Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2022 Feb;26(1):31-39. 10.14701/ahbps.21-101.
Impact of the extent of resection of neuroendocrine tumor liver metastases on survival: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of HPB and Liver Transplantation, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham, United Kingdom
- 2Institute of Translational Medicine, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham, United Kingdom
- 3Department of Neuroendocrine Medicine and Hepatology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham, United Kingdom
- 4HPB and Liver Transplant Unit, Newcastle University, Newcastle Upon Tyne, United Kingdom
- KMID: 2526830
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.21-101
Abstract
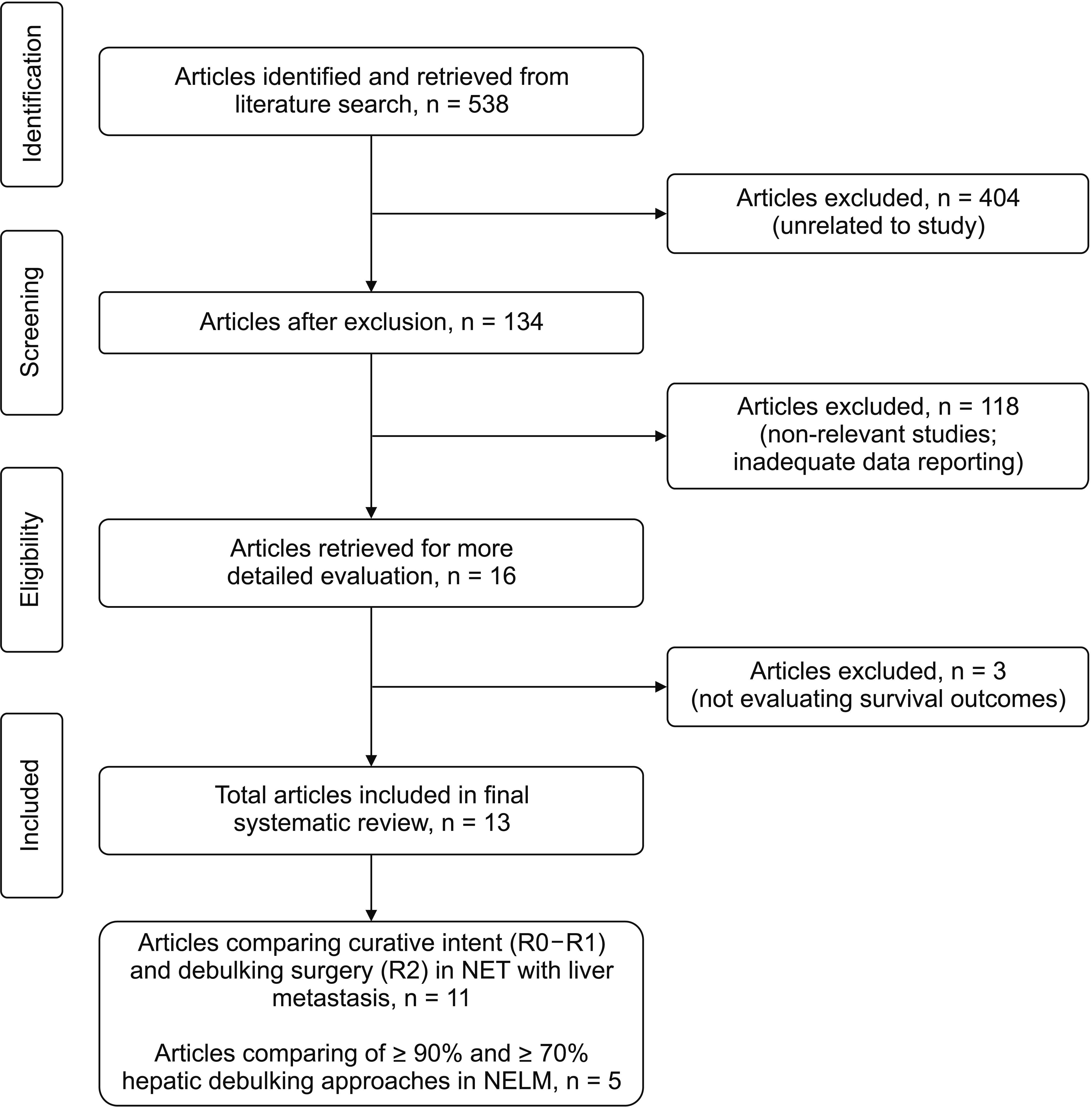
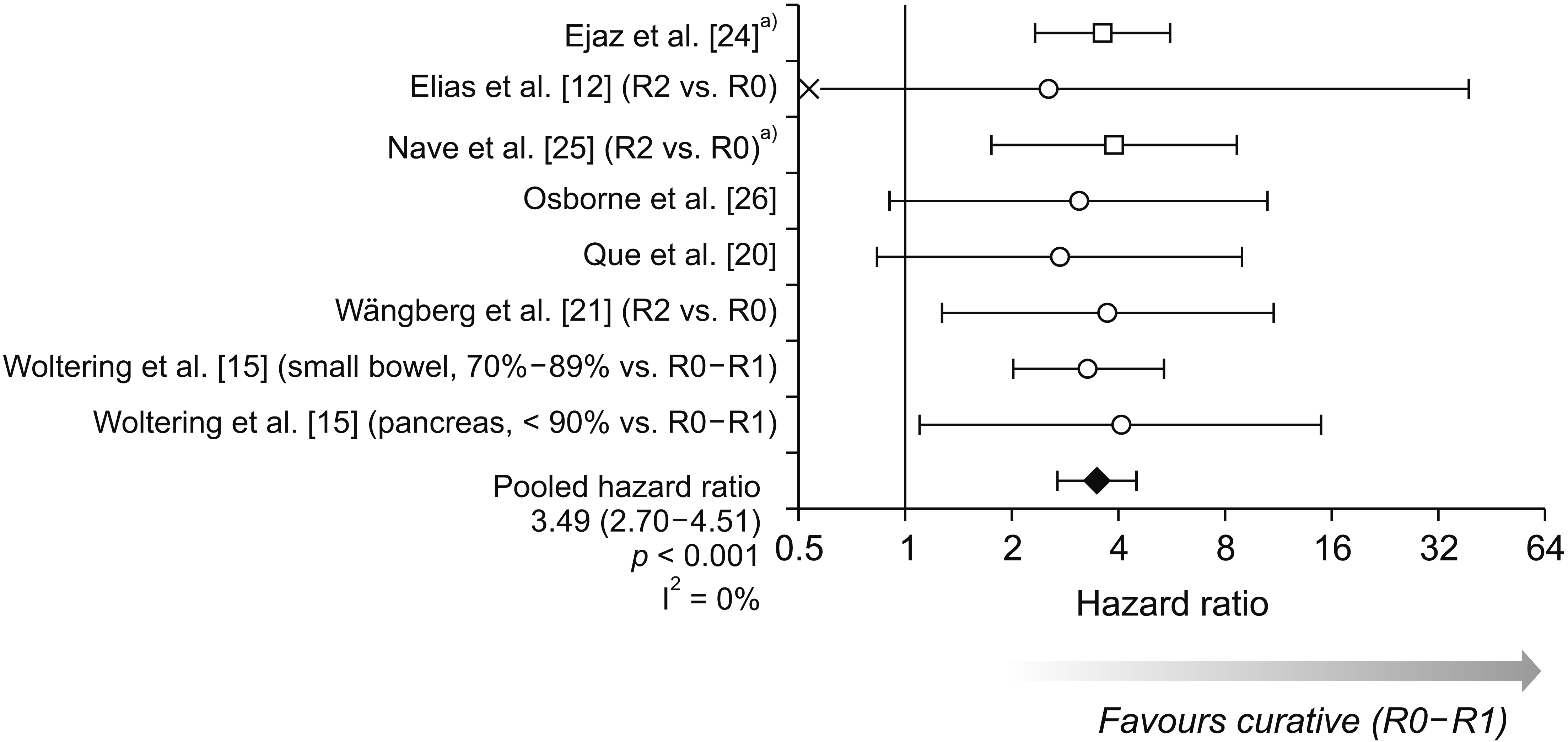
- In patients with neuroendocrine tumors with liver metastases (NETLMs), complete resection of both the primary and liver metastases is a potentially curative option. When complete resection is not possible, debulking of the tumour burden has been proposed to prolong survival. The objective of this systematic review was to evaluate the effect of curative surgery (R0-R1) and debulking surgery (R2) on overall survival (OS) in NETLMs. For the subgroup of R2 resections, outcomes were compared by the degree of hepatic debulking (≥ 90% or ≥ 70%). A systematic review of the literature was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis (PRISMA) guidelines using PubMed, Medline, CINAHL, Cochrane, and Embase databases. Hazard ratios (HRs) were estimated for each study and pooled using a random-effects inverse-variance meta-analysis model. Of 538 articles retrieved, 11 studies (1,729 patients) reported comparisons between curative and debulking surgeries. After pooling these studies, OS was found to be significantly shorter in debulking resections, with an HR of 3.49 (95% confidence interval, 2.70–4.51; p < 0.001). Five studies (654 patients) compared outcomes between ≥ 90% and ≥ 70% hepatic debulking approaches. Whilst these studies reported a tendency for OS and progression-free survival to be shorter in those with a lower degree of debulking, they did not report sufficient data for this to be assessed in a formal meta-analysis. In patients with NETLM, OS following surgical resection is the best to achieve R0-R1 resection. There is also evidence for a progressive reduction in survival benefit with lesser debulking of tumour load.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Modlin IM, Champaneria MC, Chan AK, Kidd M. 2007; A three-decade analysis of 3,911 small intestinal neuroendocrine tumors: the rapid pace of no progress. Am J Gastroenterol. 102:1464–1473. DOI: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01185.x. PMID: 17391319.
Article2. Spolverato G, Bagante F, Wagner D, Buettner S, Gupta R, Kim Y, et al. 2015; Quality of life after treatment of neuroendocrine liver metastasis. J Surg Res. 198:155–164. DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2015.05.048. PMID: 26095419.
Article3. Rindi G, Klöppel G, Couvelard A, Komminoth P, Körner M, Lopes JM, et al. 2007; TNM staging of midgut and hindgut (neuro) endocrine tumors: a consensus proposal including a grading system. Virchows Arch. 451:757–762. DOI: 10.1007/s00428-007-0452-1. PMID: 17674042.
