J Korean Med Sci.
2022 Feb;37(7):e56. 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e56.
Efficacy and Safety of Pregabalin for Muscle Cramps in Liver Cirrhosis: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Neurology, Neuroscience Research Institute, Seoul National University Medical Research Council, Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Neurology, Ajou University Medical Center, Ajou University College of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
- 5Department of Neurology, Konkuk University Hospital, Konkuk University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2526518
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e56
Abstract
- Background
Muscle cramp is possibly related to peripheral nerve hyperexcitability (PNH), and one of the most debilitating symptoms frequently encountered in patients with liver cirrhosis. We investigated whether pregabalin, a gamma-aminobutyric acid analogue, can suppress neuronal excitability and reduce muscle cramps in cirrhotic patients.
Methods
We conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in which study participants with cirrhosis from a single tertiary center were enrolled. Primary endpoint was the relative change in cramp frequency from the run-in to standard dose treatment phase (4 weeks per each). Secondary endpoints included the responder rate, and the changes in cramp frequency during sleep, pain intensity, health-related quality of life (Liver Disease Quality of Life Instrument, Short Form-36) and electrophysiological measures of PNH.
Results
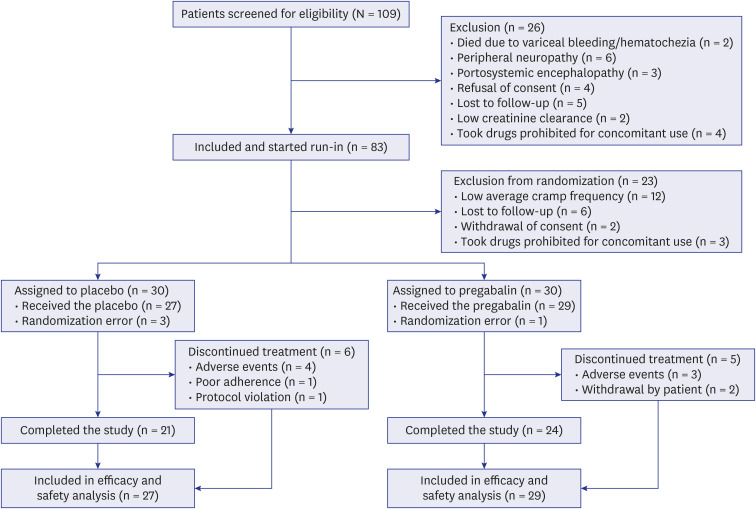
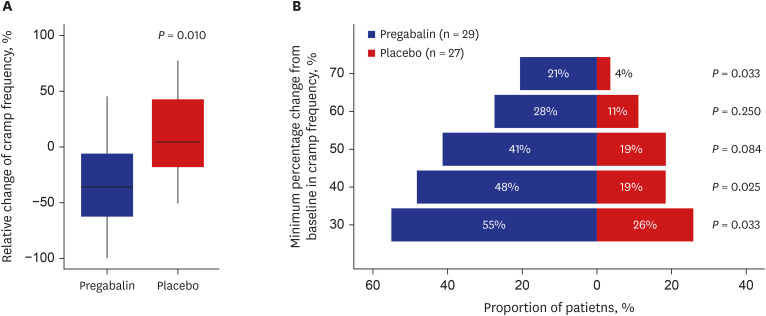
This study was terminated early because of insufficient accrual. 80% (n = 56) of the target number of participants (n = 70) were randomized to pregabalin (n = 29) or placebo (n = 27). Median baseline frequency of muscle cramps (interquartile range) was 5.8 (3.5–10) per week in the pregabalin group and 6.5 (4.0–10) in the placebo group (P = 0.970). The primary analysis showed a significant reduction in cramp frequency with pregabalin compared to placebo (−36% vs. 4.5% for the percentage change, P = 0.010). Secondary outcomes did not differ significantly between the two groups. Adverse effects with pregabalin were mainly dizziness and lethargy.
