Anat Cell Biol.
2022 Mar;55(1):79-91. 10.5115/acb.21.170.
Does oral ciprofloxacin affect the structure of thoracic aorta in adult and senile male albino rats? A clue to fluoroquinolones-induced risk of aortic dissection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy and Embryology, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt
- 2Department of Physiological Sciences, Fakeeh College for Medical Sciences, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
- KMID: 2527672
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.21.170
Abstract
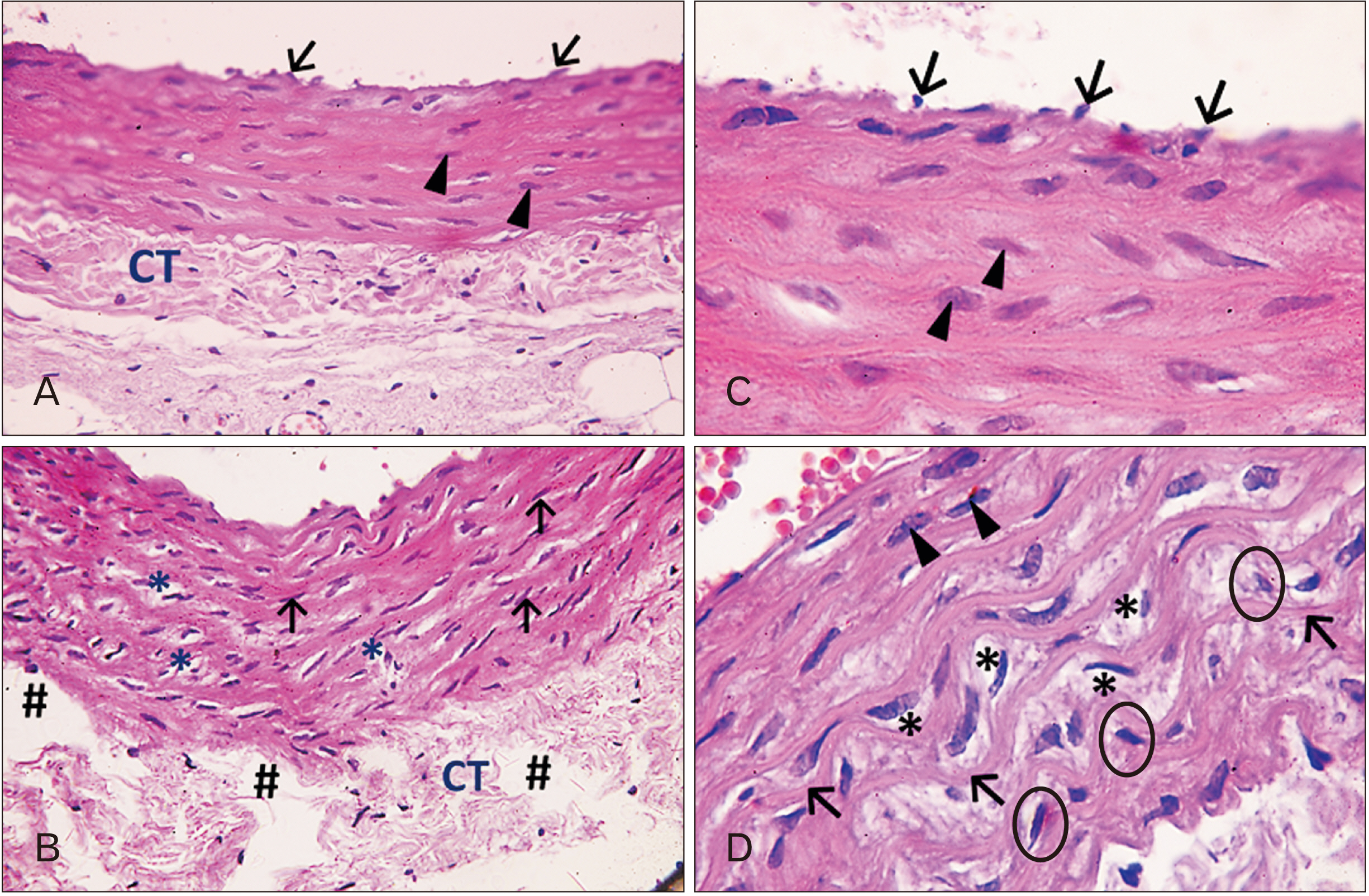
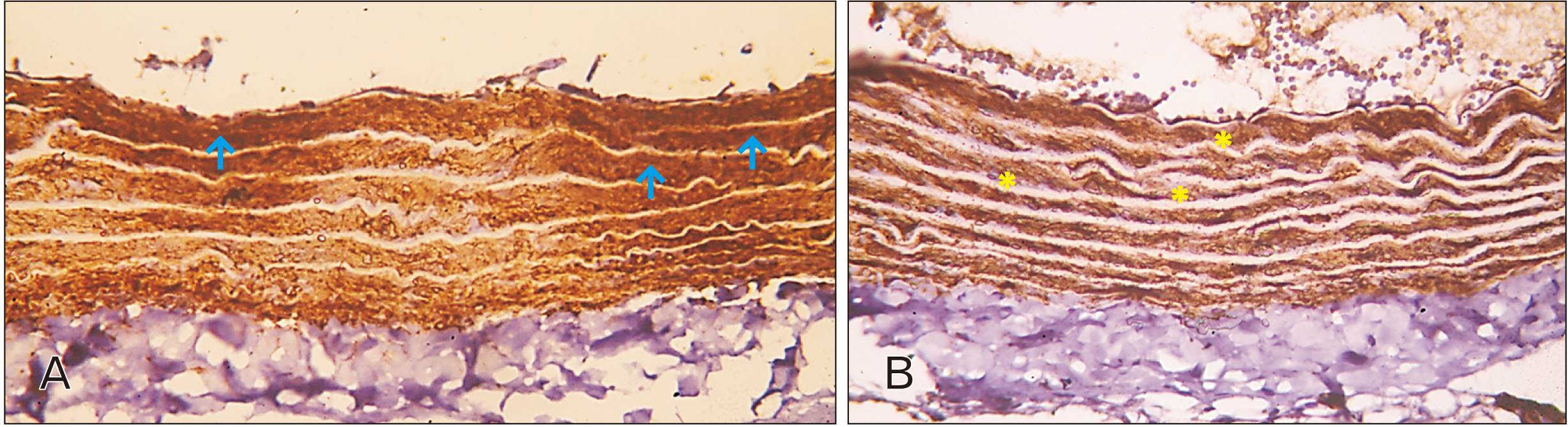
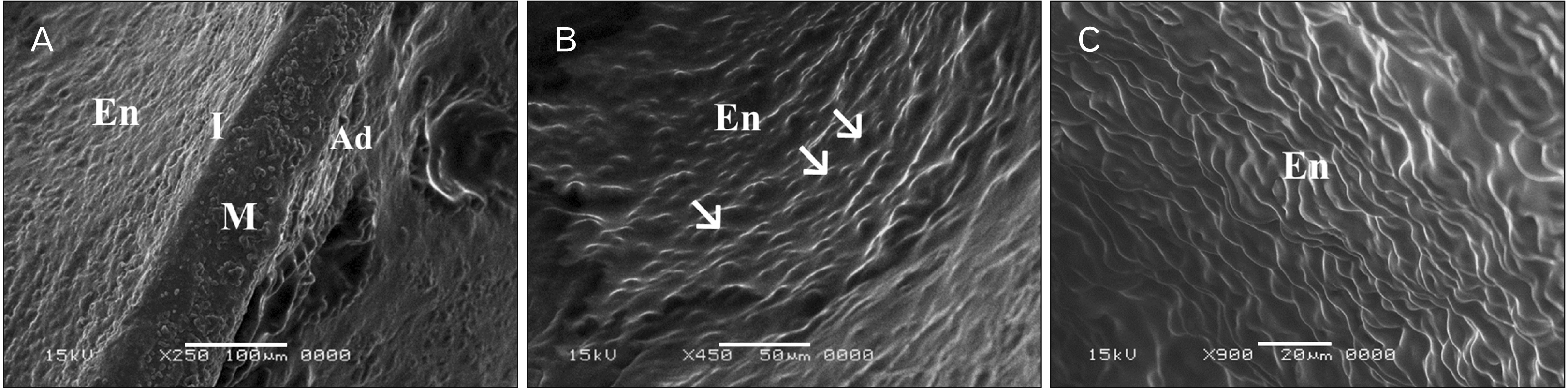
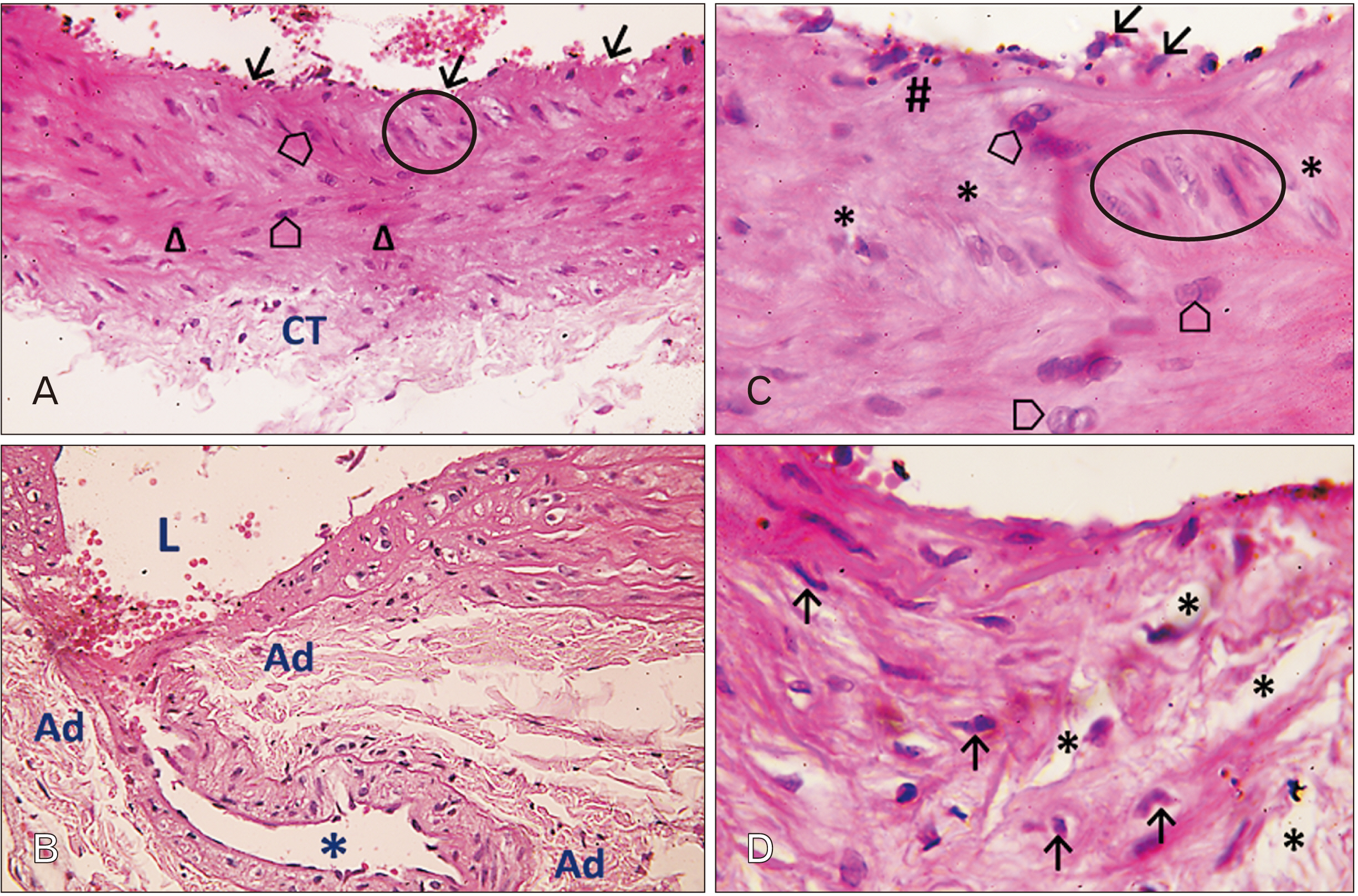
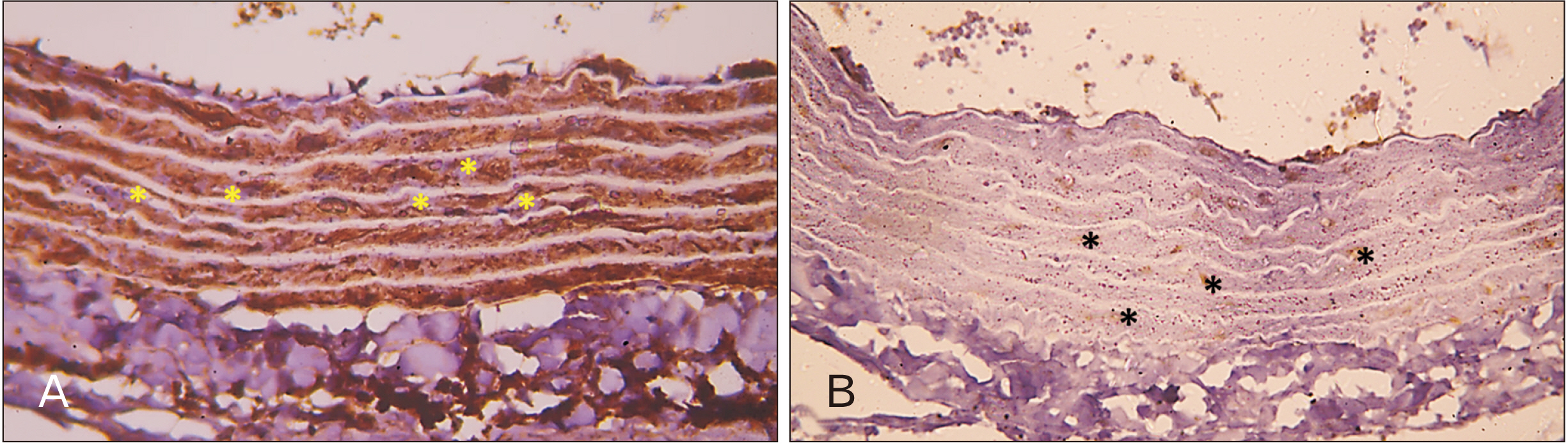
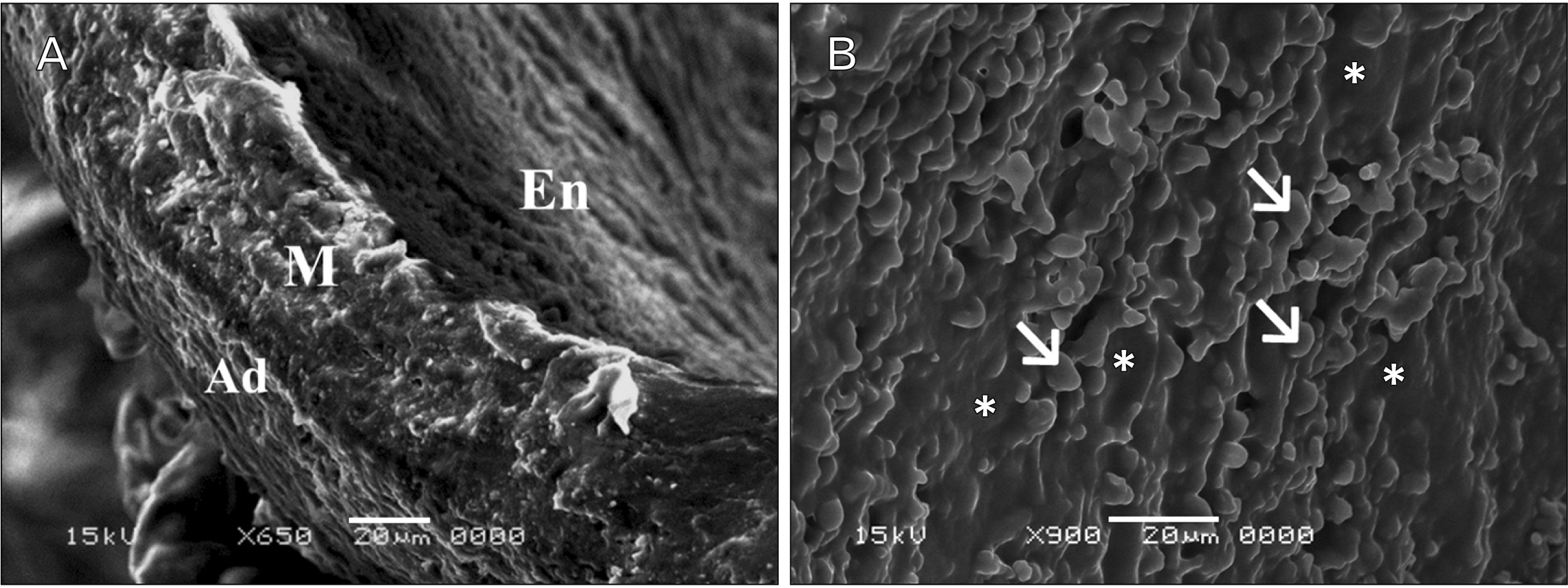
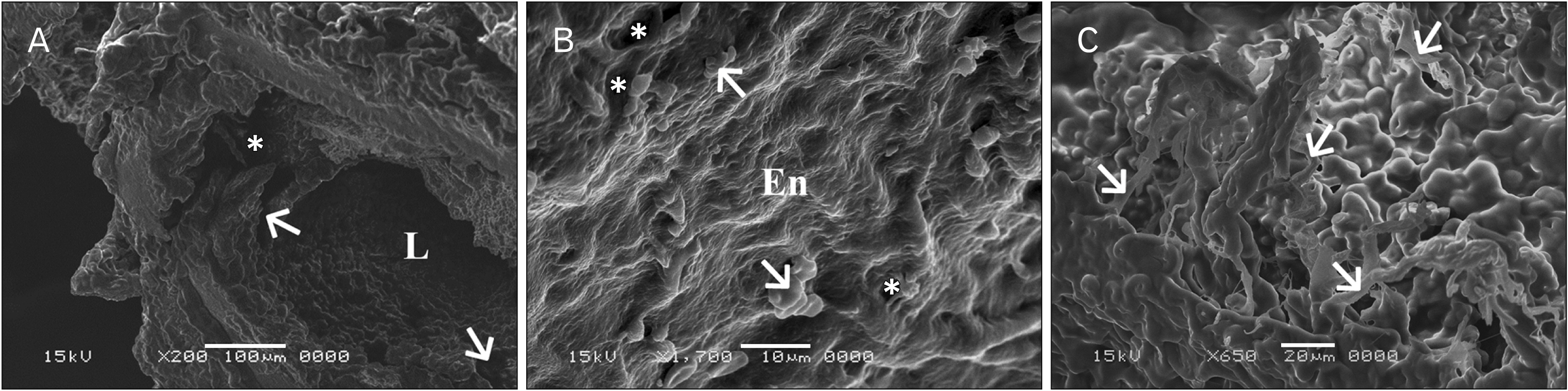
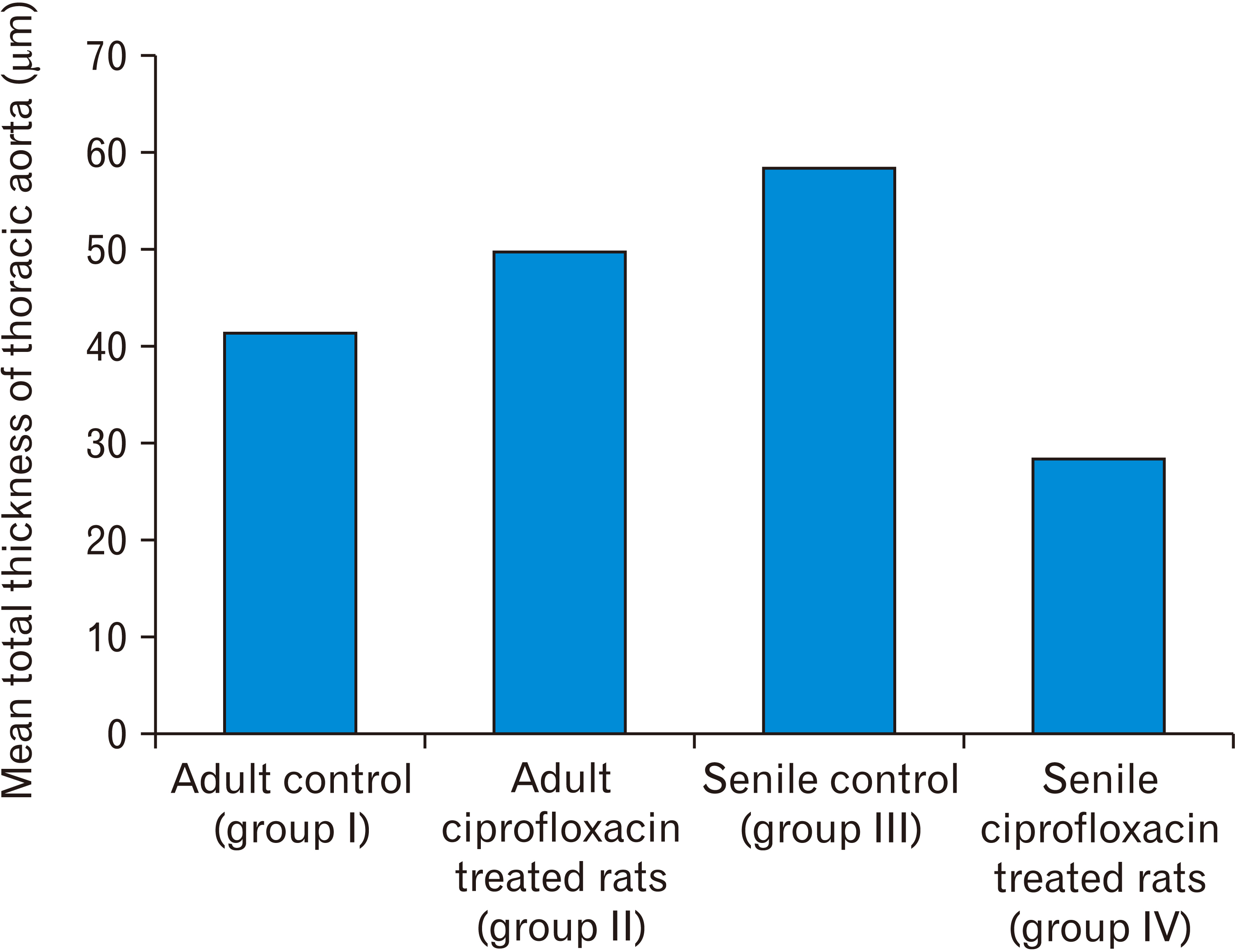
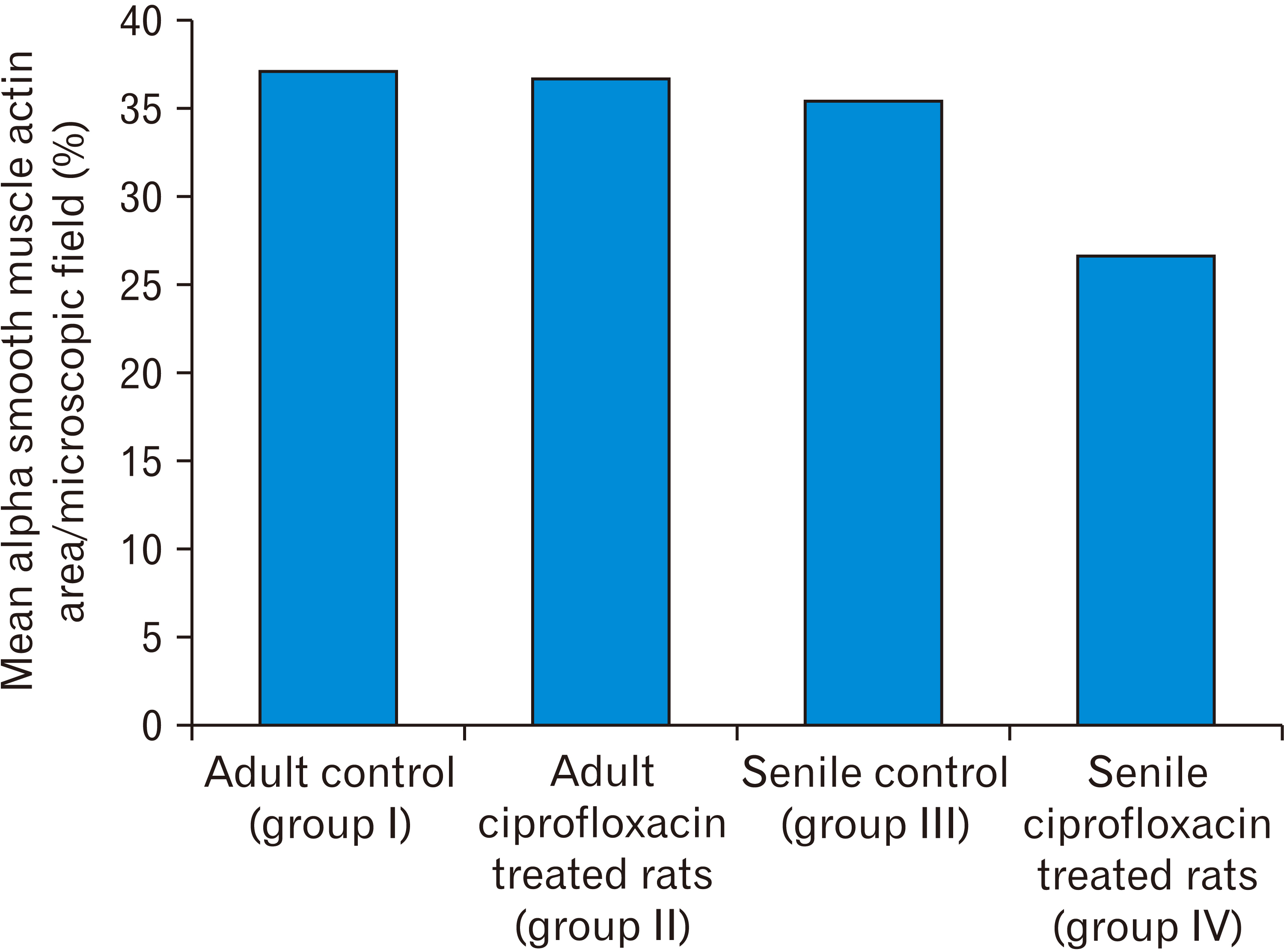
- In this study, the effect of oral ciprofloxacin on the structure of the thoracic aorta in rats was investigated. Twenty four male albino rats were divided into 