Korean J Orthod.
2022 Mar;52(2):112-122. 10.4041/kjod.2022.52.2.112.
Deep learning for the classification of cervical maturation degree and pubertal growth spurts: A pilot study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Computer Engineering, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran, Iran
- 2Topic Group Dental Diagnostics and Digital Dentistry, ITU/WHO Focus Group AI on Health, Berlin, Germany
- 3Dentofacial Deformities Research Center, Research Institute of Dental Sciences & Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 4Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS), Tehran, Iran
- 5Dentofacial Deformities Research Center, Research Institute of Dental Sciences, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 6Department of Computer Engineering, Sirjan University of Technology, Kerman, Iran
- 7Private Practice, New York, USA
- KMID: 2527455
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2022.52.2.112
Abstract
Objective
This study aimed to present and evaluate a new deep learning model for determining cervical vertebral maturation (CVM) degree and growth spurts by analyzing lateral cephalometric radiographs.
Methods
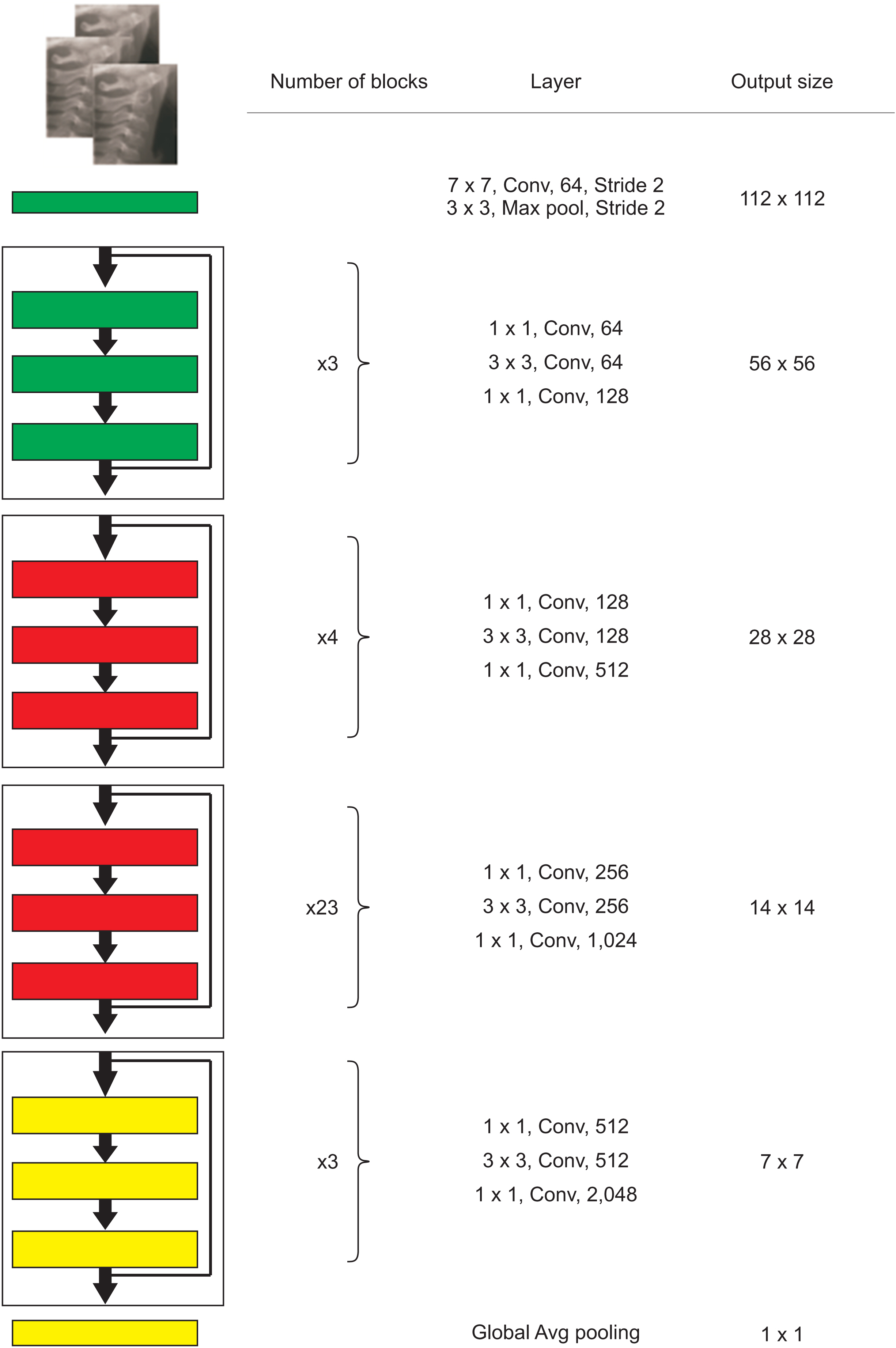
The study sample included 890 cephalograms. The images were classified into six cervical stages independently by two orthodontists. The images were also categorized into three degrees on the basis of the growth spurt: pre-pubertal, growth spurt, and post-pubertal. Subsequently, the samples were fed to a transfer learning model implemented using the Python programming language and PyTorch library. In the last step, the test set of cephalograms was randomly coded and provided to two new orthodontists in order to compare their diagnosis to the artificial intelligence (AI) model’s performance using weighted kappa and Cohen’s kappa statistical analyses.
