Korean J Pain.
2022 Apr;35(2):202-208. 10.3344/kjp.2022.35.2.202.
Splanchnic nerve neurolysis via the transdiscal approach under fluoroscopic guidance: a retrospective study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pain Management, The Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China
- 2Department of Pain Management, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China
- 3Department of Anesthesiology, The Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China
- KMID: 2527771
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2022.35.2.202
Abstract
- Background
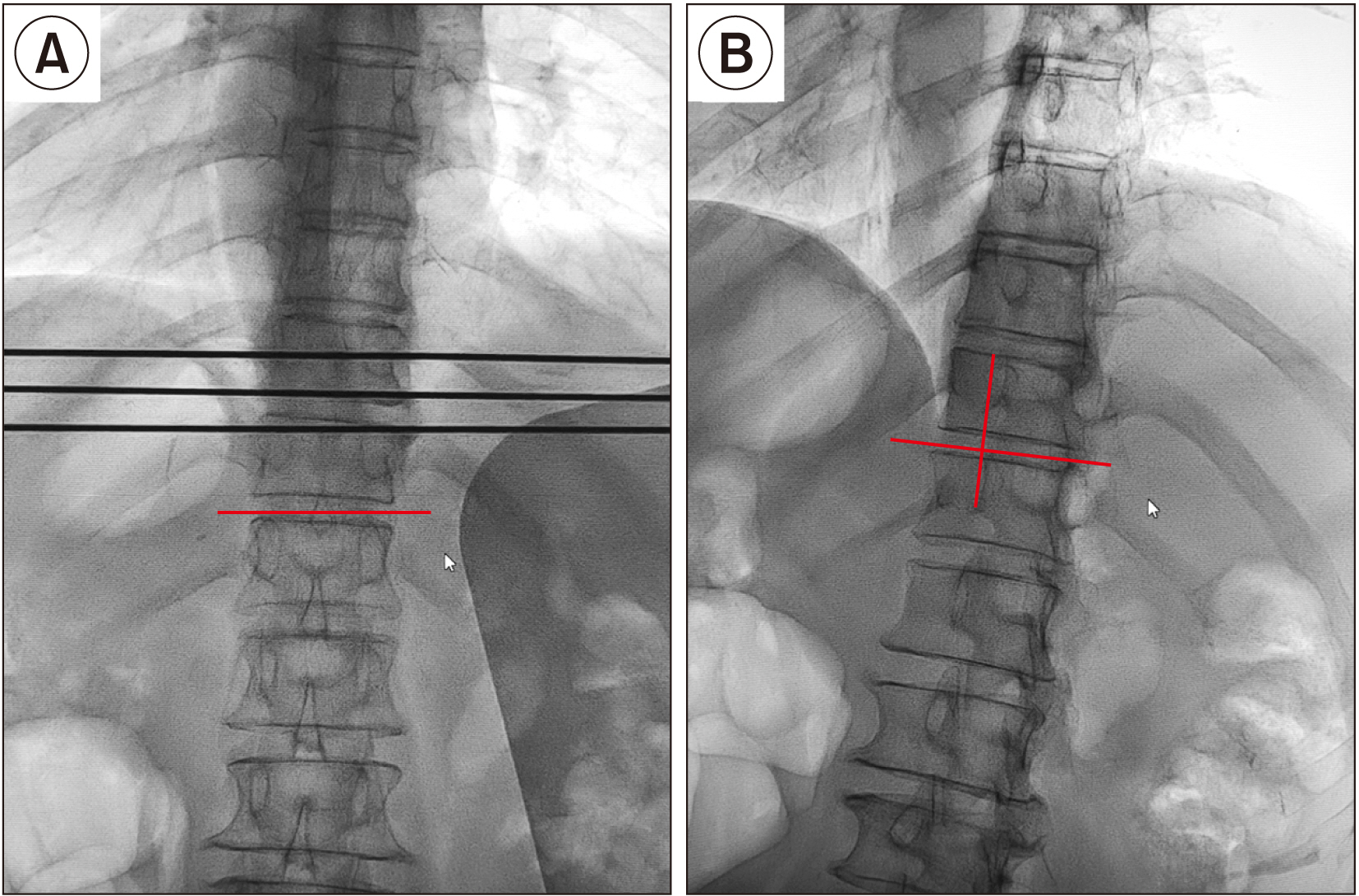
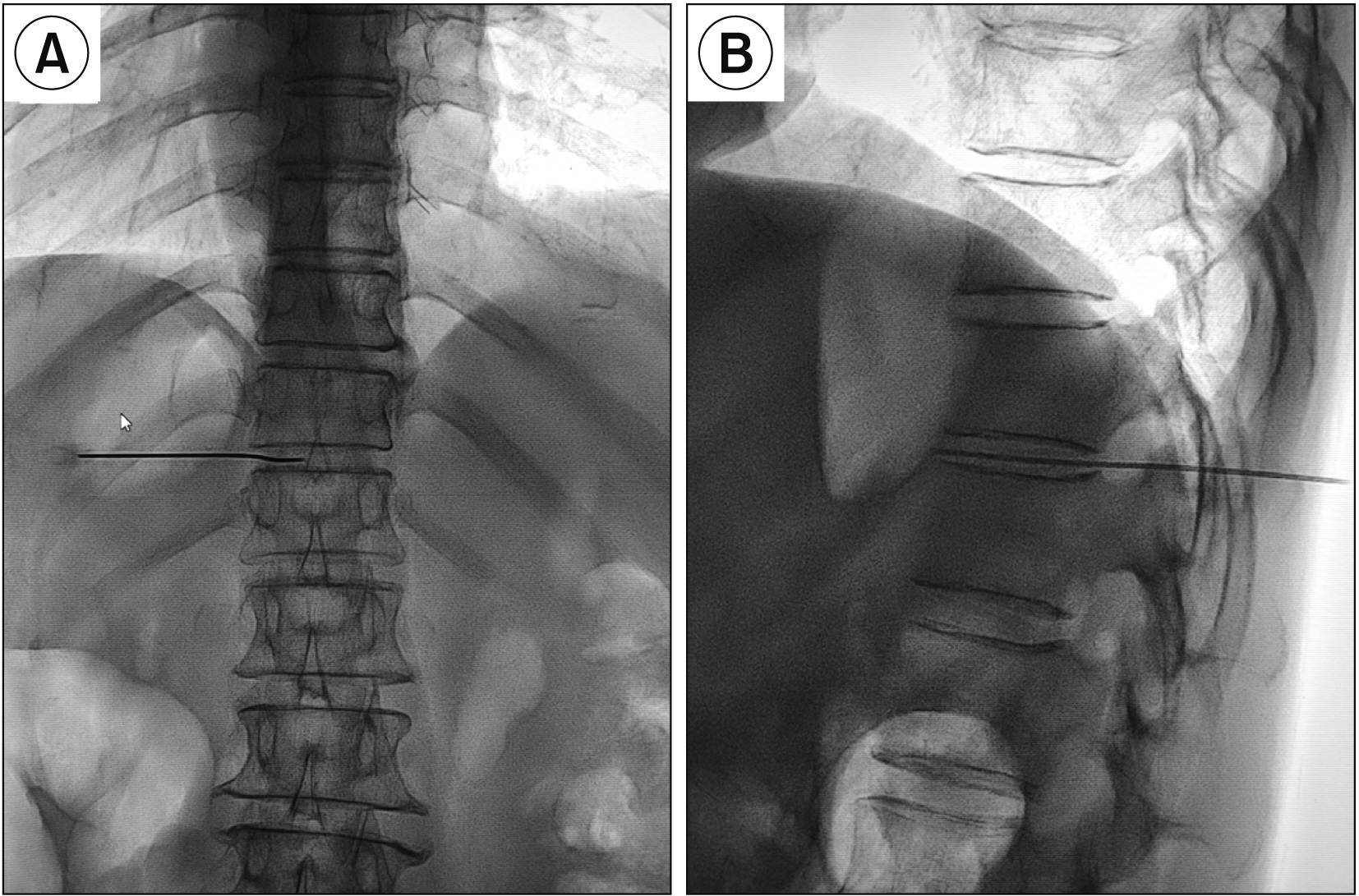