Conclusion
With multiple problems emerging from premature termination in mind, the results suggested an acceptable safety profile and favorable effect of pregabalin in reducing muscle cramps compared to placebo in cirrhotic patients.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Layzer RB. Muscle pain, cramps, and fatigue. Engel AG, Franzini-Armstrong C, editors. Myology. New York, NY, USA: McGraw Hill;1994. p. 1754–1768.2. Abrams GA, Concato J, Fallon MB. Muscle cramps in patients with cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996; 91(7):1363–1366. PMID: 8677996.3. Konikoff F, Theodor E. Painful muscle cramps. A symptom of liver cirrhosis? J Clin Gastroenterol. 1986; 8(6):669–672. PMID: 3805668.4. Chatrath H, Liangpunsakul S, Ghabril M, Otte J, Chalasani N, Vuppalanchi R. Prevalence and morbidity associated with muscle cramps in patients with cirrhosis. Am J Med. 2012; 125(10):1019–1025. PMID: 22835465.
Article5. Iwasa M, Karino Y, Kawaguchi T, Nakanishi H, Miyaaki H, Shiraki M, et al. Relationship of muscle cramps to quality of life and sleep disturbance in patients with chronic liver diseases: a nationwide study. Liver Int. 2018; 38(12):2309–2316. PMID: 29582541.
Article6. Kato A, Tanaka H, Kawaguchi T, Kanazawa H, Iwasa M, Sakaida I, et al. Nutritional management contributes to improvement in minimal hepatic encephalopathy and quality of life in patients with liver cirrhosis: a preliminary, prospective, open-label study. Hepatol Res. 2013; 43(5):452–458. PMID: 22994429.
Article7. Marchesini G, Bianchi G, Amodio P, Salerno F, Merli M, Panella C, et al. Factors associated with poor health-related quality of life of patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2001; 120(1):170–178. PMID: 11208726.
Article8. Mehta SS, Fallon MB. Muscle cramps in liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 11(11):1385–1391. PMID: 23542334.
Article9. Lee KH, Kim NY, Ko YH, Ko JJ, Oh JH, Lee CG, et al. Muscle cramps in patients with chronic liver disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1998; 32(3):346–354.10. Cho JH, Choi JI, Geum MS, Tak WY, Kweon YO, Kim SK, et al. Muscle cramps in liver cirrhosis: clinical features and related factors. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1999; 34(1):76–82.12. Katzberg HD. Neurogenic muscle cramps. J Neurol. 2015; 262(8):1814–1821. PMID: 25673127.
Article13. Knill-Jones RP, Goodwill CJ, Dayan AD, Williams R. Peripheral neuropathy in chronic liver disease: clinical, electrodiagnostic, and nerve biopsy findings. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1972; 35(1):22–30. PMID: 4337271.
Article14. Ng K, Lin CS, Murray NM, Burroughs AK, Bostock H. Conduction and excitability properties of peripheral nerves in end-stage liver disease. Muscle Nerve. 2007; 35(6):730–738. PMID: 17387740.
Article15. Vidot H, Carey S, Allman-Farinelli M, Shackel N. Systematic review: the treatment of muscle cramps in patients with cirrhosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014; 40(3):221–232. PMID: 24942957.
Article16. Kugelmas M. Preliminary observation: oral zinc sulfate replacement is effective in treating muscle cramps in cirrhotic patients. J Am Coll Nutr. 2000; 19(1):13–15. PMID: 10682870.
Article17. Chandok N, Tan P, Uhanova J, Shankar N, Marotta P. A pilot study of vitamin E for the treatment of cirrhotic muscle cramps. Liver Int. 2011; 31(4):586–587. PMID: 21382169.