Results
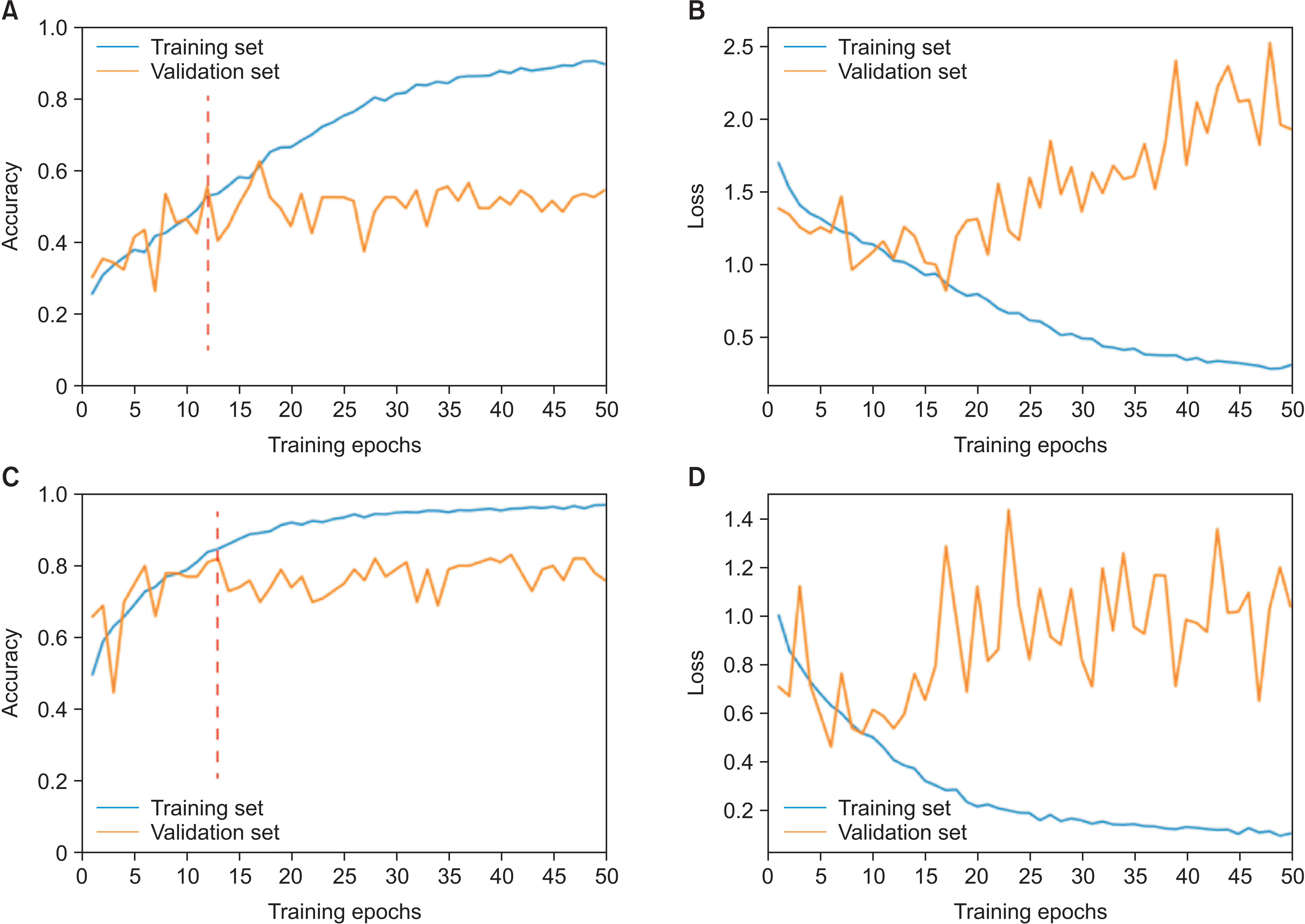
The model’s validation and test accuracy for the six-class CVM diagnosis were 62.63% and 61.62%, respectively. Moreover, the model’s validation and test accuracy for the three-class classification were 75.76% and 82.83%, respectively. Furthermore, substantial agreements were observed between the two orthodontists as well as one of them and the AI model.
