J Korean Foot Ankle Soc.
2022 Mar;26(1):16-21. 10.14193/jkfas.2022.26.1.16.
Diagnosis and Management of Suspected Deltoid Injury
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea
- KMID: 2527007
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14193/jkfas.2022.26.1.16
Abstract
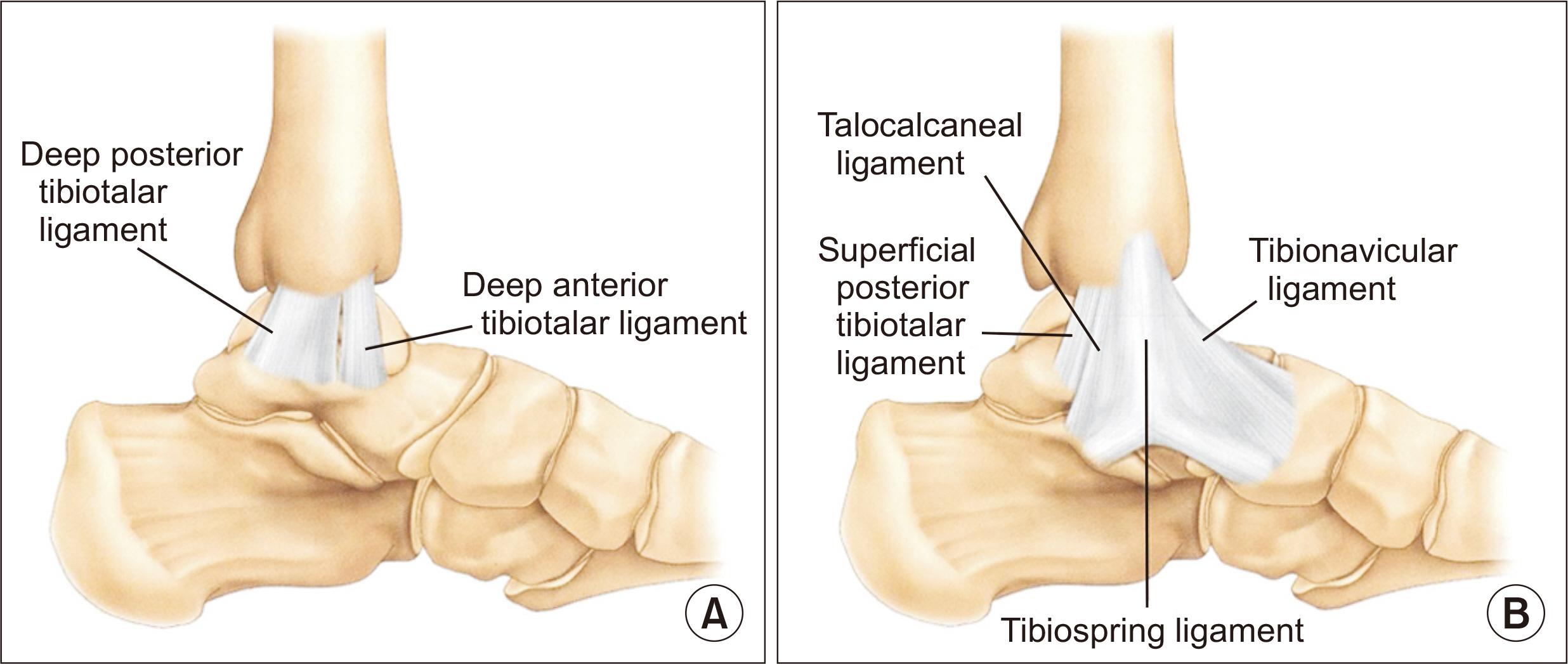
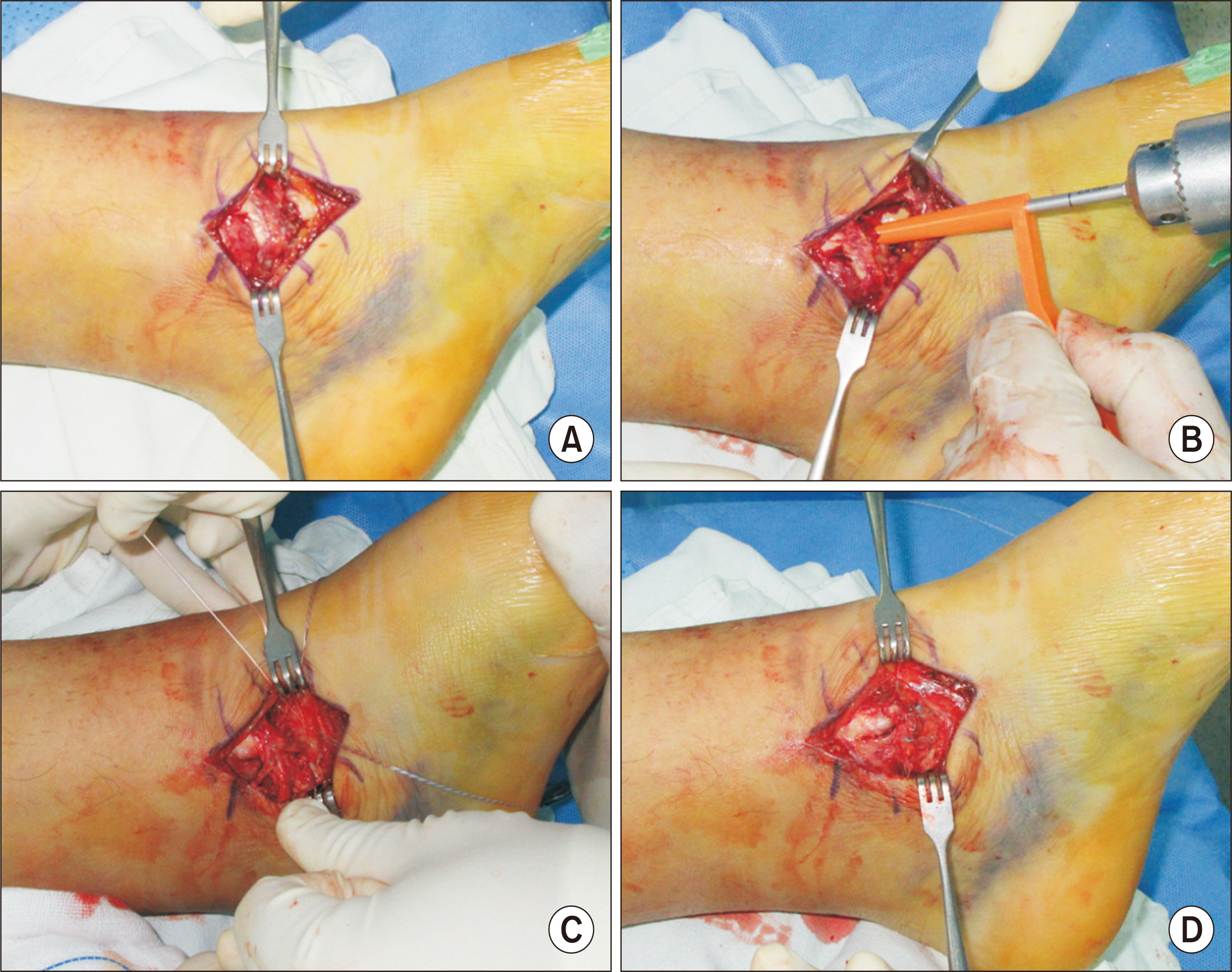
- When an ankle lateral malleolar fracture is accompanied by a deltoid ligament rupture without a medial malleolar fracture, such an injury is called a bimalleolar equivalent fracture. This means that even if there is no bony injury on the medial side, there may be functional instability of the ankle joint due to damage to the deltoid ligament. Manual or gravity external rotational stress radiography is used to differentiate an ankle bimalleolar equivalent fracture from an isolated lateral malleolar fracture. If the medial joint gap is widened on the stress radiography, the deltoid ligament injury can be diagnosed, and surgical treatment for fibula fractures is recommended. After open reduction of the fibula fracture (with syndesmotic fixation if needed), a decision on the repair of the deltoid ligament is taken depending on the surgeons’ preference and intraoperative findings. The deltoid ligament repair is performed by inserting a suture anchor (or anchors) in the medial malleolus and fixing the deep and superficial deltoid ligaments to the medial malleolus. The only randomized study to evaluate the utility of deltoid ligament sutures in ankle fractures did not support