Article18. Konikoff F, Ben-Amitay G, Halpern Z, Weisman Y, Fishel B, Theodor E, et al. Vitamin E and cirrhotic muscle cramps. Isr J Med Sci. 1991; 27(4):221–223. PMID: 2010278.19. Sako K, Imamura Y, Nishimata H, Tahara K, Kubozono O, Tsubouchi H. Branched-chain amino acids supplements in the late evening decrease the frequency of muscle cramps with advanced hepatic cirrhosis. Hepatol Res. 2003; 26(4):327–329. PMID: 12963433.
Article20. Vidot H, Cvejic E, Carey S, Strasser SI, McCaughan GW, Allman-Farinelli M, et al. Randomised clinical trial: oral taurine supplementation versus placebo reduces muscle cramps in patients with chronic liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018; 48(7):704–712. PMID: 30136291.
Article21. Nakanishi H, Kurosaki M, Tsuchiya K, Nakakuki N, Takada H, Matsuda S, et al. L-carnitine reduces muscle cramps in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 13(8):1540–1543. PMID: 25496816.
Article22. Motoo Y, Taga H, Yamaguchi Y, Watanabe H, Okai T, Sawabu N. Effect of niuche-shen-qi-wan on painful muscle cramps in patients with liver cirrhosis: a preliminary report. Am J Chin Med. 1997; 25(1):97–102. PMID: 9167002.
Article23. Kobayashi Y, Kawasaki T, Yoshimi T, Nakajima T, Kanai K. Muscle cramps in chronic liver diseases and treatment with antispastic agent (eperisone hydrochloride). Dig Dis Sci. 1992; 37(7):1145–1146. PMID: 1618065.
Article24. Elfert AA, Abo Ali L, Soliman S, Zakaria S, Shehab El-Din I, Elkhalawany W, et al. Randomized placebo-controlled study of baclofen in the treatment of muscle cramps in patients with liver cirrhosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016; 28(11):1280–1284. PMID: 27467714.
Article25. Angeli P, Albino G, Carraro P, Dalla Pria M, Merkel C, Caregaro L, et al. Cirrhosis and muscle cramps: evidence of a causal relationship. Hepatology. 1996; 23(2):264–273. PMID: 8591851.
Article26. Lee FY, Lee SD, Tsai YT, Lai KH, Chao Y, Lin HC, et al. A randomized controlled trial of quinidine in the treatment of cirrhotic patients with muscle cramps. J Hepatol. 1991; 12(2):236–240. PMID: 2051002.
Article27. Kim KM, Lee DH, Lee Y, Yi H, Cho YJ, Lee BI, et al. Efficacy of phenytoin for nocturnal muscle cramps: a preliminary study. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2014; 32(4):254–258.28. Kim GI, Kang SH, Kim JI, Chae GH, Heo WS, Jeong JH, et al. The clinical feature of the muscle cramps and the effects of eperisone hydrochloride in treatment for the muscle cramps of the patients with liver cirrhosis. Korean J Med. 2006; 70(6):643–649.29. Jang ES, Hwang SH, Kim JW, Jeong SH. Effectiveness of 4-week oral taurine treatment for muscle cramps in patients with liver cirrhosis: a single-arm pilot study. Yonsei Med J. 2021; 62(1):21–28. PMID: 33381931.
Article30. Gajraj NM. Pregabalin for pain management. Pain Pract. 2005; 5(2):95–102. PMID: 17177755.
Article31. Taylor CP, Angelotti T, Fauman E. Pharmacology and mechanism of action of pregabalin: the calcium channel alpha2-delta (alpha2-delta) subunit as a target for antiepileptic drug discovery. Epilepsy Res. 2007; 73(2):137–150. PMID: 17126531.
Article32. Serrao M, Rossi P, Cardinali P, Valente G, Parisi L, Pierelli F. Gabapentin treatment for muscle cramps: an open-label trial. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2000; 23(1):45–49. PMID: 10682230.
Article33. Randinitis EJ, Posvar EL, Alvey CW, Sedman AJ, Cook JA, Bockbrader HN. Pharmacokinetics of pregabalin in subjects with various degrees of renal function. J Clin Pharmacol. 2003; 43(3):277–283. PMID: 12638396.