Conclusions
The newly developed AI model had reasonable accuracy in detecting the CVM stage and high reliability in detecting the pubertal stage. However, its accuracy was still less than that of human observers. With further improvements in data quality, this model should be able to provide practical assistance to practicing dentists in the future.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Baccetti T, Franchi L, McNamara JA Jr. 2005; The cervical vertebral maturation (CVM) method for the assessment of optimal treatment timing in dentofacial orthopedics. Semin Orthod. 11:119–29. DOI: 10.1053/j.sodo.2005.04.005.
Article2. Hunter CJ. 1966; The correlation of facial growth with body height and skeletal maturation at adolescence. Angle Orthod. 36:44–54. DOI: 10.1043/0003-3219(1966)036<0044:TCOFGW>2.0.CO;2. PMID: 5218761.3. McNamara JA Jr, Franchi L. 2018; The cervical vertebral maturation method: a user's guide. Angle Orthod. 88:133–43. DOI: 10.2319/111517-787.1. PMID: 29337631. PMCID: PMC8312535.
Article4. Franchi L, Baccetti T, De Toffol L, Polimeni A, Cozza P. 2008; Phases of the dentition for the assessment of skeletal maturity: a diagnostic performance study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 133:395–400. quiz 476.e1–2. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.02.040. PMID: 18331939.
Article5. Flores-Mir C, Nebbe B, Major PW. 2004; Use of skeletal maturation based on hand-wrist radiographic analysis as a predictor of facial growth: a systematic review. Angle Orthod. 74:118–24. DOI: 10.1043/0003-3219(2004)074<0118:UOSMBO>2.0.CO;2. PMID: 15038500.6. Zhao XG, Lin J, Jiang JH, Wang Q, Ng SH. 2012; Validity and reliability of a method for assessment of cervical vertebral maturation. Angle Orthod. 82:229–34. DOI: 10.2319/051511-333.1. PMID: 21875315. PMCID: PMC8867953.
Article7. Nestman TS, Marshall SD, Qian F, Holton N, Franciscus RG, Southard TE. 2011; Cervical vertebrae maturation method morphologic criteria: poor reproducibility. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 140:182–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2011.04.013. PMID: 21803255.
Article8. Makaremi M, Lacaule C, Mohammad-Djafari A. 2019; Deep learning and artificial intelligence for the determination of the cervical vertebra maturation degree from lateral radiography. Entropy. 21:1222. DOI: 10.3390/e21121222. PMCID: PMC7514567.
Article9. Khanagar SB, Al-Ehaideb A, Maganur PC, Vishwanathaiah S, Patil S, Baeshen HA, et al. 2021; Developments, application, and performance of artificial intelligence in dentistry - a systematic review. J Dent Sci. 16:508–22. DOI: 10.1016/j.jds.2020.06.019. PMID: 33384840. PMCID: PMC7770297.
Article10. Amasya H, Yildirim D, Aydogan T, Kemaloglu N, Orhan K. 2020; Cervical vertebral maturation assessment on lateral cephalometric radiographs using artificial intelligence: comparison of machine learning classifier models. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 49:20190441. DOI: 10.1259/dmfr.20190441. PMID: 32105499. PMCID: PMC7333473.
Article11. LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. 2015; Deep learning. Nature. 521:436–44. DOI: 10.1038/nature14539. PMID: 26017442. PMCID: PMC8942293.
Article12. Schwendicke F, Samek W, Krois J. 2020; Artificial intelligence in dentistry: chances and challenges. J Dent Res. 99:769–74. DOI: 10.1177/0022034520915714. PMID: 32315260. PMCID: PMC7309354.
Article13. Mohammad-Rahimi H, Nadimi M, Ghalyanchi-Langeroudi A, Taheri M, Ghafouri-Fard S. 2021; Application of machine learning in diagnosis of COVID-19 through X-ray and CT images: a scoping review. Front Cardiovasc Med. 8:638011. DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.638011. PMID: 33842563. PMCID: PMC8027078. PMID: 3d26d1f99b334befa87fe1bafca467c0.