4 groups (6 rats/group): group I (adult control), group II (adult rats treated with ciprof loxacin), group III (senile control), and group IV (senile rats treated with ciprof loxacin). Rats in groups II and IV received ciprofloxacin via oral gavage in a daily dose of 3.5 mg/kg/d for 14 days, while control rats received equivalent amount of distilled water used to dissolve the drug. After 2 weeks, all rats were sacrificed, thoracic aortae were dissected, and half of the specimens were processed for paraffin sections and examined by light microscopy. The other half of the specimens were prepared for scanning electron microscopy. Sections from rats treated with ciprofloxacin showed evident damaging effect on aortic wall particularly in (group IV). Aortic intima showed, focal desquamation of the lining epithelium. Tunica media exhibited loss of the normal concentric arrangement and degeneration of the smooth muscle cells. Immune staining for alpha smooth muscle actin showed muscle damage. Interestingly, some sections in (group IV) showed out-pouch (aneurysm like) of the aortic wall. There was dense collagen fibers deposition. Scanning electron microscopic observations of (group IV) revealed uneven intima, adherent blood cells and fibrin filaments to damaged intima, and out-pouch formation. It was concluded that oral ciprofloxacin caused deleterious structural changes in the thoracic aortic wall of rats explaining clinical observations of fluoroquinolones induced risk of aortic dissection and aneurysm.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Etminan M, Sodhi M, Ganjizadeh-Zavareh S, Carleton B, Kezouh A, Brophy JM. 2019; Oral fluoroquinolones and risk of mitral and aortic regurgitation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 74:1444–50. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.07.035. PMID: 31514945.2. Michalak K, Sobolewska-Włodarczyk A, Włodarczyk M, Sobolewska J, Woźniak P, Sobolewski B. 2017; Treatment of the fluoroquinolone-associated disability: the pathobiochemical implications. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017:8023935. DOI: 10.1155/2017/8023935. PMID: 29147464. PMCID: PMC5632915.