the deltoid ligament suture, but the study itself had many limitations. An appropriately powered, randomized, controlled trial of the deltoid ligament repair with both patient-reported outcome and radiographic outcome evaluation is needed in the future.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee S, Lin J, Hamid KS, Bohl DD. 2019; Deltoid ligament rupture in ankle fracture: diagnosis and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 27:e648–58. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-18-00198. DOI: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-18-00198. PMID: 30475279.2. Campbell KJ, Michalski MP, Wilson KJ, Goldsmith MT, Wijdicks CA, LaPrade RF, et al. 2014; The ligament anatomy of the deltoid complex of the ankle: a qualitative and quantitative anatomical study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 96:e62. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.M.00870. DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.M.00870. PMID: 24740670.
Article3. Korean Foot and Ankle Society. 2019. Textbook of the foot and ankle. 2nd ed. Panmuneducation;Seoul:4. Milner CE, Soames RW. 1998; The medial collateral ligaments of the human ankle joint: anatomical variations. Foot Ankle Int. 19:289–92. doi: 10.1177/107110079801900504. DOI: 10.1177/107110079801900504. PMID: 9622418.
Article5. Rasmussen O, Kromann-Andersen C, Boe S. 1983; Deltoid ligament. Functional analysis of the medial collateral ligamentous apparatus of the ankle joint. Acta Orthop Scand. 54:36–44. doi: 10.3109/17453678308992867. DOI: 10.3109/17453678308992867. PMID: 6829280.
