J Korean Foot Ankle Soc.
2022 Mar;26(1):54-58. 10.14193/jkfas.2022.26.1.54.
Intra-Osseous Nerve Transposition in Iatrogenic Injury of the Superficial Peroneal Nerve: Two Case Reports
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Yes Hospital Guro, Korea
- 2Seojong Sports Medicine & Performance Center, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2527013
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14193/jkfas.2022.26.1.54
Abstract
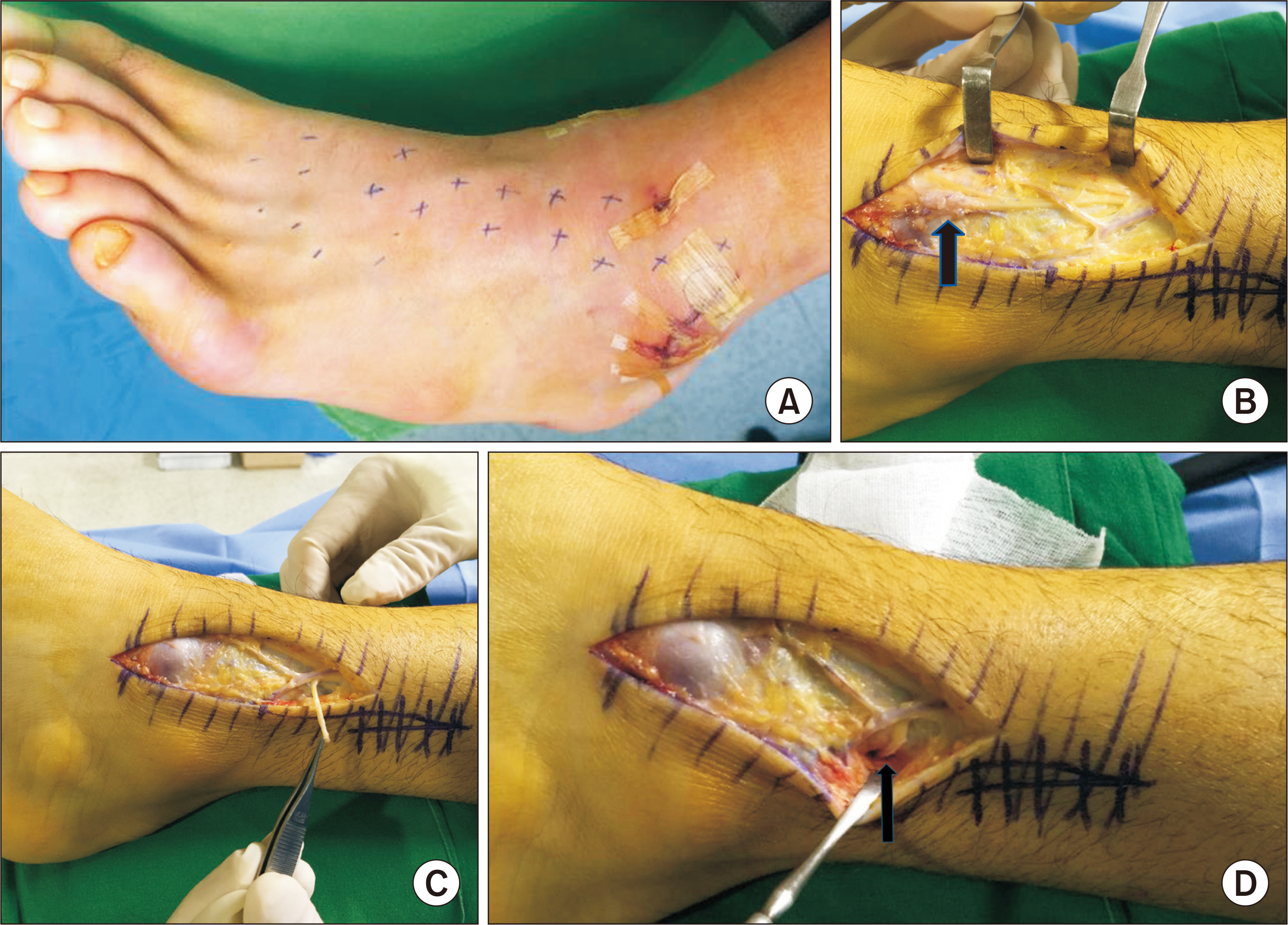
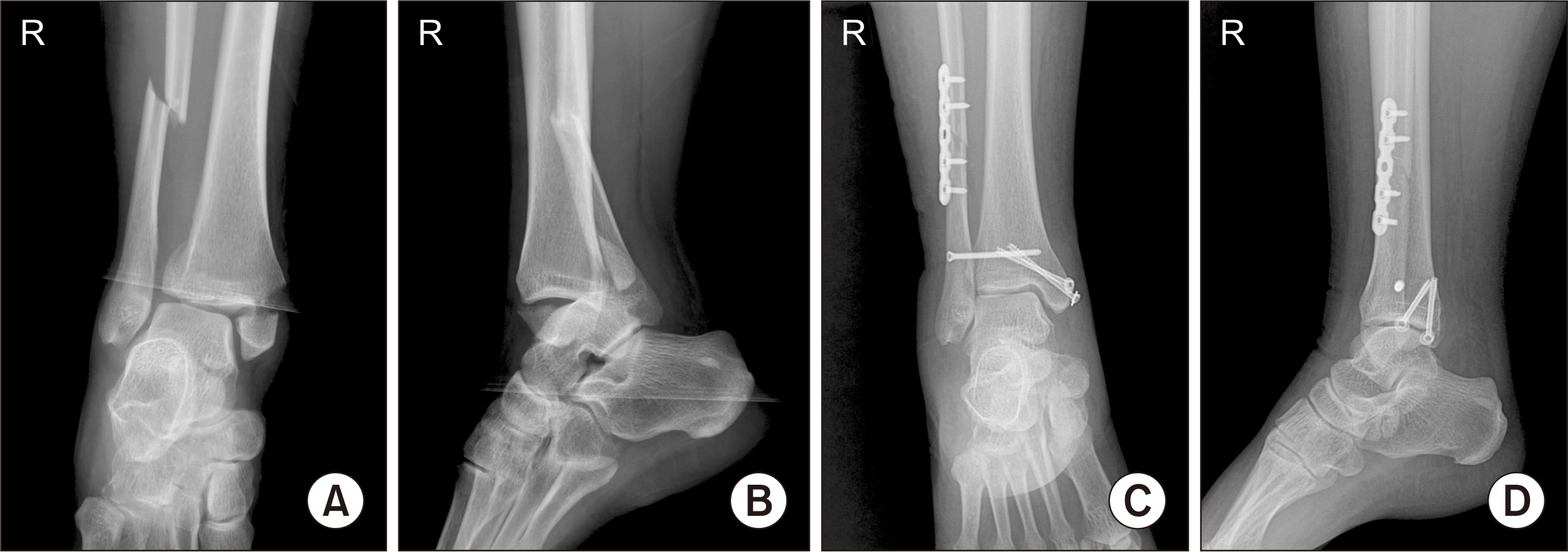
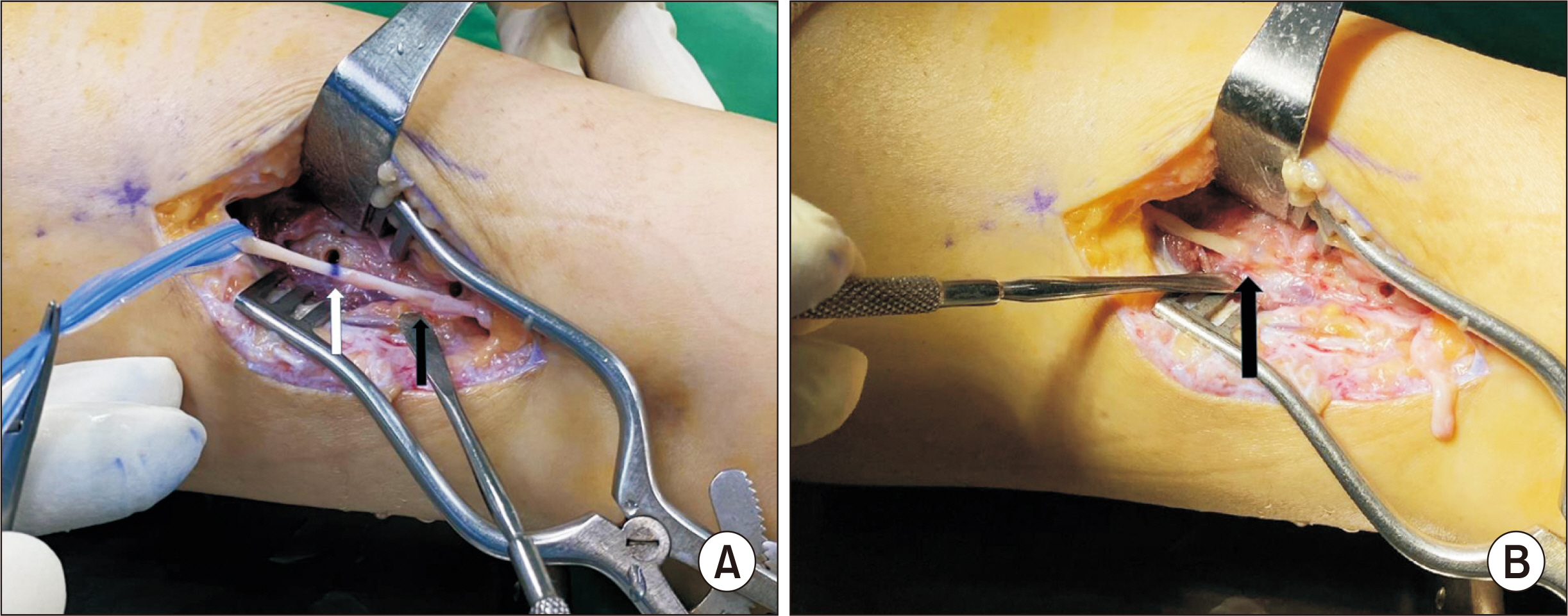
- Superficial peroneal nerve (SPN) injuries happen occasionally during surgical treatment of fibular fracture, lateral ankle ligament repair, etc. These injuries are caused because of the variable location of the SPN. It is the injuries are usually treated by steroid injections or anticonvulsants. However, neural symptoms may not respond to treatment and may persist and progress to a painful neuroma. Intractable pain may need surgical treatment. We examined two cases of iatrogenic postoperative SPN injury, and we treated them with transection of the SPN and the intraosseous transposition of the proximal nerve stump using the thrombin-fibrinogen complex with satisfactory outcomes. We report these two cases with a review of the relevant literature.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Redfern DJ, Sauvé PS, Sakellariou A. 2003; Investigation of incidence of superficial peroneal nerve injury following ankle fracture. Foot Ankle Int. 24:771–4. doi: 10.1177/107110070302401006. DOI: 10.1177/107110070302401006. PMID: 14587991.
