J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2022 Mar;65(2):245-254. 10.3340/jkns.2021.0120.
Arterial Wall Imaging in Angiographically Occult Spontaneous Subarachnoid Hemorrhage : New Insight into the Usual Suspect
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Armed Forces Capital Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- KMID: 2527181
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2021.0120
Abstract
Objective
: The etiology of angiographically occult spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage (AOsSAH) is unclear. Threedimensional (3D) high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging (HVM) might be useful in detecting the hidden arterial wall angiopathy in patients with AOsSAH. We aimed to demonstrate the feasibility of HVM for detecting the arterial cause of AOsSAH.
Methods
: Patients, who were diagnosed with AOsSAH in the first evaluations and underwent HVM, were enrolled. Their clinical and radiologic data were retrospectively reviewed. Especially, focal enhancement of arterial wall on HVM and repetitive catheterized angiograms were precisely compared.
Results
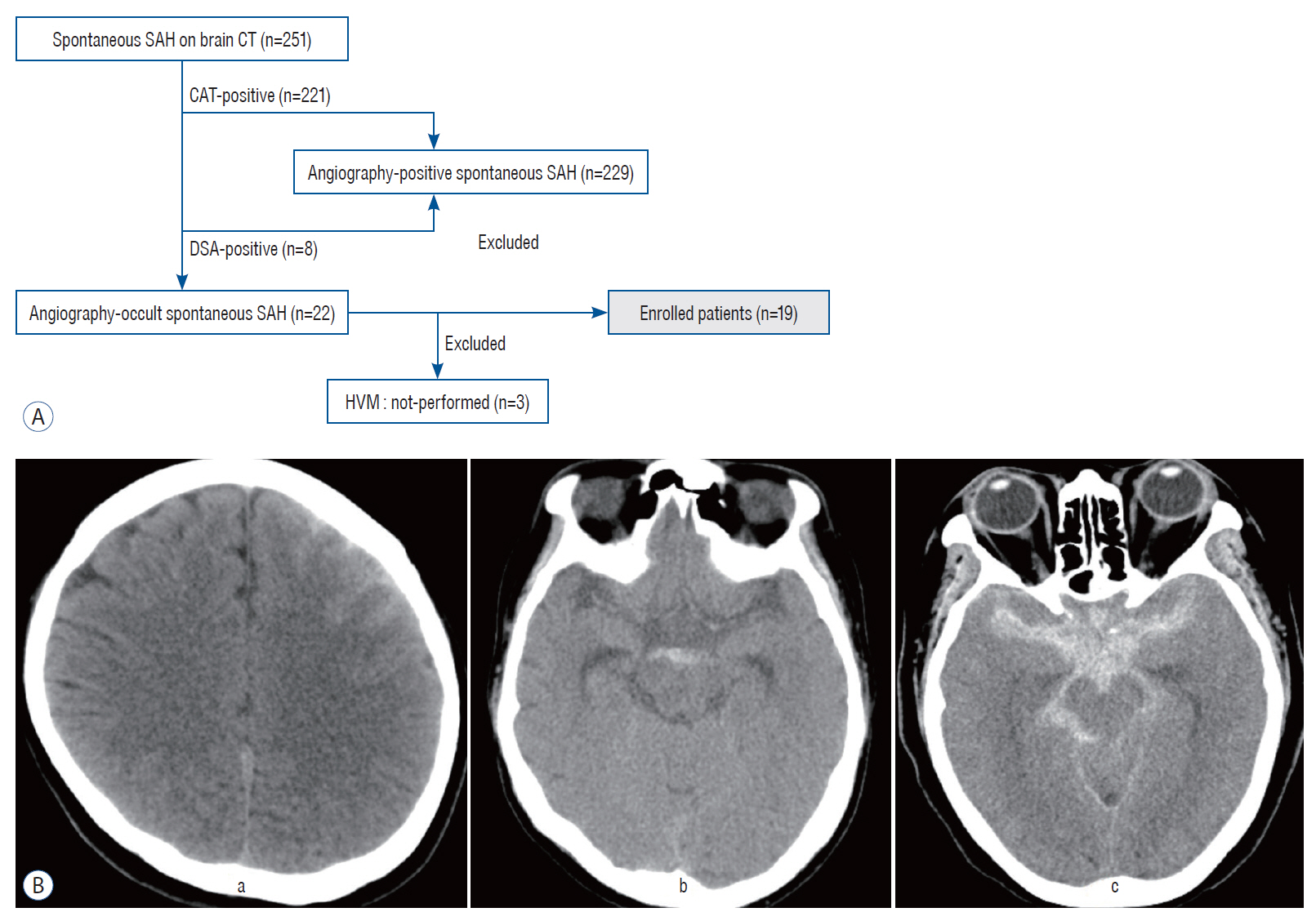
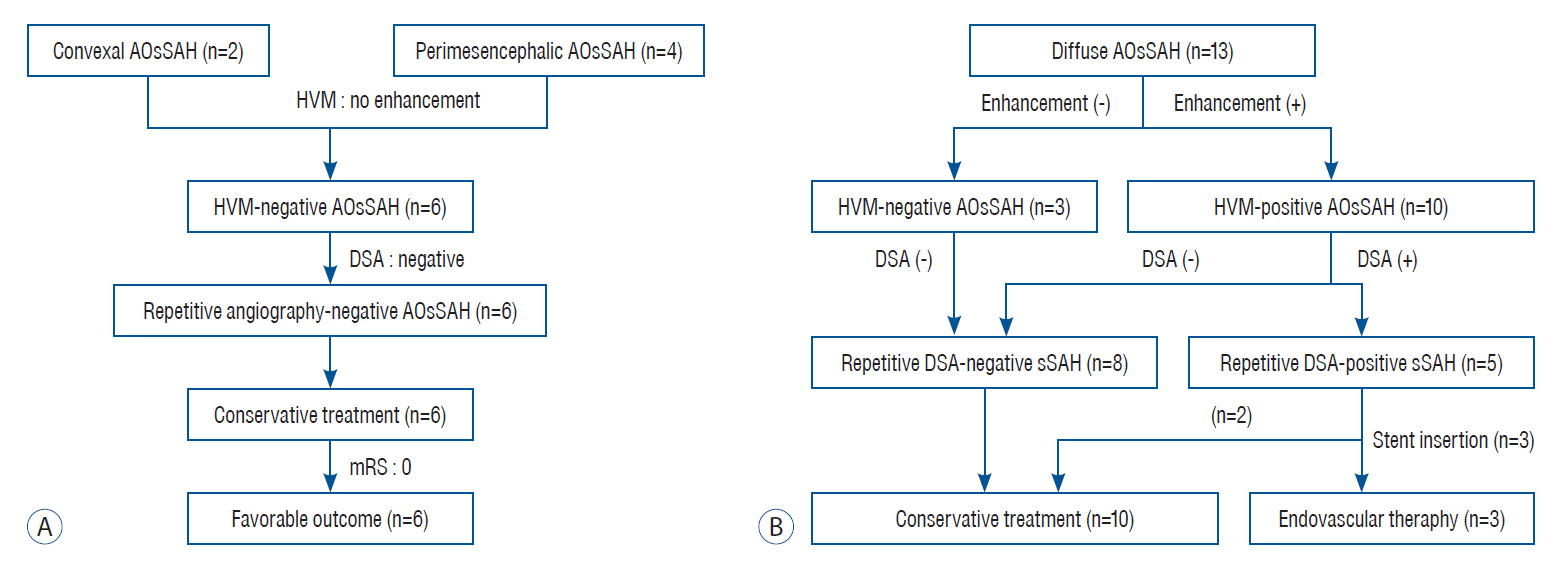
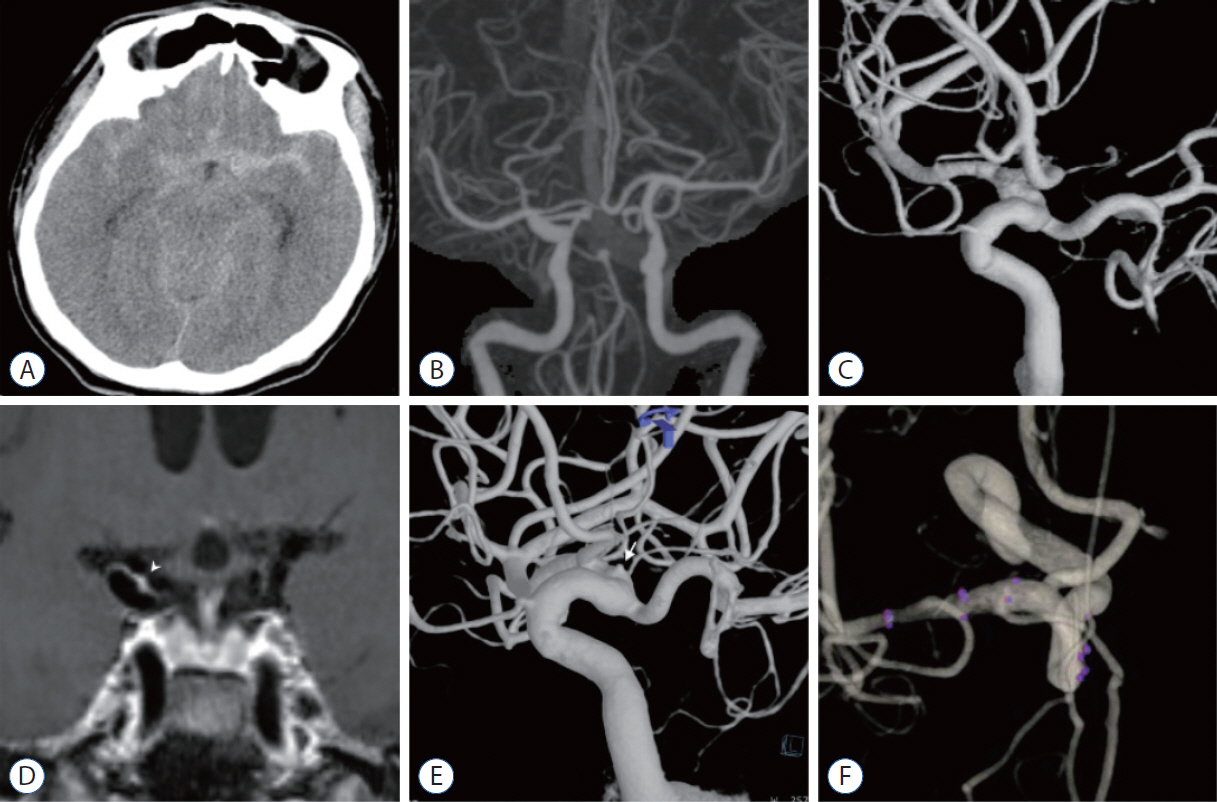
: Among 251 patients with spontaneous SAH, 22 patients were diagnosed with AOsSAH in the first evaluations (8.76%). After excluding three patients who did not undergo 3D-HVM, 19 patients were enrolled and classified as convexal (n=2) or perimesencephalic (n=4), and diffuse (n=13) groups. In convexal and perimesencephalic groups, no focal enhancement on HVM and no positive findings on repetitive angiography were noted. In diffuse group, 10 patients showed focal enhancement of arterial wall on HVM (10/13, 76.9%). Repeated angiography with 3D reconstruction revealed four patients of angiographically positive causative arteriopathy and possible lesion in one case in the concordant location of intramural enhancement on 3D-HVM (5/10, 50%). Three of them were treated with endovascular stent insertion. All patients, except one, recovered with good clinical outcome (3-month modified Rankin score, 0 and 1).