Article6. Hintermann B, Knupp M, Pagenstert GI. 2006; Deltoid ligament injuries: diagnosis and management. Foot Ankle Clin. 11:625–37. doi: 10.1016/j.fcl.2006.08.001. DOI: 10.1016/j.fcl.2006.08.001. PMID: 16971253.
Article7. Lack W, Phisitkul P, Femino JE. 2012; Anatomic deltoid ligament repair with anchor-to-post suture reinforcement: technique tip. Iowa Orthop J. 32:227–30. PMID: 23576946. PMCID: PMC3565408.8. Woo SH, Bae SY, Chung HJ. 2018; Short-term results of a ruptured deltoid ligament repair during an acute ankle fracture fixation. Foot Ankle Int. 39:35–45. doi: 10.1177/1071100717732383. DOI: 10.1177/1071100717732383. PMID: 29078057.
Article9. Ramsey PL, Hamilton W. 1976; Changes in tibiotalar area of contact caused by lateral talar shift. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 58:356–7. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-197658030-00010. PMID: 1262367.
Article10. Clarke HJ, Michelson JD, Cox QG, Jinnah RH. 1991; Tibio-talar stability in bimalleolar ankle fractures: a dynamic in vitro contact area study. Foot Ankle. 11:222–7. doi: 10.1177/107110079101100407. DOI: 10.1177/107110079101100407. PMID: 1855708.
Article11. van den Bekerom MP, Mutsaerts EL, van Dijk CN. 2009; Evaluation of the integrity of the deltoid ligament in supination external rotation ankle fractures: a systematic review of the literature. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 129:227–35. doi: 10.1007/s00402-008-0768-6. DOI: 10.1007/s00402-008-0768-6. PMID: 18953550.
