI: 10.4274/jpr.galenos.2020.82474.
Article18. Ramadurg UY, Gupta A. 2014; Impact of an educational intervention on increasing the knowledge and changing the attitude and beliefs towards organ donation among medical students. J Clin Diagn Res. 8:JC05–7. DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/6594.4347. PMID: 24995198. PMCID: PMC4080019.
Article19. Spigner C, Weaver M, Cárdenas V, Allen MD. 2002; Organ donation and transplantation: ethnic differences in knowledge and opinions among urban high school students. Ethn Health. 7:87–101. DOI: 10.1080/1355785022000038579. PMID: 12511196.
Article20. Aghayan HR, Arjmand B, Emami-Razavi SH, Jafarian A, Shabanzadeh AR, Jalali F, et al. 2009; Organ donation workshop: a survey on nurses' knowledge and attitudes toward organ and tissue donation in Iran. Int J Artif Organs. 32:739–44. DOI: 10.1177/039139880903201005. PMID: 19943235.21. Ghaffari M, Rakhshanderou S, Najafizadeh K, Ramezankhani A, Latifi M. 2019; Determinants of medical students for intention to organ donation: application of theory of planned behavior. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 30:1375–80. DOI: 10.4103/1319-2442.275481. PMID: 31929284.
Article22. Pouraghaei M, Tagizadieh M, Tagizadieh A, Moharamzadeh P, Esfahanian S, Shahsavari Nia K. 2015; Knowledge and attitude regarding organ donation among relatives of patients referred to the emergency department. Emerg (Tehran). 3:33–9. PMID: 26512367. PMCID: PMC4614608.23. Heydari ST, Hoseinzadeh A, Ghaffarpasand F, Hedjazi A, Zarenezhad M, Moafian G, et al. 2013; Epidemiological characteristics of fatal traffic accidents in Fars province, Iran: a community-based survey. Public Health. 127:704–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.puhe.2013.05.003. PMID: 23871394.
Article24. Bilgel H, Sadikoglu G, Goktas O, Bilgel N. 2004; A survey of the public attitudes towards organ donation in a Turkish community and of the changes that have taken place in the last 12 years. Transpl Int. 17:126–30. DOI: 10.1111/j.1432-2277.2004.tb00416.x. PMID: 14745490.
Article25. Sehat M, Naieni KH, Asadi-Lari M, Foroushani AR, Malek-Afzali H. 2012; Socioeconomic status and incidence of traffic accidents in metropolitan Tehran: a population-based study. Int J Prev Med. 3:181–90. PMID: 22448311. PMCID: PMC3309632.26. Barcellos FC, Araujo CL, da Costa JD. 2005; Organ donation: a population-based study. Clin Transplant. 19:33–7. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2005.00280.x. PMID: 15659131.
Article27. Siminoff LA, Gordon N, Hewlett J, Arnold RM. 2001; Factors influencing families' consent for donation of solid organs for transplantation. JAMA. 286:71–7. DOI: 10.1001/jama.286.1.71. PMID: 11434829.
Article28. Seth AK, Nambiar P, Joshi A, Ramprasad R, Choubey R, Puri P, et al. 2009; First prospective study on brain stem death and attitudes toward organ donation in India. Liver Transpl. 15:1443–7. DOI: 10.1002/lt.21912. PMID: 19877266.
Article29. Vishteh HR, Ghorbani F, Ghobadi O, Shafaghi S, Barbati ME, Louyeh AR, et al. 2010; Causes and follow-up outcomes of brain dead patients in Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences hospitals. Pejouhandeh. 15:e171–8.30. Rodrigue JR, Cornell DL, Howard RJ. 2008; Pediatric organ donation: what factors most influence parents' donation decisions? Pediatr Crit Care Med. 9:180–5. DOI: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e3181668605. PMID: 18477931. PMCID: PMC2410299.
Article31. Yousefi H, Roshani A, Nazari F. 2014; Experiences of the families concerning organ donation of a family member with brain death. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 19:323–30. PMID: 24949074. PMCID: PMC4061636.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Factors associated with the willingness for the organ donation among community dwelling individuals
- Assessment of hospital deceased organ donation potential at St. Luke’s Medical Center–Quezon City
- Determination of factors influencing family decision upon organ or tissue donation request in potential deceased organ donors in Malaysia: a 22-years national audit
- Analysis of Factors Affecting Emergency Physicians’ Attitudes toward Deceased Organ & Tissue Donation
- Willingness and attitude of the Arab world population towards solid organ