Conclusion
: 3D-HVM was useful in detecting hidden true arteriopathy in AOsSAH. It may provide new insights into the etiologic investigation of AOsSAH by proving information about the arterial wall status.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Vessel Wall Imaging in Angiogram-Negative Diffuse Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Reveals a Ruptured Lenticulostriate Aneurysm
Huy Quang Phi, Suehyb Ghazi Alkhatib, Scott Bruce Raymond, Omar Aftab Choudhri, Jae Won Song
Neurointervention. 2024;19(2):118-122. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2024.00185.
Reference
-
References
1. Beseoglu K, Pannes S, Steiger HJ, Hänggi D. Long-term outcome and quality of life after nonaneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 152:409–416. 2010.
Article2. Bhogal P, Uff C, Makalanda HL. Vessel wall MRI and intracranial aneurysms. J Neurointerv Surg. 8:1160–1162. 2016.
Article3. Boswell S, Thorell W, Gogela S, Lyden E, Surdell D. Angiogram-negative subarachnoid hemorrhage: outcomes data and review of the literature. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 22:750–757. 2013.
Article4. Buyukkaya R, Yıldırım N, Cebeci H, Kocaeli H, Dusak A, Ocakoğlu G, et al. The relationship between perimesencephalic subarachnoid hemorrhage and deep venous system drainage pattern and calibrations. Clin Imaging. 38:226–230. 2014.
Article5. Cánovas D, Gil A, Jato M, de Miquel M, Rubio F. Clinical outcome of spontaneous non-aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in 108 patients. Eur J Neurol. 19:457–461. 2012.
Article6. Chung JW, Kim BJ, Choi BS, Sohn CH, Bae HJ, Yoon BW, et al. High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging reveals hidden etiologies of symptomatic vertebral arterial lesions. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 23:293–302. 2014.
Article7. Edjlali M, Gentric JC, Régent-Rodriguez C, Trystram D, Hassen WB, Lion S, et al. Does aneurysmal wall enhancement on vessel wall MRI help to distinguish stable from unstable intracranial aneurysms? Stroke. 45:3704–3706. 2014.
Article8. Germans MR, Coert BA, Majoie CB, van den Berg R, Lycklama À Nijeholt G, Rinkel GJ, et al. Yield of spinal imaging in nonaneurysmal, nonperimesencephalic subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurology. 84:1337–1340. 2015.
Article9. Kalra VB, Wu X, Matouk CC, Malhotra A. Use of follow-up imaging in isolated perimesencephalic subarachnoid hemorrhage: a meta-analysis. Stroke. 46:401–406. 2015.
Article10. Kapadia A, Schweizer TA, Spears J, Cusimano M, Macdonald RL. Nonaneurysmal perimesencephalic subarachnoid hemorrhage: diagnosis, pathophysiology, clinical characteristics, and long-term outcome. World Neurosurg. 82:1131–1143. 2014.
Article11. Khan AA, Smith JD, Kirkman MA, Robertson FJ, Wong K, Dott C, et al. Angiogram negative subarachnoid haemorrhage: outcomes and the role of repeat angiography. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 115:1470–1475. 2013.
Article12. Kim YW, Lawson MF, Hoh BL. Nonaneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: an update. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 14:328–334. 2012.
Article13. Konczalla J, Kashefiolasl S, Brawanski N, Lescher S, Senft C, Platz J, et al. Cerebral vasospasm and delayed cerebral infarctions in 225 patients with non-aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: the underestimated risk of Fisher 3 blood distribution. J Neurointerv Surg. 8:1247–1252. 2016.
Article14. Konczalla J, Kashefiolasl S, Brawanski N, Senft C, Seifert V, Platz J. Increasing numbers of nonaneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in the last 15 years: antithrombotic medication as reason and prognostic factor? J Neurosurg. 124:1731–1737. 2016.