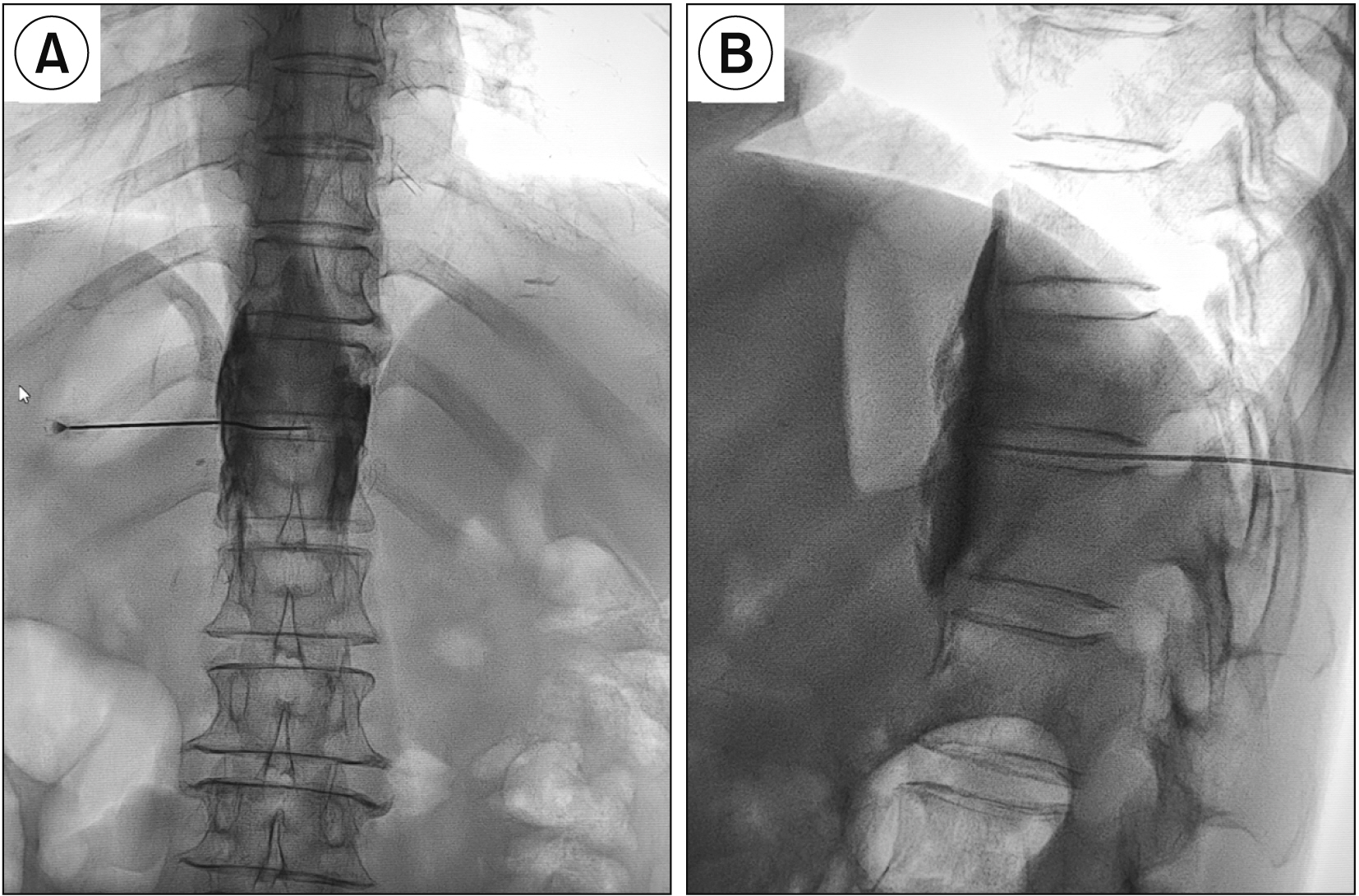
Neurolytic celiac plexus block (NCPB) is a typical treatment for severe epigastric cancer pain, but the therapeutic effect is often affected by the variation of local anatomical structures induced by the tumor. Greater and lesser splanchnic nerve neurolysis (SNN) had similar effects to the NCPB, and was recently performed with a paravertebral approach under the image guidance, or with the transdiscal approach under the guidance of computed tomography. This study observed the feasibility and safety of SNN via a transdiscal approach under fluoroscopic guidance.
Methods
The follow-up records of 34 patients with epigastric cancer pain who underwent the splanchnic nerve block via the T11-12 transdiscal approach under fluoroscopic guidance were investigated retrospectively. The numerical rating scale (NRS), the patient satisfaction scale (PSS) and quality of life (QOL) of the patient, the dose of morphine consumed, and the occurrence and severity of adverse events were recorded preoperatively and 1 day, 1 week, 1 month, and 2 months after surgery.
Results
Compared with the preoperative scores, the NRS scores and daily morphine consumption decreased and the QOL and PSS scores increased at each postoperative time point (P < 0.001). No patients experienced serious complications.
