J Rheum Dis.
2022 Apr;29(2):116-122. 10.4078/jrd.2022.29.2.116.
Idiopathic Inflammatory Arthritis in the Auditory Canal in a Patient With Hearing Impairment: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Uijeongbu Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University School of Medicine, Uijeongbu, Korea
- 2Departments of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Departments of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2527551
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2022.29.2.116
Abstract
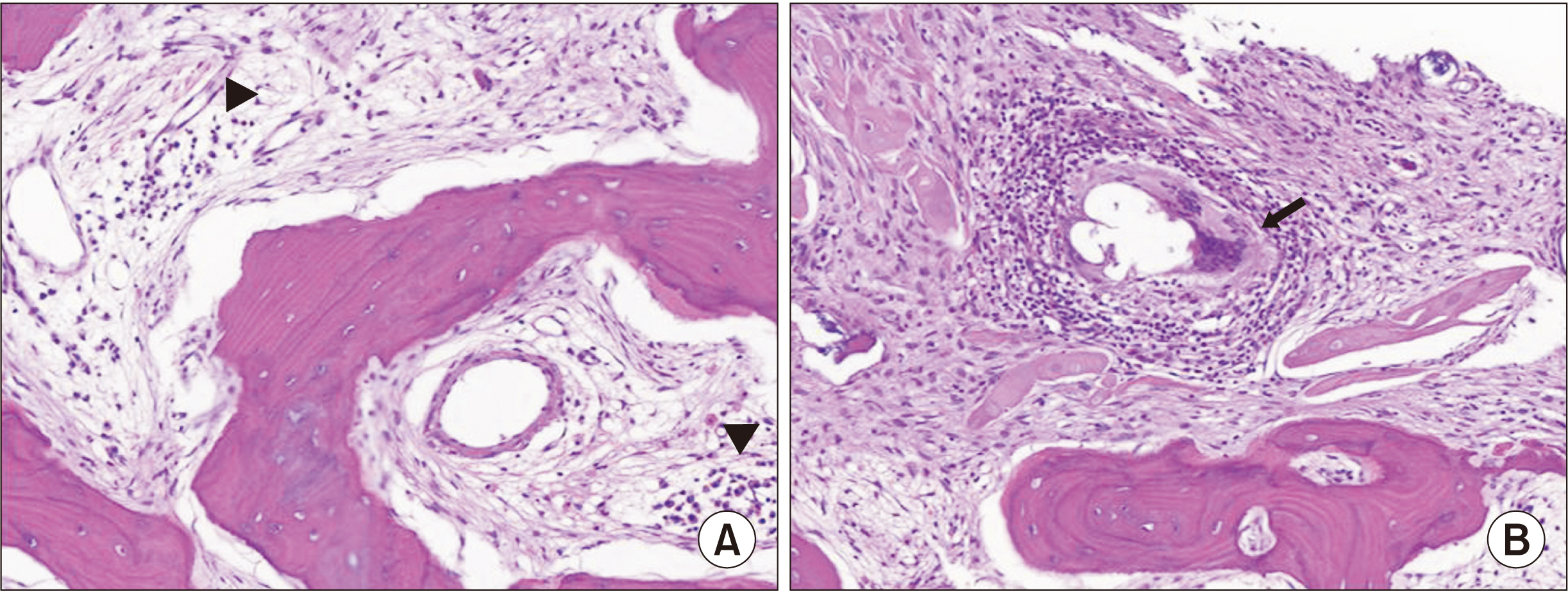
- Inflammatory arthritis can affect the auditory system during the disease course. Although most cases show asymptomatic hearing impairment, it can result in hearing loss. Here we describe the case of a 70-year-old female with hearing impairment associated with idiopathic inflammatory arthritis in her auditory system. She had suffered from hearing difficulties for decades; however, the causes of her hearing impairment had not been evaluated. Pure tone audiometry showed severe sensorineural hearing loss requiring a cochlear implant. The workup for the cochlear implant revealed erosive changes in the incudomalleolar and incudostapedial joints with soft tissue swelling on temporal bone computed tomography. Bone pathology revealed plasmacytic infiltration and granulomatous inflammation. Laboratory examinations showed elevated levels of inflammatory markers; otherwise, she had negative results for all autoantibodies. In patients with idiopathic hearing loss, inflammatory arthritis of the middle ear without peripheral arthritis can provide a clue regarding the cause of the hearing loss.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rahne T, Clauß F, Plontke SK, Keyßer G. 2017; Prevalence of hearing impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA, Wegener's granulomatosis), or systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 36:1501–10. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-017-3651-4. PMID: 28455828.