Article4. Boudreaux JP, Klimstra DS, Hassan MM, Woltering EA, Jensen RT, Goldsmith SJ, et al. 2010; The NANETS consensus guideline for the diagnosis and management of neuroendocrine tumors: well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors of the jejunum, ileum, appendix, and cecum. Pancreas. 39:753–766. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181ebb2a5. PMID: 20664473.
Article5. Thompson GB, van Heerden JA, Grant CS, Carney JA, Ilstrup DM. 1988; Islet cell carcinomas of the pancreas: a twenty-year experience. Surgery. 104:1011–1017. PMID: 2904180.6. Chen H, Hardacre JM, Uzar A, Cameron JL, Choti MA. 1998; Isolated liver metastases from neuroendocrine tumors: does resection prolong survival? J Am Coll Surg. 187:88–92. discussion 92–93. DOI: 10.1016/S1072-7515(98)00099-4. PMID: 9660030.
Article7. Farley HA, Pommier RF. 2016; Treatment of neuroendocrine liver metastases. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 25:217–225. DOI: 10.1016/j.soc.2015.08.010. PMID: 26610783.
Article8. Metz DC, Jensen RT. 2008; Gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors: pancreatic endocrine tumors. Gastroenterology. 135:1469–1492. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.05.047. PMID: 18703061. PMCID: PMC2612755.
Article9. Sarmiento JM, Heywood G, Rubin J, Ilstrup DM, Nagorney DM, Que FG. 2003; Surgical treatment of neuroendocrine metastases to the liver: a plea for resection to increase survival. J Am Coll Surg. 197:29–37. DOI: 10.1016/S1072-7515(03)00230-8. PMID: 12831921.10. Glazer ES, Tseng JF, Al-Refaie W, Solorzano CC, Liu P, Willborn KA, et al. 2010; Long-term survival after surgical management of neuroendocrine hepatic metastases. HPB (Oxford). 12:427–433. DOI: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2010.00198.x. PMID: 20662794. PMCID: PMC3028584.