Article15. Konczalla J, Schuss P, Platz J, Vatter H, Seifert V, Güresir E. Clinical outcome and prognostic factors of patients with angiogram-negative and non-perimesencephalic subarachnoid hemorrhage: benign prognosis like perimesencephalic SAH or same risk as aneurysmal SAH? Neurosurg Rev. 38:121–127. discussion 127. 2015.
Article16. Lehman VT, Brinjikji W, Kallmes DF, Huston J 3rd, Lanzino G, Rabinstein AA, et al. Clinical interpretation of high-resolution vessel wall MRI of intracranial arterial diseases. Br J Radiol. 89:20160496. 2016.
Article17. Macdonald RL, Schweizer TA. Spontaneous subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet. 389:655–666. 2017.
Article18. Marder CP, Narla V, Fink JR, Tozer Fink KR. Subarachnoid hemorrhage: beyond aneurysms. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 202:25–37. 2014.
Article19. Mossa-Basha M, Alexander M, Gaddikeri S, Yuan C, Gandhi D. Vessel wall imaging for intracranial vascular disease evaluation. J Neurointerv Surg. 8:1154–1159. 2016.
Article20. Nagahata S, Nagahata M, Obara M, Kondo R, Minagawa N, Sato S, et al. Wall enhancement of the intracranial aneurysms revealed by magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging using three-dimensional turbo spin-echo sequence with motion-sensitized driven-equilibrium: a sign of ruptured aneurysm? Clin Neuroradiol. 26:277–283. 2016.
Article21. Natori T, Sasaki M, Miyoshi M, Ohba H, Oura MY, Narumi S, et al. Detection of vessel wall lesions in spontaneous symptomatic vertebrobasilar artery dissection using T1-weighted 3-dimensional Imaging. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 23:2419–2424. 2014.
Article22. Park SQ, Kwon OK, Kim SH, Oh CW, Han MH. Pre-mesencephalic subarachnoid hemorrhage: rupture of tiny aneurysms of the basilar artery perforator. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 151:1639–1646. 2009.
Article23. Rinkel GJ, Wijdicks EF, Vermeulen M, Ramos LM, Tanghe HL, Hasan D, et al. Nonaneurysmal perimesencephalic subarachnoid hemorrhage: CT and MR patterns that differ from aneurysmal rupture. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 12:829–834. 1991.24. Rogg JM, Smeaton S, Doberstein C, Goldstein JH, Tung GA, Haas RA. Assessment of the value of MR imaging for examining patients with angiographically negative subarachnoid hemorrhage. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 172:201–206. 1999.
Article25. Schievink WI, Wijdicks EF. Origin of pretruncal nonaneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: ruptured vein, perforating artery, or intramural hematoma? Mayo Clin Proc. 75:1169–1173. 2000.
Article26. Tan HW, Chen X, Maingard J, Barras CD, Logan C, Thijs V, et al. Intracranial vessel wall imaging with magnetic resonance imaging: current techniques and applications. World Neurosurg. 112:186–198. 2018.
Article27. Woodfield J, Rane N, Cudlip S, Byrne JV. Value of delayed MRI in angiogram-negative subarachnoid haemorrhage. Clin Radiol. 69:350–356. 2014.
Article28. Yu DW, Jung YJ, Choi BY, Chang CH. Subarachnoid hemorrhage with negative baseline digital subtraction angiography: is repeat digital subtraction angiography necessary? J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 14:210–215. 2012.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Angiographically Occult Vascular Malformations of the Brain: Report of Three Cases
- Symptomatic Tarlov Cyst Following Spontaneous Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
- Angiographically Occult Vascular Malformation of the Cauda Equina Presenting Massive Spinal Subdural and Subarachnoid Hematoma
- Spontaneous Spinal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Report of a Case
- Angiographically occult arteriovenous malformations causing intracerebral hemorrhage