Article3. Singh S, Nautiyal A. 2017; Aortic dissection and aortic aneurysms associated with fluoroquinolones: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med. 130:1449–57.e9. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.06.029. PMID: 28739200.
Article4. Jackson MA, Schutze GE. Committee on Infectious Diseases. 2016; The use of systemic and topical fluoroquinolones. Pediatrics. 138:e20162706. DOI: 10.1542/peds.2016-2706. PMID: 27940800.
Article5. Stephenson AL, Wu W, Cortes D, Rochon PA. 2013; Tendon injury and fluoroquinolone use: a systematic review. Drug Saf. 36:709–21. DOI: 10.1007/s40264-013-0089-8. PMID: 23888427.
Article6. Raguideau F, Lemaitre M, Dray-Spira R, Zureik M. 2016; Association between oral fluoroquinolone use and retinal detachment. JAMA Ophthalmol. 134:415–21. DOI: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2015.6205. PMID: 26967005.
Article7. Lee CC, Lee MT, Chen YS, Lee SH, Chen YS, Chen SC, Chang SC. 2015; Risk of aortic dissection and aortic aneurysm in patients taking oral fluoroquinolone. JAMA Intern Med. 175:1839–47. DOI: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.5389. PMID: 26436523.
Article8. Daneman N, Lu H, Redelmeier DA. 2015; Fluoroquinolones and collagen associated severe adverse events: a longitudinal cohort study. BMJ Open. 5:e010077. DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010077. PMID: 26582407. PMCID: PMC4654346.
Article9. Pasternak B, Inghammar M, Svanström H. 2018; Fluoroquinolone use and risk of aortic aneurysm and dissection: nationwide cohort study. BMJ. 360:k678. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.k678. PMID: 29519881. PMCID: PMC5842359.
Article10. Clouse WD, Hallett JW Jr, Schaff HV, Spittell PC, Rowland CM, Ilstrup DM, Melton LJ 3rd. 2004; Acute aortic dissection: population-based incidence compared with degenerative aortic aneurysm rupture. Mayo Clin Proc. 79:176–80. DOI: 10.4065/79.2.176. PMID: 14959911.
Article11. Kent KC. 2014; Clinical practice. Abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 371:2101–8. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMcp1401430. PMID: 25427112.12. Goldfinger JZ, Halperin JL, Marin ML, Stewart AS, Eagle KA, Fuster V. 2014; Thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection. J Am Coll Cardiol. 64:1725–39. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.08.025. PMID: 25323262.
Article13. Corps AN, Harrall RL, Curry VA, Fenwick SA, Hazleman BL, Riley GP. 2002; Ciprofloxacin enhances the stimulation of matrix metalloproteinase 3 expression by interleukin-1beta in human tendon-derived cells. A potential mechanism of fluoroquinolone-induced tendinopathy. Arthritis Rheum. 46:3034–40. DOI: 10.1002/art.10617. PMID: 12428247.14. Tsai WC, Hsu CC, Chen CP, Chang HN, Wong AM, Lin MS, Pang JH. 2011; Ciprofloxacin up-regulates tendon cells to express matrix metalloproteinase-2 with degradation of type I collagen. J Orthop Res. 29:67–73. DOI: 10.1002/jor.21196. PMID: 20602464.
Article15. Chang HN, Pang JH, Chen CP, Ko PC, Lin MS, Tsai WC, Yang YM. 2012; The effect of aging on migration, proliferation, and collagen expression of tenocytes in response to ciprofloxacin. J Orthop Res. 30:764–8. DOI: 10.1002/jor.21576. PMID: 22021103.
Article16. Paget GE, Barnes JM. Laurenc DR, Bacharach AL, editors. 1964. Chapter 6- toxicity tests. Evaluation of Drug Activities. Academic Press;New York: p. 135–66. DOI: 10.1016/B978-1-4832-2845-7.50012-8.17. LeMaire SA, Zhang L, Luo W, Ren P, Azares AR, Wang Y, Zhang C, Coselli JS, Shen YH. 2018; Effect of ciprofloxacin on susceptibility to aortic dissection and rupture in mice. JAMA Surg. 153:e181804. DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2018.1804. PMID: 30046809. PMCID: PMC6233654.
Article18. Bancroft JD, Gamble M. 2008. Theory and practice of histological techniques. 6th ed. Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier;Philadelphia: p. 440.19. Graham L, Orenstein JM. 2007; Processing tissue and cells for transmission electron microscopy in diagnostic pathology and research. Nat Protoc. 2:2439–50. DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2007.304. PMID: 17947985. PMCID: PMC7086545.
Article20. Lee CC, Lee MG, Hsieh R, Porta L, Lee WC, Lee SH, Chang SS. 2018; Oral fluoroquinolone and the risk of aortic dissection. J Am Coll Cardiol. 72:1369–78. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.06.067. PMID: 30213330.21. Wang SW, Huang YB, Huang JW, Chiu CC, Lai WT, Chen CY. 2015; Epidemiology, clinical features, and prescribing patterns of aortic aneurysm in Asian population from 2005 to 2011. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e1716. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001716. PMID: 26469911. PMCID: PMC4616784.