Article2. Amor-Dorado JC, Barreira-Fernandez MP, Pina T, Vázquez-Rodríguez TR, Llorca J, González-Gay MA. 2014; Investigations into audiovestibular manifestations in patients with psoriatic arthritis. J Rheumatol. 41:2018–26. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.140559. PMID: 25179845.
Article3. Adam M, Erkan AN, Arslan D, Leblebici B, Ozlüoglu L, Nafiz Akman M. 2008; High-frequency sensorineural hearing loss in patients with ankylosing spondylitis:is it an extrarticuler feature of disease? Rheumatol Int. 28:413–7. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-007-0458-7. PMID: 17899090.
Article4. Dagli M, Sivas Acar F, Karabulut H, Eryilmaz A, Erkol Inal E. 2007; Evaluation of hearing and cochlear function by DPOAE and audiometric tests in patients with ankylosing spondilitis. Rheumatol Int. 27:511–6. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-006-0249-6. PMID: 17094003.
Article5. Casellini C, Citera G, Rosemffet M, Ruggeri S, Saviotti A, Maldonado Cocco JA. 2005; Audiovestibular disorders in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J Clin Rheumatol. 11:81–5. DOI: 10.1097/01.rhu.0000158542.43099.35. PMID: 16357708.
Article6. Ikiz AO, Unsal E, Kirkim G, Erdag TK, Guneri EA. 2007; Hearing loss and middle ear involvement in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 71:1079–85. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2007.03.017. PMID: 17482280.
Article7. Siamopoulou-Mavridou A, Asimakopoulos D, Mavridis A, Skevas A, Moutsopoulos HM. 1990; Middle ear function in patients with juvenile chronic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 49:620–3. DOI: 10.1136/ard.49.8.620. PMID: 2396868. PMCID: PMC1004177.
Article8. Magarò M, Ceresia G, Frustaci A. 1984; Arthritis of the middle ear in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 43:658–9. DOI: 10.1136/ard.43.4.658. PMID: 6476926. PMCID: PMC1001432.
Article9. Amor-Dorado JC, Barreira-Fernandez MP, Vazquez-Rodriguez TR, Gomez-Acebo I, Miranda-Filloy JA, Diaz de Teran T, et al. 2011; Audiovestibular manifestations in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Medicine (Baltimore). 90:99–109. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0b013e3182079866. PMID: 21358443.
Article10. Mancini P, Atturo F, Di Mario A, Portanova G, Ralli M, De Virgilio A, et al. 2018; Hearing loss in autoimmune disorders: prevalence and therapeutic options. Autoimmun Rev. 17:644–52. DOI: 10.1016/j.autrev.2018.01.014. PMID: 29729446.
Article11. Ozcan M, Karakus MF, Gündüz OH, Tuncel U, Sahin H. 2002; Hearing loss and middle ear involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 22:16–9. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-002-0185-z. PMID: 12120906.
Article12. Lee SY, Kong IG, Oh DJ, Choi HG. 2019; Increased risk of sudden sensory neural hearing loss in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a longitudinal follow-up study using a national sample cohort. Clin Rheumatol. 38:683–9. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-018-4333-6. PMID: 30324407.
Article13. Emamifar A, Bjoerndal K, Hansen IM. 2016; Is hearing impairment associated with rheumatoid arthritis? A review. Open Rheumatol J. 10:26–32. DOI: 10.2174/1874312901610010026. PMID: 27053970. PMCID: PMC4797675.
Article14. Lobo FS, Dossi MO, Batista L, Shinzato MM. 2016; Hearing impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: association with anti-citrullinated protein antibodies. Clin Rheumatol. 35:2327–32. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-016-3278-x. PMID: 27112144.
Article15. Emamifar A, Hansen IMJ. 2018; An update on hearing impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Otol. 13:1–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.joto.2017.10.002. PMID: 29937858. PMCID: PMC6002624.
Article16. Chaitidis N, Theocharis P, Festas C, Aritzi I. 2020; Association of rheumatoid arthritis with hearing loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int. 40:1771–9. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-020-04609-1. PMID: 32488430.
Article17. Takatsu M, Higaki M, Kinoshita H, Mizushima Y, Koizuka I. 2005; Ear involvement in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Otol Neurotol. 26:755–61. DOI: 10.1097/01.mao.0000178138.19848.bd. PMID: 16015180.
Article18. Milisavljevic D, Stankovic M, Zivic M, Radovanovic Z, Stankovic P. 2010; Changes in auditory ossicles in rheumatoid arthritis: scanning electron microscopic study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 267:363–6. DOI: 10.1007/s00405-009-1072-y. PMID: 19727791.