Article12. McConnell T, Creevy W, Tornetta P 3rd. 2004; Stress examination of supination external rotation-type fibular fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 86:2171–8. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200410000-00007. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-200410000-00007. PMID: 15466725.
Article13. Nwosu K, Schneiderman BA, Shymon SJ, Harris T. 2018; A medial malleolar "fleck sign" may predict ankle instability in ligamentous supination external rotation ankle fractures. Foot Ankle Spec. 11:246–51. doi: 10.1177/1938640017729494. DOI: 10.1177/1938640017729494. PMID: 28877594.
Article14. Tornetta P 3rd. 2000; Competence of the deltoid ligament in bimalleolar ankle fractures after medial malleolar fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 82:843–8. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200006000-00011. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-200006000-00011. PMID: 10859104.
Article15. DeAngelis NA, Eskander MS, French BG. 2007; Does medial tenderness predict deep deltoid ligament incompetence in supination-external rotation type ankle fractures? J Orthop Trauma. 21:244–7. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0b013e3180413835. DOI: 10.1097/BOT.0b013e3180413835. PMID: 17414551.
Article16. Hsu AR, Lareau CR, Anderson RB. 2015; Repair of acute superficial deltoid complex avulsion during ankle fracture fixation in National Football League players. Foot Ankle Int. 36:1272–8. doi: 10.1177/1071100715593374. DOI: 10.1177/1071100715593374. PMID: 26160387.
Article17. Tourne Y, Charbel A, Picard F, Montbarbon E, Saragaglia D. 1999; Surgical treatment of bi- and trimalleolar ankle fractures: should the medial collateral ligament be sutured or not? J Foot Ankle Surg. 38:24–9. doi: 10.1016/S1067-2516(99)80084-2. DOI: 10.1016/S1067-2516(99)80084-2. PMID: 10028466.
Article18. Zeegers AV, van der Werken C. 1989; Rupture of the deltoid ligament in ankle fractures: should it be repaired? Injury. 20:39–41. doi: 10.1016/0020-1383(89)90043-0. DOI: 10.1016/0020-1383(89)90043-0. PMID: 2592064.
Article19. Maynou C, Lesage P, Mestdagh H, Butruille Y. 1997; [Is surgical treatment of deltoid ligament rupture necessary in ankle fractures?]. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 83:652–7. French doi: RCO-11-1997-83-7-0035-1040-101019-ART81. PMID: 9515134.20. Strömsöe K, Höqevold HE, Skjeldal S, Alho A. 1995; The repair of a ruptured deltoid ligament is not necessary in ankle fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 77:920–1. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.77B6.7593106. DOI: 10.1302/0301-620X.77B6.7593106.21. Mococain P, Bejarano-Pineda L, Glisson R, Kadakia RJ, Akoh CC, Chen J, et al. 2020; Biomechanical effect on joint stability of including deltoid ligament repair in an ankle fracture soft tissue injury model with deltoid and syndesmotic disruption. Foot Ankle Int. 41:1158–64. doi: 10.1177/1071100720929007. DOI: 10.1177/1071100720929007. PMID: 32545997.
Article22. Jones CR, Nunley JA 2nd. 2015; Deltoid ligament repair versus syndesmotic fixation in bimalleolar equivalent ankle fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 29:245–9. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000220. DOI: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000220. PMID: 25186845.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Medial malleolar fracture associated with deltoid ligament rupture following ankle pronation injury
- Delayed surgical repair of the deltoid following acromioplasty: a case report
- Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for corticosteroid-induced deltoid myopathy in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus: a case report
- Reconstruction of Medial Malleolus and Deltoid Ligament using Bone - Patella Tendon Graft in a Child: Case Report
- Deltoid Muscle Rupture Combined with Massive Rotator Cuff Tear