Article11. Mayo SC, de Jong MC, Pulitano C, Clary BM, Reddy SK, Gamblin TC, et al. 2010; Surgical management of hepatic neuroendocrine tumor metastasis: results from an international multi-institutional analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:3129–3136. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-010-1154-5. PMID: 20585879.
Article12. Elias D, Lasser P, Ducreux M, Duvillard P, Ouellet JF, Dromain C, et al. 2003; Liver resection (and associated extrahepatic resections) for metastatic well-differentiated endocrine tumors: a 15-year single center prospective study. Surgery. 133:375–382. DOI: 10.1067/msy.2003.114. PMID: 12717354.
Article13. Maxwell JE, Sherman SK, O'Dorisio TM, Bellizzi AM, Howe JR. 2016; Liver-directed surgery of neuroendocrine metastases: what is the optimal strategy? Surgery. 159:320–333. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2015.05.040. PMID: 26454679. PMCID: PMC4688152.
Article14. Morgan RE, Pommier SJ, Pommier RF. 2018; Expanded criteria for debulking of liver metastasis also apply to pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Surgery. 163:218–225. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2017.05.030. PMID: 29103583.
Article15. Woltering EA, Voros BA, Beyer DT, Wang YZ, Thiagarajan R, Ryan P, et al. 2017; Aggressive surgical approach to the management of neuroendocrine tumors: a report of 1,000 surgical cytoreductions by a single institution. J Am Coll Surg. 224:434–447. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2016.12.032. PMID: 28088602.
Article16. Scott AT, Breheny PJ, Keck KJ, Bellizzi AM, Dillon JS, O'Dorisio TM, et al. 2019; Effective cytoreduction can be achieved in patients with numerous neuroendocrine tumor liver metastases (NETLMs). Surgery. 165:166–175. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2018.04.070. PMID: 30343949. PMCID: PMC6637412.
Article17. Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. 2019; RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 366:l4898. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.l4898. PMID: 31462531.
Article18. Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett S, Sydes MR. 2007; Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials. 8:16. DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-8-16. PMID: 17555582. PMCID: PMC1920534.
Article19. The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. 2014. Review manager (RevMan). Version 5.2.3. The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration;Copenhagen:20. Que FG, Nagorney DM, Batts KP, Linz LJ, Kvols LK. 1995; Hepatic resection for metastatic neuroendocrine carcinomas. Am J Surg. 169:36–42. discussion 42–43. DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9610(99)80107-X. PMID: 7817996.
Article21. Wängberg B, Westberg G, Tylén U, Tisell L, Jansson S, Nilsson O, et al. 1996; Survival of patients with disseminated midgut carcinoid tumors after aggressive tumor reduction. World J Surg. 20:892–899. discussion 899DOI: 10.1007/s002689900136. PMID: 8678968.
Article22. Graff-Baker AN, Sauer DA, Pommier SJ, Pommier RF. 2014; Expanded criteria for carcinoid liver debulking: maintaining survival and increasing the number of eligible patients. Surgery. 156:1369–1376. discussion 1376–1377. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2014.08.009. PMID: 25456912.
Article23. Chamberlain RS, Canes D, Brown KT, Saltz L, Jarnagin W, Fong Y, et al. 2000; Hepatic neuroendocrine metastases: does intervention alter outcomes? J Am Coll Surg. 190:432–445. DOI: 10.1016/S1072-7515(00)00222-2. PMID: 10757381.24. Ejaz A, Reames BN, Maithel S, Poultsides GA, Bauer TW, Fields RC, et al. 2018; Cytoreductive debulking surgery among patients with neuroendocrine liver metastasis: a multi-institutional analysis. HPB (Oxford). 20:277–284. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2017.08.039. PMID: 28964630.
Article25. Nave H, Mössinger E, Feist H, Lang H, Raab H. 2001; Surgery as primary treatment in patients with liver metastases from carcinoid tumors: a retrospective, unicentric study over 13 years. Surgery. 129:170–175. DOI: 10.1067/msy.2001.110426. PMID: 11174710.