Article34. Bockbrader HN, Wesche D, Miller R, Chapel S, Janiczek N, Burger P. A comparison of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of pregabalin and gabapentin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2010; 49(10):661–669. PMID: 20818832.
Article35. Bajaj JS, Cordoba J, Mullen KD, Amodio P, Shawcross DL, Butterworth RF, et al. Review article: the design of clinical trials in hepatic encephalopathy--an International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism (ISHEN) consensus statement. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 33(7):739–747. PMID: 21306407.
Article36. Lee M, Kim W, Choi Y, Kim S, Kim D, Yu SJ, et al. Spontaneous evolution in bilirubin levels predicts liver-related mortality in patients with alcoholic hepatitis. PLoS One. 2014; 9(7):e100870. PMID: 25013906.
Article37. Gralnek IM, Hays RD, Kilbourne A, Rosen HR, Keeffe EB, Artinian L, et al. Development and evaluation of the liver disease quality of life instrument in persons with advanced, chronic liver disease--the LDQOL 1.0. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000; 95(12):3552–3565. PMID: 11151892.
Article38. Kim S, Choi KH, Hwang SG, Lee JH, Kwak SY, Park PW, et al. Validation of the Korean version of liver disease quality of life (LDQOL 1.0) instrument. Korean J Hepatol. 2007; 13(1):44–50. PMID: 17380074.39. McHorney CA, Ware JE Jr, Raczek AE. The MOS 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36): II. Psychometric and clinical tests of validity in measuring physical and mental health constructs. Med Care. 1993; 31(3):247–263. PMID: 8450681.40. Benatar M, Chapman KM, Rutkove SB. Repetitive nerve stimulation for the evaluation of peripheral nerve hyperexcitability. J Neurol Sci. 2004; 221(1-2):47–52. PMID: 15178213.
Article41. Bodkin CL, Kennelly KD, Boylan KB, Crook JE, Heckman MG, Rubin DI. Defining normal duration for afterdischarges with repetitive nerve stimulation: a pilot study. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2009; 26(1):45–49. PMID: 19151616.
Article42. Parisi L, Serrao M, Rossi P, Valente G, Fattapposta F, Pierelli F, et al. Afterdischarge activity in neuropathic patients with frequent muscle cramps. Acta Neurol Scand. 2000; 102(6):359–362. PMID: 11125750.
Article43. Abd-Elsalam S, Arafa M, Elkadeem M, Elfert A, Soliman S, Elkhalawany W, et al. Randomized-controlled trial of methocarbamol as a novel treatment for muscle cramps in cirrhotic patients. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019; 31(4):499–502. PMID: 30444744.
Article44. Farver DK, Lavin MN. Quinine-induced hepatotoxicity. Ann Pharmacother. 1999; 33(1):32–34. PMID: 9972382.
Article45. Gottschall JL, Neahring B, McFarland JG, Wu GG, Weitekamp LA, Aster RH. Quinine-induced immune thrombocytopenia with hemolytic uremic syndrome: clinical and serological findings in nine patients and review of literature. Am J Hematol. 1994; 47(4):283–289. PMID: 7977300.
Article46. Townend BS, Sturm JW, Whyte S. Quinine associated blindness. Aust Fam Physician. 2004; 33(8):627–628. PMID: 15373380.47. Woodfield R, Goodyear-Smith F, Arroll B. N-of-1 trials of quinine efficacy in skeletal muscle cramps of the leg. Br J Gen Pract. 2005; 55(512):181–185. PMID: 15808032.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pharmacotherapy of Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Pregabalin
- Pregabalin versus Gabapentin Efficacy in the Management of Neuropathic Pain Associated with Failed Back Surgery Syndrome
- Muscle Cramps in Liver Cirrhosis : Clinical Features and Related Factors
- Muscle Cramps in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease
- Effectiveness of 4-Week Oral Taurine Treatment for Muscle Cramps in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: A Single-Arm Pilot Study