Conclusions
SNN via the transdiscal approach under flouroscopic guidance was an effective, safe, and easy operation for epigastric cancer pain, with fewer complications.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Comments on splanchnic nerve neurolysis via the transdiscal approach under fluoroscopic guidance: a retrospective study
Victor M. Silva-Ortiz, Ricardo Plancarte-Sanchez, B. Carolina Hernández-Porras
Korean J Pain. 2022;35(3):356-357. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2022.35.3.356.
Reference
-
1. Shwita AH, Amr YM, Okab MI. 2015; Comparative study of the effects of the retrocrural celiac plexus block versus splanchnic nerve block, C-arm guided, for upper gastrointestinal tract tumors on pain relief and the quality of life at a six-month follow up. Korean J Pain. 28:22–31. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2015.28.1.22. PMID: 25589943. PMCID: PMC4293503.
Article2. Sir E, Batur Sir GD. 2019; Evaluating treatment modalities in chronic pain treatment by the multi-criteria decision making procedure. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 19:191. DOI: 10.1186/s12911-019-0925-6. PMID: 31615483. PMCID: PMC6794880. PMID: f438c097df464e818a2275784188bfff.
Article3. Rahman A, Rahman R, Macrinici G, Li S. 2018; Low volume neurolytic retrocrural celiac plexus block for visceral cancer pain: retrospective review of 507 patients with severe malignancy related pain due to primary abdominal cancer or metastatic disease. Pain Physician. 21:497–504. DOI: 10.36076/ppj.2018.5.497. PMID: 30282394.4. Koyyalagunta D, Engle MP, Yu J, Feng L, Novy DM. 2016; The effectiveness of alcohol versus phenol based splanchnic nerve neurolysis for the treatment of intra-abdominal cancer pain. Pain Physician. 19:281–92. DOI: 10.36076/ppj/2019.19.281. PMID: 27228515.5. Kong YG, Shin JW, Leem JG, Suh JH. 2013; Computed tomography (CT) simulated fluoroscopy-guided transdiscal approach in transcrural celiac plexus block. Korean J Pain. 26:396–400. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2013.26.4.396. PMID: 24156008. PMCID: PMC3800714.
Article6. Bhatnagar S, Thulkar S, Dhamija E, Khandelwal I, Nandi R, Chana G. 2017; Evaluation of outcomes of ultrasound guided celiac plexus neurolysis using immediate post procedure computed tomography: an observational study. Indian J Gastroenterol. 36:282–8. DOI: 10.1007/s12664-017-0780-2. PMID: 28828591.
Article7. Tewari S, Agarwal A, Dhiraaj S, Gautam SK, Khuba S, Madabushi R, et al. 2016; Comparative evaluation of retrocrural versus transaortic neurolytic celiac plexus block for pain relief in patients with upper abdominal malignancy: a retrospective observational study. Indian J Palliat Care. 22:301–6. DOI: 10.4103/0973-1075.185041. PMID: 27559259. PMCID: PMC4973491.
Article8. Ahmed A, Arora D. 2017; Fluoroscopy-guided neurolytic splanchnic nerve block for intractable pain from upper abdominal malignancies in patients with distorted celiac axis anatomy: an effective alternative to celiac plexus neurolysis - a retrospective study. Indian J Palliat Care. 23:274–81. DOI: 10.4103/IJPC.IJPC_28_17. PMID: 28827930. PMCID: PMC5545952.
Article9. Loukas M, Klaassen Z, Merbs W, Tubbs RS, Gielecki J, Zurada A. 2010; A review of the thoracic splanchnic nerves and celiac ganglia. Clin Anat. 23:512–22. DOI: 10.1002/ca.20964. PMID: 20235178.
Article10. Süleyman Ozyalçin N, Talu GK, Camlica H, Erdine S. 2004; Efficacy of coeliac plexus and splanchnic nerve blockades in body and tail located pancreatic cancer pain. Eur J Pain. 8:539–45. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejpain.2004.01.001. PMID: 15531222.
Article11. Kapural L, Lee N, Badhey H, McRoberts WP, Jolly S. 2019; Splanchnic block at T11 provides a longer relief than celiac plexus block from nonmalignant, chronic abdominal pain. Pain Manag. 9:115–21. DOI: 10.2217/pmt-2018-0056. PMID: 30681022.