Article19. Jeong H, Eun YH, Park EJ, Chae JY, Kim H, Lee J, et al. 2016; Rheumatoid arthritis is associated with low-/mid-frequency hearing impairment: data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arthritis Rheumatol. 68(10 Suppl):1551.20. Oztürk A, Yalçin S, Kaygusuz I, Sahin S, Gök U, Karlidag T, et al. 2004; High-frequency hearing loss and middle ear involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Otolaryngol. 25:411–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2004.06.001. PMID: 15547810.
Article21. Salvinelli F, Cancilleri F, Casale M, Luccarelli V, Di Peco V, D'Ascanio L, et al. 2004; Hearing thresholds in patients affected by rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 29:75–9. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2273.2004.00783.x. PMID: 14961856.
Article22. Goodwill CJ, Lord IJ, Jones RP. 1972; Hearing in rheumatoid arthritis. A clinical and audiometric survey. Ann Rheum Dis. 31:170–3. DOI: 10.1136/ard.31.3.170. PMID: 5032449. PMCID: PMC1005892.
Article23. Rosenberg JN, Moffat DA, Ramsden RT, Gibson WP, Booth JB. 1978; Middle ear function in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 37:522–4. DOI: 10.1136/ard.37.6.522. PMID: 312056. PMCID: PMC1000288.
Article24. Poorey VK, Khatri R. 2001; Study of auditory function in rheumatoid arthritis. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 53:261–3. DOI: 10.1007/BF02991542. PMID: 23119817. PMCID: PMC3450498.
Article25. Halligan CS, Bauch CD, Brey RH, Achenbach SJ, Bamlet WR, McDonald TJ, et al. 2006; Hearing loss in rheumatoid arthritis. Laryngoscope. 116:2044–9. DOI: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000241365.54017.32. PMID: 17075400.
Article26. Tavernier L, Ranfaing E. 2011; Rheumatoid arthritis involved in the ear drum. Otol Neurotol. 32:e5–6. DOI: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e3181d2f039. PMID: 20142795.
Article27. Pascual-Ramos V, Contreras-Yáñez I, Enríquez L, Valdés S, Ramírez-Anguiano J. 2012; Hearing impairment in a tertiary- care-level population of Mexican rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Clin Rheumatol. 18:393–8. DOI: 10.1097/RHU.0b013e31827732d3. PMID: 23188202.28. Ahmadzadeh A, Daraei M, Jalessi M, Peyvandi AA, Amini E, Ranjbar LA, et al. 2017; Hearing status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Laryngol Otol. 131:895–9. DOI: 10.1017/S0022215117001670. PMID: 28807082.
Article29. Walling AD, Dickson GM. 2012; Hearing loss in older adults. Am Fam Physician. 85:1150–6.30. Magliocca KR, Vivas EX, Griffith CC. 2018; Idiopathic, infectious and reactive lesions of the ear and temporal bone. Head Neck Pathol. 12:328–49. DOI: 10.1007/s12105-018-0952-0. PMID: 30069844. PMCID: PMC6081288.
Article31. Jacobs RP, Moore M, Brower A. 1987; Wegener's granulomatosis presenting with erosive arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 30:943–6. DOI: 10.1002/art.1780300817. PMID: 3632735.
Article32. Sodhi A, Naik S, Pai A, Anuradha A. 2015; Rheumatoid arthritis affecting temporomandibular joint. Contemp Clin Dent. 6:124–7. DOI: 10.4103/0976-237X.149308. PMID: 25684928. PMCID: PMC4319332.
Article33. Tyndel FJ, Davidson GS, Birman H, Modzelewski ZA, Acker JJ. 1994; Sarcoidosis of the middle ear. Chest. 105:1582–3. DOI: 10.1378/chest.105.5.1582. PMID: 8181361.
Article34. Chen R, Schwander M, Barbe MF, Chan MM. 2016; Ossicular bone damage and hearing loss in rheumatoid arthritis: a correlated functional and high resolution morphometric study in collagen-induced arthritic mice. PLoS One. 11:e0164078. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164078. PMID: 27690307. PMCID: PMC5045188.
Article35. Yildirim A, Surucu G, Dogan S, Karabiber M. 2016; Relationship between disease activity and hearing impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with controls. Clin Rheumatol. 35:309–14. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-015-3129-1. PMID: 26615612.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis involving the External Auditory Canal
- Hearing Difficulty According To Traumatic Disk Displacement: A Case Report
- A Case of Compound Nevus of the External Auditory Canal
- A Case of Pleomorphic Adenoma of the External Auditory Canal
- A Case of Intradermal Nevus of the External Auditory Canal