Article26. Osborne DA, Zervos EE, Strosberg J, Boe BA, Malafa M, Rosemurgy AS, et al. 2006; Improved outcome with cytoreduction versus embolization for symptomatic hepatic metastases of carcinoid and neuroendocrine tumors. Ann Surg Oncol. 13:572–581. DOI: 10.1245/ASO.2006.03.071. PMID: 16511671.
Article27. Ellis L, Shale MJ, Coleman MP. 2010; Carcinoid tumors of the gastrointestinal tract: trends in incidence in England since 1971. Am J Gastroenterol. 105:2563–2569. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2010.341. PMID: 20823835.
Article28. McEntee GP, Nagorney DM, Kvols LK, Moertel CG, Grant CS. 1990; Cytoreductive hepatic surgery for neuroendocrine tumors. Surgery. 108:1091–1096. PMID: 1701060.29. Chambers AJ, Pasieka JL, Dixon E, Rorstad O. 2008; The palliative benefit of aggressive surgical intervention for both hepatic and mesenteric metastases from neuroendocrine tumors. Surgery. 144:645–651. discussion 651–653. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2008.06.008. PMID: 18847650.
Article30. Mayo SC, de Jong MC, Bloomston M, Pulitano C, Clary BM, Reddy SK, et al. 2011; Surgery versus intra-arterial therapy for neuroendocrine liver metastasis: a multicenter international analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:3657–3665. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-011-1832-y. PMID: 21681380.
Article31. Kennedy AS, Dezarn WA, McNeillie P, Coldwell D, Nutting C, Carter D, et al. 2008; Radioembolization for unresectable neuroendocrine hepatic metastases using resin 90Y-microspheres: early results in 148 patients. Am J Clin Oncol. 31:271–279. DOI: 10.1097/COC.0b013e31815e4557. PMID: 18525307.
Article32. Lacin S, Oz I, Ozkan E, Kucuk O, Bilgic S. 2011; Intra-arterial treatment with 90yttrium microspheres in treatment-refractory and unresectable liver metastases of neuroendocrine tumors and the use of 111in-octreotide scintigraphy in the evaluation of treatment response. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 26:631–637. DOI: 10.1089/cbr.2011.0957. PMID: 21950557.
Article33. Ezziddin S, Meyer C, Kahancova S, Haslerud T, Willinek W, Wilhelm K, et al. 2012; 90Y Radioembolization after radiation exposure from peptide receptor radionuclide therapy. J Nucl Med. 53:1663–1669. DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.112.107482. PMID: 22988059.
Article34. Niederle B, Pape UF, Costa F, Gross D, Kelestimur F, Knigge U, et al. 2016; ENETS consensus guidelines update for neuroendocrine neoplasms of the jejunum and ileum. Neuroendocrinology. 103:125–138. DOI: 10.1159/000443170. PMID: 26758972.
Article35. Máthé Z, Tagkalos E, Paul A, Molmenti EP, Kóbori L, Fouzas I, et al. 2011; Liver transplantation for hepatic metastases of neuroendocrine pancreatic tumors: a survival-based analysis. Transplantation. 91:575–582. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3182081312. PMID: 21200365.
Article36. Mazzaferro V, Sposito C, Coppa J, Miceli R, Bhoori S, Bongini M, et al. 2016; The long-term benefit of liver transplantation for hepatic metastases from neuroendocrine tumors. Am J Transplant. 16:2892–2902. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.13831. PMID: 27134017.
Article37. Whiting P, Savović J, Higgins JP, Caldwell DM, Reeves BC, Shea B, et al. 2016; ROBIS: a new tool to assess risk of bias in systematic reviews was developed. J Clin Epidemiol. 69:225–234. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2015.06.005. PMID: 26092286. PMCID: PMC4687950.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Supramaximal Resection for Glioblastoma: Redefining the Extent of Resection Criteria and Its Impact on Survival
- Resection of Colorectal Liver Metastases
- Surgical Results of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
- Clinical Results of Hepatic Resection for Metastatic Noncolorectal Nonneuroendocrine Tumor
- Treatment of Liver Metastases