Article12. Plancarte R, Guajardo-Rosas J, Reyes-Chiquete D, Chejne-Gómez F, Plancarte A, González-Buendía NI, et al. 2010; Management of chronic upper abdominal pain in cancer: transdiscal blockade of the splanchnic nerves. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 35:500–6. DOI: 10.1097/AAP.0b013e3181fa6b42. PMID: 20975463.13. Chen M, Yu H, Sun S, Pan T, Wang Z, Fu S, et al. 2015; Clinical research of percutaneous bilateral splanchnic nerve lesion for pain relief in patients with pancreatic cancer under X-ray guidance. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:20092–6. PMID: 26884922. PMCID: PMC4723767.14. Oh TK, Lee WJ, Woo SM, Kim NW, Yim J, Kim DH. 2017; Impact of celiac plexus neurolysis on survival in patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer: a retrospective, propensity score matching analysis. Pain Physician. 20:E357–65. DOI: 10.36076/ppj.2017.E365. PMID: 28339435.15. Baek SW, Erdek MA. 2019; Time-dependent change in pain threshold following neurolytic celiac plexus block. Pain Manag. 9:543–50. DOI: 10.2217/pmt-2019-0021. PMID: 31729281.
Article16. Edelstein MR, Gabriel RT, Elbich JD, Wolfe LG, Sydnor MK. 2017; Pain outcomes in patients undergoing CT-guided celiac plexus neurolysis for intractable abdominal visceral pain. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 34:111–4. DOI: 10.1177/1049909115604670. PMID: 26345319.
Article17. Yoon DM, Yoon KB, Baek IC, Ko SH, Kim SH. 2018; Predictors of analgesic efficacy of neurolytic celiac plexus block in patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer: the importance of timing. Support Care Cancer. 26:2023–30. DOI: 10.1007/s00520-018-4043-2. PMID: 29344736.
Article18. Garcia-Eroles X, Mayoral V, Montero A, Serra J, Porta J. 2007; Celiac plexus block: a new technique using the left lateral approach. Clin J Pain. 23:635–7. DOI: 10.1097/AJP.0b013e31812e6aa8. PMID: 17710015.
Article19. Amr SA, Reyad RM, Othman AH, Mohamad MF, Mostafa MM, Alieldin NH, et al. 2018; Comparison between radiofrequency ablation and chemical neurolysis of thoracic splanchnic nerves for the management of abdominal cancer pain, randomized trial. Eur J Pain. 22:1782–90. DOI: 10.1002/ejp.1274. PMID: 29975804.
Article20. Cornman-Homonoff J, Holzwanger DJ, Lee KS, Madoff DC, Li D. 2017; Celiac plexus block and neurolysis in the management of chronic upper abdominal pain. Semin Intervent Radiol. 34:376–86. DOI: 10.1055/s-0037-1608861. PMID: 29249862. PMCID: PMC5730442.
Article21. Oguz G, Senel G, Kocak N. 2018; Transient paraplegia after neurolytic splanchnic block in a patient with metastatic colon carcinoma. Korean J Pain. 31:50–3. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2018.31.1.50. PMID: 29372026. PMCID: PMC5780216.
Article22. Chun-jing H, yi-ran L, hao-xiong N. 2012; Effects of dorsal root ganglion destruction by adriamycin in patients with postherpetic neuralgia. Acta Cir Bras. 27:404–9. DOI: 10.1590/S0102-86502012000600008. PMID: 22666758.
Article23. Rumsby MG, Finean JB. 1966; The action of organic solvents on the myelin sheath of peripheral nerve tissue. II. Short-chain aliphatic alcohols. J Neurochem. 13:1509–11. DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb04312.x. PMID: 5962029.
Article24. Liliang PC, Hung CM, Lu K, Chen HJ. 2018; Fluoroscopically-guided superior hypogastric plexus neurolysis using a single needle: a modified technique for a posterolateral transdiscal approach. Pain Physician. 21:E341–5. DOI: 10.36076/ppj.2018.4.E341. PMID: 30045600.25. Turker G, Basagan-Mogol E, Gurbet A, Ozturk C, Uckunkaya N, Sahin S. 2005; A new technique for superior hypogastric plexus block: the posteromedian transdiscal approach. Tohoku J Exp Med. 206:277–81. DOI: 10.1620/tjem.206.277. PMID: 15942158.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comments on splanchnic nerve neurolysis via the transdiscal approach under fluoroscopic guidance: a retrospective study
- Splanchnic Nerve Block with Transdiscal Approach
- CT Guided Celiac Plexus and Splanchnic Nerve Neurolysis: The Modified Anterior Approach
- Transdiscal Superior Hypogastric Plexus Block with the Patient in Oblique Position
- Transdiscal Superior Hypogastric Plexus Block for Postparaplegic Pelvic Pain