Article14. Mohammad-Rahimi H, Nadimi M, Rohban MH, Shamsoddin E, Lee VY, Motamedian SR. 2021; Machine learning and orthodontics, current trends and the future opportunities: a scoping review. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 160:170–92.e4. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2021.02.013. PMID: 34103190.
Article15. Ravishankar H, Sudhakar P, Venkataramani R, Thiruvenkadam S, Annangi P, Babu N, et al. 2016. Understanding the mechanisms of deep transfer learning for medical images. Springer International Publishing;Cham: p. 188–96. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-46976-8_20.16. Kök H, Acilar AM, İzgi MS. 2019; Usage and comparison of artificial intelligence algorithms for determination of growth and development by cervical vertebrae stages in orthodontics. Prog Orthod. 20:41. DOI: 10.1186/s40510-019-0295-8. PMID: 31728776. PMCID: PMC6856254. PMID: 9e00597c2a594eeeac0d562615036f6b.
Article17. Mongan J, Moy L, Kahn CE Jr. 2020; Checklist for Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging (CLAIM): a guide for authors and reviewers. Radiol Artif Intell. 2:e200029. DOI: 10.1148/ryai.2020200029. PMID: 33937821. PMCID: PMC8017414.
Article18. Wang CW, Huang CT, Lee JH, Li CH, Chang SW, Siao MJ, et al. 2016; A benchmark for comparison of dental radiography analysis algorithms. Med Image Anal. 31:63–76. DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2016.02.004. PMID: 26974042.
Article19. Landis JR, Koch GG. 1977; The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 33:159–74. DOI: 10.2307/2529310. PMID: 843571.
Article20. Tajmir SH, Lee H, Shailam R, Gale HI, Nguyen JC, Westra SJ, et al. 2019; Artificial intelligence-assisted interpretation of bone age radiographs improves accuracy and decreases variability. Skeletal Radiol. 48:275–83. DOI: 10.1007/s00256-018-3033-2. PMID: 30069585.
Article21. Graber LW, Vanarsdall RL Jr, Vig KWL, Huang GJ. 2016. Orthodontics: current principles and techniques. 6th ed. Elsevier;St. Louis:22. Yu HJ, Cho SR, Kim MJ, Kim WH, Kim JW, Choi J. 2020; Automated skeletal classification with lateral cephalometry based on artificial intelligence. J Dent Res. 99:249–56. DOI: 10.1177/0022034520901715. PMID: 31977286.
Article23. Amasya H, Cesur E, Yıldırım D, Orhan K. 2020; Validation of cervical vertebral maturation stages: artificial intelligence vs human observer visual analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 158:e173–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2020.08.014. PMID: 33250108.
Article24. Yu Y, Lin H, Meng J, Wei X, Guo H, Zhao Z. 2017; Deep transfer learning for modality classification of medical images. Information. 8:91. DOI: 10.3390/info8030091.
Article25. He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. 2016. Deep residual learning for image recognition. Paper presented at: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2016 Jun 27-30; Las Vegas, USA. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers;Piscataway: p. 770–8. DOI: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. PMID: 26180094.
Article26. Wang W, Liang D, Chen Q, Iwamoto Y, Han XH, Zhang Q, et al. Chen YW, Jain LC, editors. 2020. Medical image classification using deep learning. Deep learning in healthcare: paradigms and applications. Springer;Cham: p. 33–51. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-32606-7_3.
Article27. Shin HC, Tenenholtz NA, Rogers JK, Schwarz CG, Senjem ML, Gunter JL, et al. 2018. Medical image synthesis for data augmentation and anonymization using generative adversarial networks. Springer International Publishing;Cham: p. 1–11. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-00536-8_1.28. Johnson JM, Khoshgoftaar TM. 2019; Survey on deep learning with class imbalance. J Big Data. 6:27. DOI: 10.1186/s40537-019-0192-5. PMID: d7c13b2130ee4ee68add6580cabd608c.
Article29. Ramentol E, Caballero Y, Bello R, Herrera F. 2012; SMOTE-RSB*: a hybrid preprocessing approach based on oversampling and undersampling for high imbalanced data-sets using SMOTE and rough sets theory. Knowl Inf Syst. 33:245–65. DOI: 10.1007/s10115-011-0465-6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A longitudinal cephalometric study of the craniofacial growth changes of Koreans aged from 8 to 16 years
- Deep Learning in Dental Radiographic Imaging
- Maturation of cervical vertebrae and mandibular growth changes
- The Effects of Growth Hormone on Pubertal Maturation
- Deep-Learning-Based Molecular Imaging Biomarkers: Toward Data-Driven Theranostics