Article22. Howard DP, Banerjee A, Fairhead JF, Handa A, Silver LE, Rothwell PM. 2015; Population-based study of incidence of acute abdominal aortic aneurysms with projected impact of screening strategy. J Am Heart Assoc. 4:e001926. DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.115.001926. PMID: 26289347. PMCID: PMC4599457.
Article23. Abu-Dief EE, Abdelrahim EA, Abdelrahim KM. 2016; Histological modifications aging aorta in male albino rat. J Cytol Histol. 7:408. DOI: 10.4172/2157-7099.1000408.
Article24. Zarkovic K, Larroque-Cardoso P, Pucelle M, Salvayre R, Waeg G, Nègre-Salvayre A, Zarkovic N. 2015; Elastin aging and lipid oxidation products in human aorta. Redox Biol. 4:109–17. DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2014.12.008. PMID: 25553420. PMCID: PMC4309857.
Article25. Komutrattananont P, Palee P, Prasitwattanaseree S, Mahakkanukrauh P. 2020; The estimation of age from elastic fibers in the tunica media of the aortic wall in a thai population: a preliminary study using aorta image analysis. Anat Cell Biol. 53:284–91. DOI: 10.5115/acb.20.094. PMID: 32727957. PMCID: PMC7527121.
Article26. Fritze O, Romero B, Schleicher M, Jacob MP, Oh DY, Starcher B, Schenke-Layland K, Bujan J, Stock UA. 2012; Age-related changes in the elastic tissue of the human aorta. J Vasc Res. 49:77–86. DOI: 10.1159/000331278. PMID: 22105095.
Article27. Greenberg SR. 1986; The association of medial collagenous tissue with atheroma formation in the aging human aorta as revealed by a special technique. Histol Histopathol. 1:323–6.28. Nakashima Y. 2010; Pathogenesis of aortic dissection: elastic fiber abnormalities and aortic medial weakness. Ann Vasc Dis. 3:28–36. DOI: 10.3400/avd.ctiia09001. PMID: 23555385. PMCID: PMC3595817.
Article29. Wilson SK, Hutchins GM. 1982; Aortic dissecting aneurysms: causative factors in 204 subjects. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 106:175–80.30. Larson EW, Edwards WD. 1984; Risk factors for aortic dissection: a necropsy study of 161 cases. Am J Cardiol. 53:849–55. DOI: 10.1016/0002-9149(84)90418-1.
Article31. Carino D, Zafar MA, Singh M, Ziganshin BA, Elefteriades JA. 2019; Fluoroquinolones and aortic diseases: is there a connection. Aorta (Stamford). 7:35–41. DOI: 10.1055/s-0039-1693468. PMID: 31529426. PMCID: PMC6748841.
Article32. Ishii T, Asuwa N. 2000; Collagen and elastin degradation by matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinase in aortic dissection. Hum Pathol. 31:640–6. DOI: 10.1053/hupa.2000.7642. PMID: 10872655.
Article33. Macura KJ, Corl FM, Fishman EK, Bluemke DA. 2003; Pathogenesis in acute aortic syndromes: aortic dissection, intramural hematoma, and penetrating atherosclerotic aortic ulcer. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 181:309–16. DOI: 10.2214/ajr.181.2.1810309. PMID: 12876003.
Article34. Vilacosta I, San Román JA. 2001; Acute aortic syndrome. Heart. 85:365–8. DOI: 10.1136/heart.85.4.365. PMID: 11250953. PMCID: PMC1729697.
Article35. Sandison ME, Dempster J, McCarron JG. 2016; The transition of smooth muscle cells from a contractile to a migratory, phagocytic phenotype: direct demonstration of phenotypic modulation. J Physiol. 594:6189–209. DOI: 10.1113/JP272729. PMID: 27393389. PMCID: PMC5088226.
Article36. Atkinson J. 1998; Aging of arterial extracellular matrix elastin: etiology and consequences. Pathol Biol (Paris). 46:555–9. French.37. James S, Schuijers J, Daffy J, Cook J, Samiric T. 2021; Ciprofloxacin reduces tenocyte viability and proteoglycan synthesis in short-term explant cultures of equine tendon. PeerJ. 9:e12003. DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12003. PMID: 34540363. PMCID: PMC8411937.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Complete Resolution of Aortic Dissection in the Descending Thoracic Aorta Treated with Endovascular Stent-Graft Implantation
- Single Stage Replacement of Entire Thoracic Aorta for Chronic Aortic Dissection
- Total Aortic Replacement: A Case Report
- Total Replacement of Aorta in Chronic Type I Aortic Dissection
- Rare Cerebral Infarction in Patient with Type B Aortic Dissection