Article2. Kim HJ, Oh JK, Oh CW, Hwang JH, Biswal S. 2010; Anterior transposition of the superficial peroneal nerve branch during the internal fixation of the lateral malleolus. J Trauma. 68:421–4. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e3181a70847. DOI: 10.1097/TA.0b013e3181a70847. PMID: 20154553.
Article3. Davidovitch RI, Egol KA. Bucholz RW, Hickman JD, Court-Brown CM, Tornetta P, editors. Ankle fractures. Rockwood and Green's fractures in adults. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2010. p. 1975–2021.4. Dellon AL, Aszmann OC. 1998; Treatment of superficial and deep peroneal neuromas by resection and translocation of the nerves into the anterolateral compartment. Foot Ankle Int. 19:300–3. doi: 10.1177/107110079801900506. DOI: 10.1177/107110079801900506. PMID: 9622420.
Article5. Lisowski FP, Oxnard CE. 2007. Anatomical terms and their derivation. World Scientific;Singapore:6. Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Grant's atlas of anatomy. 12th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2009.7. Huene DB, Bunnell WP. 1995; Operative anatomy of nerves encountered in the lateral approach to the distal part of the fibula. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 77:1021–4. doi: 10.2106/00004623-199507000-00007. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-199507000-00007. PMID: 7608223.
Article8. Styf J. 1989; Entrapment of the superficial peroneal nerve. Diagnosis and results of decompression. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 71:131–5. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.71B1.2914984. DOI: 10.1302/0301-620X.71B1.2914984. PMID: 2914984.
Article9. Gessini L, Jandolo B, Pietrangeli A. 1984; The anterior tarsal syndrome. Report of four cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 66:786–7. doi: 10.2106/00004623-198466050-00023. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-198466050-00023. PMID: 6725331.
Article10. Mass DP, Ciano MC, Tortosa R, Newmeyer WL, Kilgore ES Jr. 1984; Treatment of painful hand neuromas by their transfer into bone. Plast Reconstr Surg. 74:182–5. doi: 10.1097/00006534-198408000-00002. DOI: 10.1097/00006534-198408000-00002. PMID: 6463143.
Article11. Goldstein SA, Sturim HS. 1985; Intraosseous nerve transposition for treatment of painful neuromas. J Hand Surg Am. 10:270–4. doi: 10.1016/S0363-5023(85)80120-9. DOI: 10.1016/S0363-5023(85)80120-9. PMID: 3980943.
Article12. Chiodo CP, Miller SD. 2004; Surgical treatment of superficial peroneal neuroma. Foot Ankle Int. 25:689–94. doi: 10.1177/107110070402501001. DOI: 10.1177/107110070402501001. PMID: 15566699.
Article13. Boldrey E. 1943; Amputation neuroma in nerves implanted in bone. Ann Surg. 118:1052–7. doi: 10.1097/00000658-194312000-00011. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-194312000-00011. PMID: 17858325. PMCID: PMC1617761.
Article14. Hemmy DC. 1981; Intramedullary nerve implantation in amputation and other traumatic neuromas. J Neurosurg. 54:842–3. doi: 10.3171/jns.1981.54.6.0842. DOI: 10.3171/jns.1981.54.6.0842. PMID: 6264052.
Article15. Sierra DH, O'Grady K, Toriumi DM, Foresman PA, Rodeheaver GT, Eberhardt A, et al. 2000; Modulation of mechanical properties in multiple-component tissue adhesives. J Biomed Mater Res. 52:534–42. doi: 10.1002/1097-4636(20001205)52:3<534::AID-JBM12>3.0.CO;2-7. DOI: 10.1002/1097-4636(20001205)52:3<534::AID-JBM12>3.0.CO;2-7. PMID: 11007622.
Article